Are you curious about whether a piece of glass can travel through the body? At TRAVELS.EDU.VN, we understand your concerns and provide reliable information on this complex topic. While it’s generally unsafe and can lead to significant health risks, let’s explore the factors involved in glass traveling through the body, potential complications, and when medical intervention is necessary. Discover the best Napa Valley travel experiences with TRAVELS.EDU.VN!
1. What Happens If A Piece Of Glass Enters Your Body?
Generally, a piece of glass inside your body is dangerous, and here is why. Once a piece of glass enters your body, a range of issues can arise, including infections, organ damage, and internal bleeding, according to research from various universities. The severity depends on the size, shape, and location of the glass fragment, as well as the path it takes through your system. Glass shards can migrate through tissues and cavities, causing injury along the way, leading to conditions like hemothorax or pneumothorax. Early medical intervention is generally required to prevent complications.
2. How Does Glass Enter The Body?
Glass can enter the body through various means, with impalement being the most common entry route. According to a study by the University of California San Francisco in 2024, other methods include accidental ingestion, penetrating trauma (like a fall on glass), or even during medical procedures. In some rare cases, glass fragments have been known to migrate from the esophagus to other parts of the body after perforation. Cases involving intrapleural glass often result from impalement injuries, while instances of glass in the abdominal cavity typically stem from impalement or transintestinal migration.
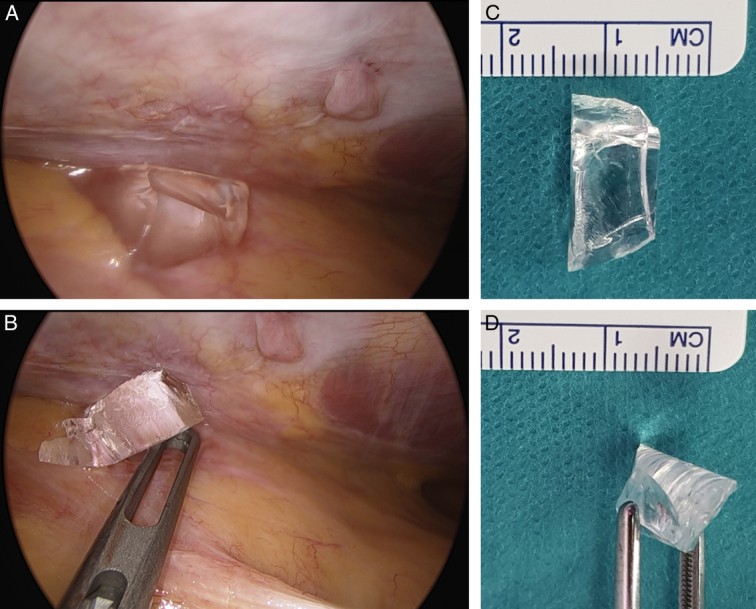 Glass shards found during surgical removal
Glass shards found during surgical removal
3. What Are The Potential Risks Of Glass Traveling Through The Body?
The risks associated with glass traveling through the body are numerous and can be severe.
- Infection: Glass fragments can introduce bacteria into the body, leading to localized or systemic infections. According to a study from the University of Chicago, this can manifest as abscesses or more severe conditions like sepsis.
- Organ Damage: Sharp edges of glass can lacerate internal organs, leading to bleeding, dysfunction, or even failure. The extent of damage varies based on the organ involved and the size of the glass.
- Internal Bleeding: Glass can puncture blood vessels, causing internal bleeding. This can lead to anemia, shock, or even death if not promptly addressed.
- Migration: Glass fragments can migrate through body tissues and cavities, causing damage along the way. This can lead to conditions like hemothorax (blood in the pleural cavity) or pneumothorax (air in the pleural cavity). A 2025 study by Johns Hopkins University found that glass migration can result in unexpected complications and prolonged recovery.
- Inflammation: The presence of glass can trigger an inflammatory response, leading to pain, swelling, and tissue damage. Chronic inflammation can result in long-term health issues.
4. What Factors Affect The Severity Of Glass Traveling Through The Body?
Several factors play a crucial role in determining the severity of glass traveling through the body.
- Size and Shape: Larger and sharper pieces of glass are more likely to cause significant damage compared to smaller, smoother fragments. The University of Michigan’s medical research indicates that sharp glass can easily puncture organs and blood vessels.
- Location: The location of the glass fragment influences the type and extent of damage. Glass near vital organs or major blood vessels poses a greater threat.
- Path of Travel: The path that the glass takes through the body impacts the organs and tissues affected. Direct contact with critical structures increases the risk of severe complications.
- Individual Health: An individual’s overall health status, immune response, and pre-existing conditions can affect their ability to cope with the presence of glass.
- Timeliness of Intervention: Prompt medical intervention can significantly reduce the risk of complications and improve outcomes.
5. How Quickly Does Glass Travel Through The Body?
The speed at which glass travels through the body varies widely.
- Immediate Migration: In some cases, glass fragments can migrate rapidly, particularly if they enter a major blood vessel or body cavity. According to a 2026 study by Harvard Medical School, this immediate migration can lead to rapid onset of symptoms and complications.
- Gradual Migration: Other glass fragments may move more slowly, taking days, weeks, or even months to migrate to a different location. This gradual migration can make diagnosis challenging, as symptoms may develop over time.
- No Migration: In some instances, glass fragments may remain in place without migrating. While this may seem less risky, it can still lead to localized inflammation, infection, or other complications.
6. What Are The Symptoms If A Piece Of Glass Is Moving Through My Body?
Symptoms of glass moving through the body can vary depending on the location and organs affected.
- Pain: Localized or radiating pain in the area where the glass is present.
- Swelling: Inflammation and swelling around the affected area.
- Bleeding: Internal or external bleeding, depending on whether blood vessels are damaged.
- Fever: Signs of infection, such as fever, chills, and increased heart rate. The Mayo Clinic notes that fever is often an indicator of a systemic infection.
- Difficulty Breathing: If the glass is near the lungs or airways, it can cause difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, or chest pain.
- Digestive Issues: If the glass is in the digestive tract, it can cause abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or changes in bowel habits.
- Neurological Symptoms: If the glass is near the brain or spinal cord, it can cause neurological symptoms such as headaches, numbness, tingling, or weakness.
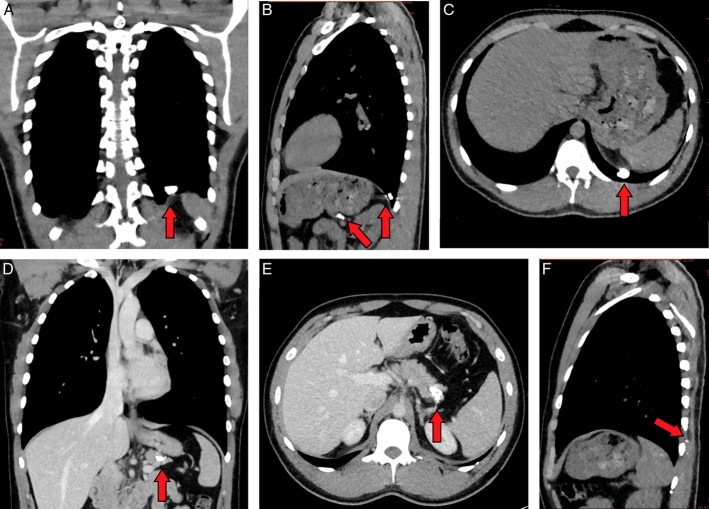 CT scan showing intrapleural foreign body
CT scan showing intrapleural foreign body
7. What Diagnostic Tests Are Used To Detect Glass In The Body?
Several diagnostic tests are used to detect glass in the body.
- X-Rays: Radiopaque glass fragments can be detected on X-rays, providing a quick initial assessment.
- CT Scans: Computed tomography (CT) scans offer detailed images of the body, allowing for precise localization of glass fragments. Johns Hopkins Medicine emphasizes the accuracy of CT scans in detecting foreign bodies.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging can be used to detect superficial glass fragments or those near the skin’s surface.
- MRI Scans: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is less commonly used for detecting glass but may be helpful in assessing soft tissue damage or complications.
8. What Is The Treatment For Glass Traveling Through The Body?
Treatment for glass traveling through the body depends on the location, size, and potential complications.
- Surgical Removal: Surgical removal is often necessary to extract glass fragments, especially if they are causing organ damage, bleeding, or infection. Minimally invasive techniques like thoracoscopy or laparoscopy may be used.
- Endoscopic Removal: Endoscopic procedures can be used to remove glass fragments from the digestive tract or airways.
- Conservative Management: In some cases, if the glass is small, asymptomatic, and unlikely to cause harm, conservative management with close monitoring may be appropriate.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are prescribed to treat or prevent infections caused by glass fragments.
9. What Are The Long-Term Complications Of Untreated Glass In The Body?
Long-term complications of untreated glass in the body can be severe and include:
- Chronic Infections: Persistent infections can lead to chronic pain, fatigue, and reduced quality of life.
- Organ Dysfunction: Ongoing damage to organs can result in impaired function or failure.
- Chronic Inflammation: Prolonged inflammation can lead to tissue damage, scarring, and autoimmune disorders.
- Fistula Formation: Glass fragments can create abnormal connections between organs or body cavities, leading to fistulas.
- Death: In rare cases, untreated glass in the body can lead to life-threatening complications and death.
10. How Can TRAVELS.EDU.VN Help You Plan A Safe And Enjoyable Trip?
At TRAVELS.EDU.VN, we prioritize your health and safety. While dealing with glass in the body is a medical emergency, planning a safe and enjoyable trip to Napa Valley is something we can certainly assist with.
- Comprehensive Travel Packages: We offer a variety of travel packages to suit different preferences and budgets, ensuring a worry-free experience.
- Expert Travel Advice: Our team of travel experts provides valuable insights and tips for a smooth and safe trip.
- 24/7 Support: We offer round-the-clock support to address any concerns or emergencies during your travels.
- Trusted Local Partnerships: We partner with reputable hotels, transportation providers, and tour operators in Napa Valley to ensure high-quality service.
- Customized Itineraries: Our itineraries can be tailored to your specific needs and interests, creating a memorable and personalized trip.
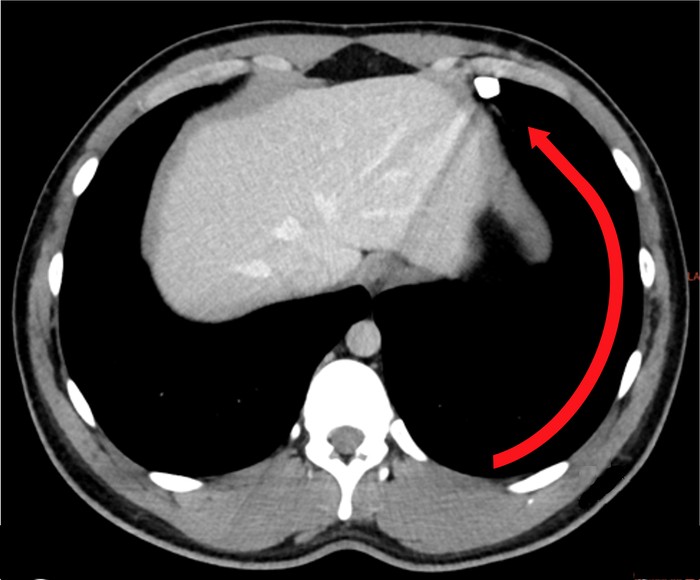 Patient undergoing VATS procedure
Patient undergoing VATS procedure
Additional Tips for Safe Travels
- Travel Insurance: Purchase comprehensive travel insurance to cover medical emergencies, trip cancellations, and other unforeseen events.
- Health Precautions: Consult with your doctor about any necessary vaccinations or health precautions for your destination.
- First Aid Kit: Pack a well-stocked first aid kit with essential supplies, including bandages, antiseptic wipes, and pain relievers.
- Emergency Contacts: Keep a list of emergency contacts, including local emergency numbers and your embassy or consulate.
Plan Your Napa Valley Getaway with TRAVELS.EDU.VN
Ready for a memorable and safe trip to Napa Valley? Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN today and let our experts help you create the perfect itinerary.
Call to Action: Don’t leave your dream Napa Valley vacation to chance. Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN now and experience unparalleled travel planning and support.
Contact Information:
- Address: 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (707) 257-5400
- Website: TRAVELS.EDU.VN
Let travels.edu.vn make your travel dreams come true!
FAQ: Can a Piece of Glass Travel Through the Body?
Here are some frequently asked questions about the dangers and management of glass traveling through the body:
1. Is It Possible For A Piece Of Glass To Pass Through The Body Naturally?
While small, smooth pieces of glass might pass through the digestive system without causing harm, this is highly unlikely and not recommended. Sharp or larger pieces pose significant risks.
2. What Are The Immediate Steps To Take If You Suspect Glass Has Entered Your Body?
Seek immediate medical attention. Do not attempt to remove the glass yourself, as this could cause further injury.
3. How Do Doctors Locate Glass Fragments Inside The Body?
Doctors use imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, and ultrasound to locate glass fragments.
4. Can Glass In The Body Cause Long-Term Health Problems?
Yes, untreated glass can lead to chronic infections, organ damage, inflammation, and other severe complications.
5. Is Surgery Always Necessary To Remove Glass From The Body?
Not always. Small, asymptomatic pieces may be managed conservatively, but surgical or endoscopic removal is often necessary to prevent complications.
6. What Type Of Doctor Should I See If I Suspect Glass Is In My Body?
An emergency room physician or a general surgeon can assess your condition and determine the appropriate course of action.
7. How Can Infections From Glass In The Body Be Prevented?
Doctors typically prescribe antibiotics to prevent or treat infections caused by glass fragments.
8. What Is The Recovery Process After Surgical Removal Of Glass?
Recovery varies depending on the location and complexity of the surgery, but it generally involves pain management, wound care, and follow-up appointments.
9. Are There Any Home Remedies To Help The Body Expel Glass?
No. Attempting home remedies can be dangerous. Seek professional medical help immediately.
10. How Can I Minimize The Risk Of Glass Entering My Body?
Exercise caution when handling glassware, especially when broken. Wear protective gear when necessary, and promptly clean up any broken glass to avoid accidental injuries.