Gl Inet Travel Router Hack is a topic of growing interest as users seek to enhance the functionality and security of these compact devices. At TRAVELS.EDU.VN, we delve into the world of GL iNet travel routers, exploring potential hacks, security vulnerabilities, and ways to maximize your travel experience. Explore the world of network customization, access control lists, and firmware modifications to unlock the full potential of your GL iNet travel router.
1. Introduction to GL iNet Travel Routers
GL iNet is known for its portable routers running OpenWrt, offering flexibility for travelers needing secure and customizable network solutions. These routers are popular for creating private Wi-Fi hotspots, extending existing networks, and maintaining security while on the go.
1.1 What Makes GL iNet Routers Attractive?
- Portability: Compact and lightweight designs make them easy to carry.
- OpenWrt Firmware: Allows extensive customization and installation of additional software.
- Security Features: VPN client and server support for secure connections.
- Versatility: Suitable for various applications, including travel, home, and small office use.
1.2 Common Use Cases for Travel Routers
- Securing Public Wi-Fi: Encrypts your internet traffic, protecting against eavesdropping.
- Creating a Private Hotspot: Connect multiple devices to a single secure connection.
- Accessing Region-Locked Content: By using a VPN, you can bypass geographical restrictions.
- Extending Wi-Fi Range: Repeats an existing Wi-Fi signal to cover a larger area.
2. Understanding the Landscape of GL iNet Router Hacks
While “hacking” often has negative connotations, in the context of GL iNet routers, it refers to customizing and modifying the device to better suit your needs. However, it’s crucial to understand the potential security implications.
2.1 Ethical Hacking vs. Malicious Hacking
- Ethical Hacking: Modifying the router for personal use, improving security, or adding features.
- Malicious Hacking: Exploiting vulnerabilities for unauthorized access or causing harm.
2.2 Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
- Security Vulnerabilities: Exploiting weaknesses in the firmware can compromise your network.
- Warranty Voiding: Modifying the router may void the manufacturer’s warranty.
- Bricking: Incorrect modifications can render the router unusable.
- Mitigation: Always back up your firmware, follow reliable guides, and understand the risks.
3. Common GL iNet Travel Router Hacks and Customizations
Let’s explore some popular hacks and customizations that users implement on their GL iNet travel routers.
3.1 VPN Configuration and Optimization
Setting up a VPN on your GL iNet router enhances your online privacy and security. TRAVELS.EDU.VN recommends using reputable VPN providers to ensure your data is protected.
3.1.1 Setting Up a VPN Client
- Access Router Interface: Log in to your GL iNet router’s web interface.
- Navigate to VPN Settings: Find the VPN client settings (usually under “VPN” or “Network”).
- Configure VPN Profile: Enter your VPN provider’s details (server address, username, password).
- Connect to VPN: Activate the VPN connection.
3.1.2 Optimizing VPN Performance
- Choose a Nearby Server: Selecting a VPN server closer to your location can reduce latency.
- Experiment with Protocols: Different VPN protocols (OpenVPN, WireGuard) offer varying speeds and security levels.
- Adjust MTU Settings: Modifying the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) can improve connection stability and speed.
3.2 Ad Blocking with AdGuard Home or Pi-hole
Blocking ads at the router level provides a cleaner browsing experience for all connected devices.
3.2.1 Installing AdGuard Home
- Access Router Interface: Log in to your GL iNet router’s web interface.
- Install AdGuard Home: Use the router’s package manager (if available) or SSH to install AdGuard Home.
- Configure DNS Settings: Point your router’s DNS settings to the AdGuard Home server.
3.2.2 Setting Up Pi-hole
- Install Pi-hole on a Separate Device: Pi-hole is typically installed on a Raspberry Pi or other Linux-based device.
- Configure Router DNS: Point your GL iNet router’s DNS settings to the Pi-hole server.
3.3 Custom DNS Configuration
Using custom DNS servers can improve privacy and security.
3.3.1 Choosing a DNS Provider
- Cloudflare: Offers fast and privacy-focused DNS services (1.1.1.1, 1.0.0.1).
- Google Public DNS: Reliable and widely used (8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4).
- Quad9: Blocks malicious domains (9.9.9.9, 149.112.112.112).
3.3.2 Configuring DNS Settings
- Access Router Interface: Log in to your GL iNet router’s web interface.
- Navigate to DNS Settings: Find the DNS settings (usually under “Network” or “WAN”).
- Enter DNS Server Addresses: Input the primary and secondary DNS server addresses.
3.4 Firmware Modification and Customization
Modifying the firmware allows you to add features or improve performance.
3.4.1 Using Custom OpenWrt Builds
- Download Custom Firmware: Find a custom OpenWrt build that suits your needs.
- Flash Firmware: Use the router’s web interface or SSH to flash the new firmware.
- Configure Router: Set up your router with the new firmware.
3.4.2 Installing Custom Packages
- Access Router via SSH: Connect to your router using SSH.
- Use Package Manager: Use the
opkgpackage manager to install additional software.
opkg update
opkg install [package name]
3.5 Advanced Network Configuration
Configuring advanced network settings can enhance performance and security.
3.5.1 Setting Up a Guest Network
- Access Router Interface: Log in to your GL iNet router’s web interface.
- Navigate to Wireless Settings: Find the wireless settings.
- Enable Guest Network: Create a separate network for guests with limited access.
3.5.2 Configuring Firewall Rules
- Access Router Interface: Log in to your GL iNet router’s web interface.
- Navigate to Firewall Settings: Find the firewall settings.
- Add Custom Rules: Define rules to allow or block specific traffic.
4. Security Vulnerabilities and Mitigation
Addressing security vulnerabilities is critical when dealing with GL iNet travel routers.
4.1 Common Vulnerabilities
- OS Command Injection: Allows attackers to run arbitrary commands on the system.
- Arbitrary File Read: Enables unauthorized access to sensitive files.
- PII Data Leakage: Exposes personal identifiable information.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Allows attackers to inject malicious scripts into websites.
- Weak Password Requirements: Makes it easier for attackers to brute force accounts.
- Password Policy Bypass: Allows users to set weak passwords.
4.2 Real-World Examples of Vulnerabilities
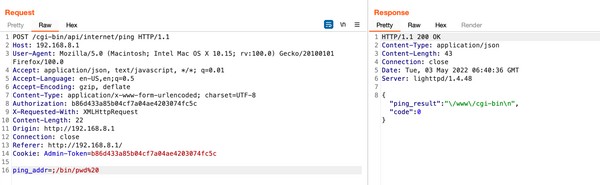
4.2.1 OS Command Injection (CVE-2022-31898)
An OS Command Injection vulnerability in GL iNet routers allows authenticated attackers to run arbitrary commands on the affected system as the application’s user. This vulnerability exists within the local web interface and remote cloud interface. It stems from improper validation of input passed through the ping (ping_addr) and traceroute (trace_addr) parameters. The vulnerability affects ALL GL.iNET product’s firmware >3.2.12.
Mitigation: Update to firmware version 3.215 or later.
4.2.2 Arbitrary File Read (CVE-2022-42055)
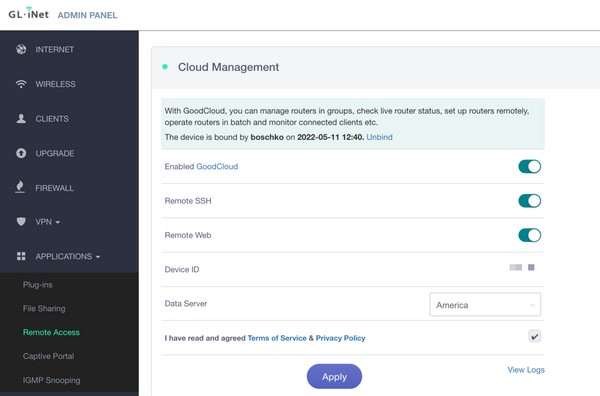
The MT300N-V2 portable router, configured along sides the vendor’s cloud management gateway (goodcloud.xyz) is vulnerable to Arbitrary File Read. The remote cloud gateway facilitates remote device access and management. This vulnerability exists within the cloud manager web interface and is only available to enterprise users. The device editing interface tools harbor the ping and traceroute functionality which is vulnerable to a broken type of command injection whose behavior is limited to performing arbitrary file reads. Successful exploitation allows an attacker to access sensitive files and data on the router.
Mitigation: Update to firmware version 3.215 or later.
4.2.3 PII Data Leakage
The MT300N-V2 portable router can be configured along sides the vendor’s cloud management gateway (goodcloud.xyz) which allows for remote access and management. This vulnerability exists within the cloud manager web interface through the device-sharing endpoint cloud-api/cloud/user/get-user?nameoremail= GET request. Successful enumeration of a user will result in that user’s PII information being disclosed.
Mitigation: Ensure the cloud management gateway is updated with the latest patches.
4.2.4 Stored Cross-Site Scripting (CVE-2022-42054)
The MT300N-V2 portable router has the ability to join itself to the remote cloud management configuration gateway (goodcloud.xyz) which allows for remote management of linked IoT devices. There exist multiple user input fields that do not properly sanitize user-supplied input. As a result, the application is vulnerable to stored cross-site scripting attacks. If this attack is leveraged against an enterprise account through the Sub Account invitation it can lead to the account takeover of the joined accounts.
Mitigation: Ensure the cloud management gateway is updated with the latest patches.
4.2.5 Weak Password Requirements & No Rate Limiting
The MT300N-V2 portable router has the ability to join itself to the remote cloud management configuration gateway with its accounts created through goodcloud.xyz which allows for remote management of linked IoT devices. The login for goodcloud.xyz was observed to have no rate limiting. Additionally, user passwords only require a minimum of 6 characters and no special characters/password policy. This makes it extremely simple for an attacker to brute force user accounts leading to account takeover.
Mitigation: Implement strong password policies and rate limiting on login attempts.
4.2.6 Password Policy Bypass
The MT300N-V2 portable router has the ability to join itself to the remote cloud management configuration gateway (goodcloud.xyz) which allows for remote management of linked IoT devices. For these cloud gateway accounts, while password complexity requirements were implemented in the original signup page, these were not added to the password reset page. The current lack of rate limiting this severely impacts the security posture of the affected users.
Mitigation: Ensure consistent password policies across all account management pages.
4.3 Best Practices for Router Security
- Update Firmware Regularly: Keep your router’s firmware up to date to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Use Strong Passwords: Use complex passwords for both the router login and Wi-Fi network.
- Enable Firewall: Ensure the router’s firewall is enabled and properly configured.
- Disable Remote Access: Unless necessary, disable remote access to the router’s web interface.
- Monitor Network Traffic: Keep an eye on network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Use a VPN: Encrypt your internet traffic to protect against eavesdropping.
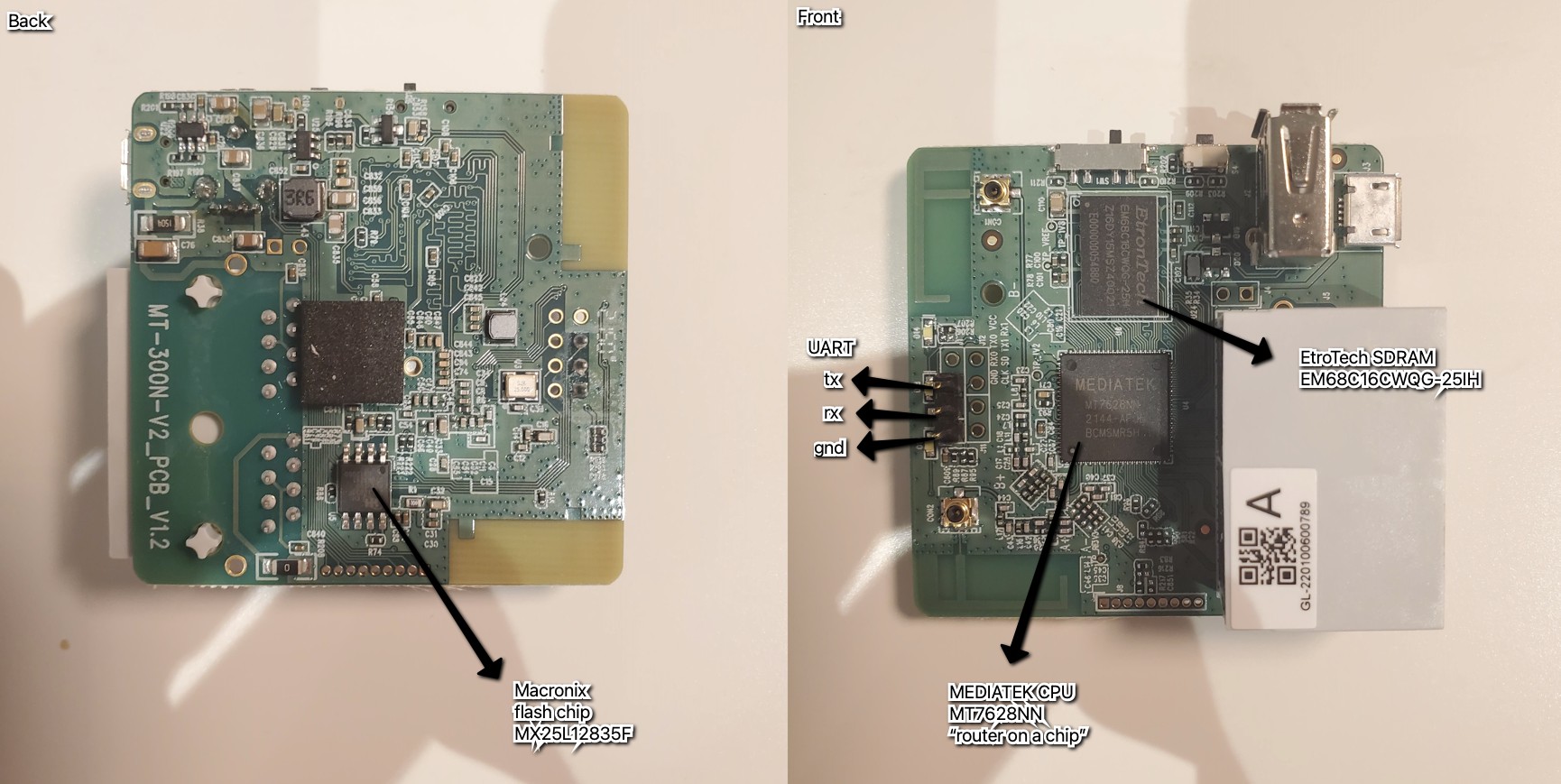
5. Hardware Teardown and Analysis
Analyzing the hardware components of GL iNet travel routers can provide insights into their capabilities and potential vulnerabilities.
5.1 Key Components
- SoC (System on a Chip): The main processor that handles routing and other functions.
- SPI Flash: Stores the router’s firmware.
- SD RAM: Provides memory for the router to operate.
- UART: Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter, used for serial communication.
- JTAG: Joint Test Action Group, an interface for debugging and programming.
5.2 Connecting to UART
UART is used to send and receive data from devices over a serial connection. This is done for purposes such as updating firmware manually, debugging, or interfacing with the underlying system. UART works by communicating through two wires, a transmitter wire (TX) and a receiver wire (RX) to talk to the micro-controller or system on a chip directly.
5.2.1 Steps to Connect to UART
- Identify UART Pins: Locate the RX, TX, and GND pins on the router’s PCB.
- Connect UART Adapter: Connect a USB-to-UART adapter to the pins.
- Configure Serial Terminal: Use a serial terminal program (e.g., PuTTY) to connect to the router.
- Access Router Shell: Access the router’s command-line interface.
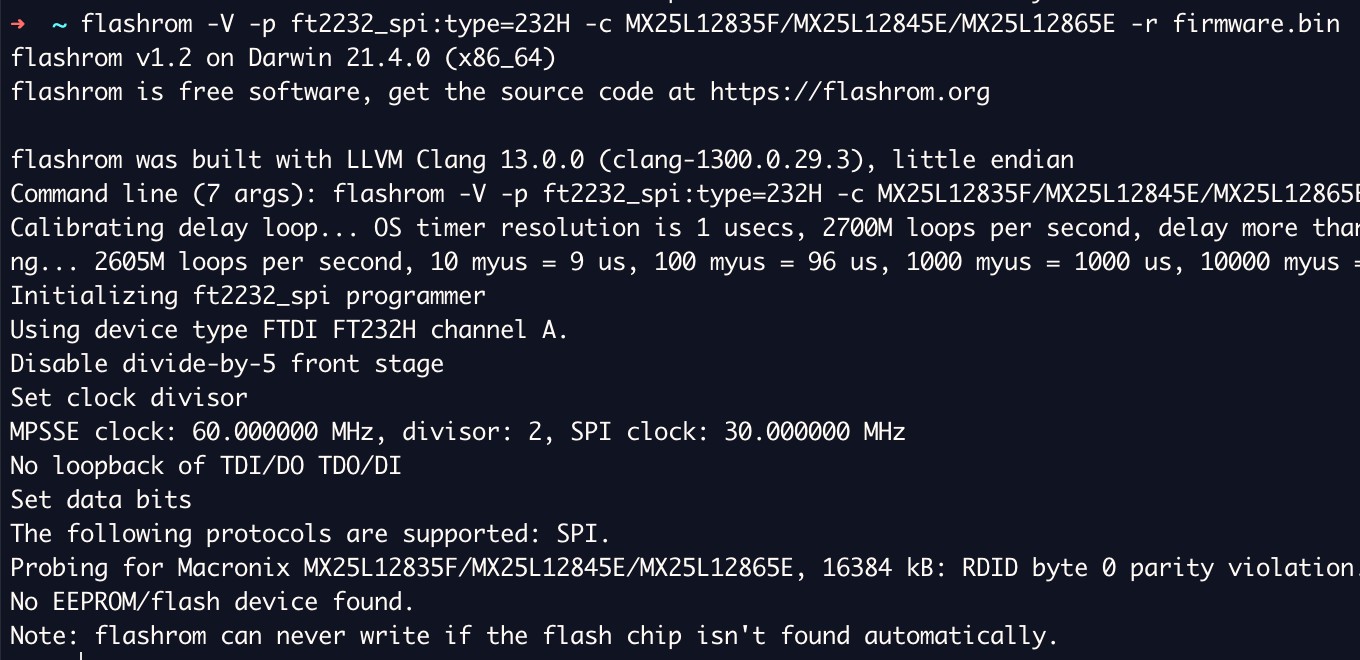
5.3 Leveraging the SPI Flash
The goal is simple, read the firmware from the chip. There are a few options like using clips universal bus interface device, unsoldering the chip from the board and connecting it to a specialized EPROM read/write device or attaching it to a Protoboard.
5.3.1 Steps to Leverage the SPI Flash
- Obtain Hardware Tools: Acquire the necessary hardware tools, such as an Attify Badge or Bus Pirate.
- Connect to SPI Flash Chip: Connect the hardware tool to the SPI flash chip.
- Dump Firmware: Use the hardware tool to dump the firmware from the chip.
- Analyze Firmware: Analyze the firmware for vulnerabilities or customization opportunities.
5.4 Hardware Obfuscation Techniques
Implementing hardware obfuscation techniques can enhance the security of IoT devices.
5.4.1 Techniques to Make IoT Hardware More Secure
- Removing PCB Silkscreen: Eliminating markings, logos, and symbols.
- Hiding Traces: Making it difficult to follow the solder mask.
- Hardware-Level Tamper Protection: Setting hardware and software fuses to prevent readout.
- Removing Test Pins and Probe Pads: Disabling debugging connections.
- Using Buried or Blind Vias: Concealing test points.
- Removing Chipset Markings: Making it harder to identify chips.
- Using Tamper-Proof Cases: Employing sensors and one-way screws.
6. Conclusion: Balancing Customization and Security
GL iNet travel routers offer a compelling blend of portability, customization, and security features. However, it’s essential to balance the desire for customization with the need to maintain a secure network. By understanding the potential vulnerabilities and implementing best practices, you can maximize the benefits of your GL iNet router while minimizing the risks.
At TRAVELS.EDU.VN, we encourage you to explore the possibilities of GL iNet travel routers responsibly. Stay informed, stay secure, and enjoy your travels with peace of mind.
7. Ready to Enhance Your Travel Experience with a GL iNet Router?
Are you planning a trip to Napa Valley and want to ensure a secure and customized network experience? Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN today for expert advice and tailored solutions for your GL iNet travel router!
Address: 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (707) 257-5400
Website: TRAVELS.EDU.VN
Let us help you optimize your travel router for a seamless and secure journey.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
8.1 What is a GL iNet travel router?
A GL iNet travel router is a portable router that runs OpenWrt and is designed for travelers who need a secure and customizable network solution.
8.2 Why should I use a travel router?
Travel routers provide secure Wi-Fi hotspots, extend existing networks, and maintain security while on the go.
8.3 What is OpenWrt?
OpenWrt is a Linux-based operating system primarily used on embedded devices to route network traffic.
8.4 How do I update the firmware on my GL iNet router?
You can update the firmware through the router’s web interface or by using SSH.
8.5 What are the benefits of using a VPN on my travel router?
Using a VPN encrypts your internet traffic, protects against eavesdropping, and allows you to access region-locked content.
8.6 Can I install custom software on my GL iNet router?
Yes, GL iNet routers support OpenWrt, allowing you to install custom packages using the opkg package manager.
8.7 How do I set up a guest network on my GL iNet router?
You can set up a guest network through the router’s web interface in the wireless settings.
8.8 What security measures should I take to protect my GL iNet router?
Update firmware regularly, use strong passwords, enable the firewall, and disable remote access if not needed.
8.9 What is hardware obfuscation?
Hardware obfuscation involves techniques to make it more difficult for attackers to reverse engineer or tamper with the hardware.
8.10 Where can I get support for my GL iNet router?
You can find support on the GL iNet website, community forums, or by contacting travels.edu.vn for expert assistance.
 GL iNet Router
GL iNet Router
 GL iNet Cloud Management
GL iNet Cloud Management
 Command Injection
Command Injection
 Flipper Zero UART Connection
Flipper Zero UART Connection
 Firmware Extraction Failure
Firmware Extraction Failure
 Hardware Obfuscation
Hardware Obfuscation