Can Humans Travel At The Speed Of Light? This question has intrigued scientists and science fiction enthusiasts alike for decades, and TRAVELS.EDU.VN aims to delve into the possibilities, limitations, and potential paradoxes of such a feat, exploring the theoretical journey, acceleration challenges, and the mind-bending effects of time dilation. Discover the science, the potential future, and the implications for interstellar travel, offering solutions to explore destinations like Napa Valley, while considering the implications for human space exploration.
1. Understanding the Speed of Light and Its Significance
The speed of light, denoted as c, is a fundamental constant in the universe, approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (186,282 miles per second). This speed is the limit at which all massless particles, like photons, travel. It also represents the maximum speed at which information or energy can travel in the universe.
1.1. Einstein’s Theory of Special Relativity
Albert Einstein’s theory of special relativity, introduced in 1905, revolutionized our understanding of space, time, and the relationship between them. A core tenet of this theory is that the speed of light in a vacuum is constant for all observers, regardless of the motion of the light source. This seemingly simple postulate has profound implications.
1.2. Mass-Energy Equivalence
One of the most famous consequences of special relativity is the mass-energy equivalence, expressed by the equation E=mc². This equation shows that energy (E) and mass (m) are interchangeable, with the speed of light squared (c²) acting as the conversion factor. It implies that as an object approaches the speed of light, its mass increases, requiring increasingly more energy to accelerate it further.
1.3. Implications for Space Travel
The speed of light presents both a tantalizing possibility and a formidable barrier for interstellar travel. On one hand, reaching even a fraction of the speed of light would dramatically reduce travel times to distant stars and galaxies. On the other hand, the energy requirements and technological challenges involved in accelerating a spacecraft to such speeds are immense.
2. The Theoretical Possibility of Near-Light-Speed Travel
While reaching the speed of light is considered impossible for objects with mass, achieving a significant fraction of it, say 99% or 99.9% of c, is theoretically conceivable. This section explores the concepts and considerations involved in near-light-speed travel.
2.1. Propulsion Systems
One of the biggest hurdles is developing propulsion systems capable of delivering the immense energy needed to accelerate a spacecraft to near-light speeds. Conventional chemical rockets are woefully inadequate for this purpose. Some theoretical propulsion systems include:
- Nuclear Propulsion: Using nuclear fission or fusion to generate thrust.
- Ion Propulsion: Accelerating ions using electric fields to produce thrust.
- Antimatter Propulsion: Using the annihilation of matter and antimatter to release energy.
- Ramjets/Scramjets: Collecting interstellar hydrogen as fuel.
2.2. Time Dilation
As an object approaches the speed of light, time dilation becomes significant. Time dilation, as predicted by special relativity, means that time passes more slowly for a moving object relative to a stationary observer. The faster the object moves, the greater the time dilation.
2.3. Length Contraction
Length contraction is another consequence of special relativity. It refers to the shortening of an object in the direction of motion as its speed approaches the speed of light. From the perspective of a stationary observer, the moving object appears compressed.
2.4. Relativistic Mass Increase
As an object accelerates towards the speed of light, its relativistic mass increases. This means that the object becomes increasingly resistant to further acceleration, requiring more and more energy to achieve even small increases in speed. This mass increase is not a change in the object’s rest mass (the mass when it’s at rest) but rather a manifestation of the increasing energy required to accelerate the object.
3. Challenges of Accelerating Humans to Near-Light Speed
The concept of accelerating humans to near-light speed presents numerous challenges, particularly related to the human body’s ability to withstand such extreme conditions.
3.1. G-Force and Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. When a spacecraft accelerates, the occupants experience g-forces, which are forces caused by the inertia of their bodies resisting the change in motion. High g-forces can be dangerous, causing blackouts, loss of consciousness, and even death.
3.2. Radiation Exposure
Space is filled with radiation, including high-energy particles from the sun, cosmic rays, and other sources. At near-light speeds, the effects of radiation are amplified due to relativistic effects. The increased energy of these particles can cause significant damage to human cells and DNA, leading to radiation sickness, cancer, and other health problems.
3.3. Maintaining Life Support
Sustaining human life on a spacecraft traveling at near-light speed poses significant challenges. Closed-loop life support systems would need to recycle air, water, and waste with extreme efficiency. Providing adequate food, medical care, and psychological support for a long-duration mission would also be essential.
3.4. Shielding and Protection
Protecting the spacecraft and its occupants from the hazards of space, such as radiation and micrometeoroids, requires advanced shielding technologies. At near-light speeds, even small particles can have devastating impacts due to their high kinetic energy.
4. The Time Dilation Effect on Human Travel
Time dilation is a crucial consideration in any discussion of near-light-speed travel. The faster a spacecraft travels, the slower time passes for the occupants relative to observers on Earth. This effect has profound implications for the duration of interstellar journeys.
4.1. Calculating Time Dilation
The time dilation factor, denoted by γ (gamma), is calculated using the following formula:
γ = 1 / √(1 – v²/c²)
Where:
- v is the velocity of the moving object.
- c is the speed of light.
This factor determines how much slower time passes for the moving object compared to a stationary observer.
4.2. The Twin Paradox
The twin paradox is a thought experiment that illustrates the counterintuitive nature of time dilation. Imagine two twins, one of whom travels to a distant star at near-light speed and returns to Earth, while the other twin remains on Earth. According to special relativity, the traveling twin will age less than the Earth-bound twin due to time dilation.
4.3. Implications for Interstellar Travel
Time dilation could make interstellar travel feasible within a human lifetime. While a journey to a distant star might take hundreds or thousands of years from the perspective of Earth, the occupants of a near-light-speed spacecraft could experience a much shorter duration.
4.4. Psychological Effects
While time dilation may make interstellar travel physically possible, the psychological effects on the travelers must also be considered. The crew would need to be prepared for the possibility of returning to Earth to find that centuries have passed, and their friends and family are long gone.
5. Potential Destinations at Near-Light Speed: A Theoretical Journey
Assuming the technological hurdles can be overcome, where might humans travel at near-light speed? Let’s explore some potential destinations and the challenges associated with reaching them.
5.1. Proxima Centauri
Proxima Centauri is the closest star to our solar system, located approximately 4.24 light-years away. Even at near-light speed, a journey to Proxima Centauri would take several years from the perspective of Earth. However, due to time dilation, the occupants of a spacecraft traveling at 99% of the speed of light might experience a journey of only a few months.
5.2. Trappist-1 System
The Trappist-1 system, located about 40 light-years away, is home to seven Earth-sized exoplanets, some of which may be habitable. A journey to Trappist-1 would be significantly longer than a trip to Proxima Centauri, but the potential discovery of life on another planet could make it worthwhile.
5.3. The Galactic Center
The center of the Milky Way galaxy, located about 26,000 light-years away, is a fascinating region containing a supermassive black hole and a dense concentration of stars. A journey to the galactic center at near-light speed would be an epic undertaking, but it could provide invaluable insights into the structure and evolution of galaxies.
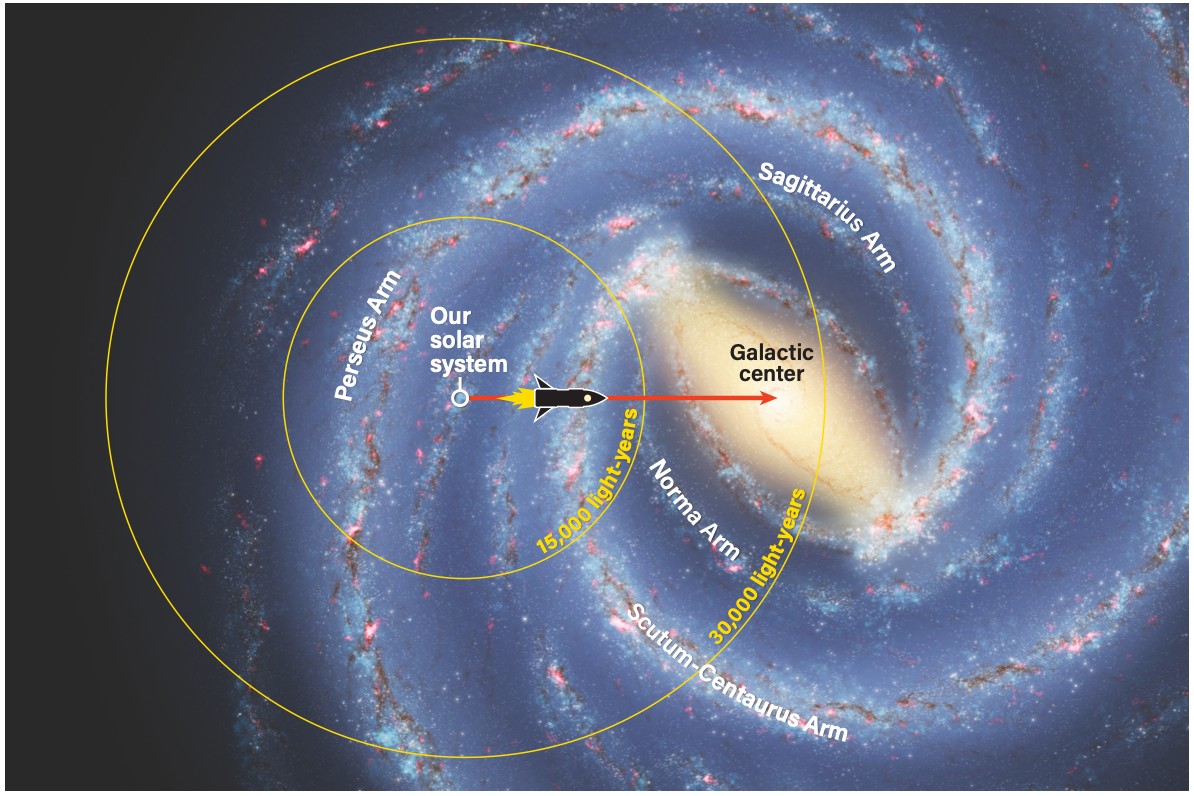 Journey to the center of the galaxy, illustrating the immense distances and time scales involved in interstellar travel
Journey to the center of the galaxy, illustrating the immense distances and time scales involved in interstellar travel
5.4. Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda galaxy, our closest galactic neighbor, is located about 2.5 million light-years away. Reaching Andromeda at near-light speed would be a multi-generational mission, requiring advanced life support systems and a highly self-sufficient crew. However, the scientific rewards of exploring another galaxy would be immense.
6. The Impact of Near-Light Speed Travel on Society and Technology
If near-light-speed travel were to become a reality, it would have a profound impact on society and technology. This section explores some of the potential consequences.
6.1. Scientific Advancements
The development of near-light-speed travel would require breakthroughs in various fields, including propulsion, materials science, and life support systems. These advancements would likely have spin-off applications in other areas, leading to technological progress across the board.
6.2. Economic Considerations
The economic costs of developing and maintaining near-light-speed travel capabilities would be enormous. Governments and private organizations would need to invest vast sums of money into research, development, and infrastructure.
6.3. Ethical Considerations
Near-light-speed travel raises a number of ethical considerations, including the potential for unintended consequences, the allocation of resources, and the impact on the environment.
6.4. Cultural and Philosophical Implications
The prospect of interstellar travel could have a profound impact on human culture and philosophy. It could lead to a greater appreciation of the vastness of the universe and our place within it. It could also raise fundamental questions about the meaning of life, the nature of consciousness, and the future of humanity.
7. Alternative Approaches to Interstellar Travel
While near-light-speed travel is one approach to interstellar exploration, there are other possibilities that may be more feasible in the near term.
7.1. Generation Ships
Generation ships are spacecraft designed to travel to distant stars over multiple generations. The original crew would live out their lives on the ship, and their descendants would continue the journey, eventually reaching the destination.
7.2. Suspended Animation
Suspended animation, also known as cryosleep or hibernation, involves slowing down or stopping the biological processes of the human body to extend lifespan. If humans could be placed in suspended animation for extended periods, interstellar travel could become more feasible.
7.3. Wormholes and Warp Drives
Wormholes and warp drives are theoretical concepts that could allow faster-than-light travel. Wormholes are hypothetical tunnels through spacetime that could connect distant points in the universe. Warp drives would involve warping spacetime around a spacecraft to allow it to travel faster than light.
8. Napa Valley: An Earthly Destination for Exploration and Relaxation
While interstellar travel remains a distant dream, TRAVELS.EDU.VN can help you explore more accessible destinations like Napa Valley, a world-renowned wine region in California.
8.1. Wine Tours and Tastings
Napa Valley is famous for its wineries and vineyards, offering a wide range of wine tours and tastings. Experience the art of winemaking and sample some of the world’s finest wines. Consider these top-rated wineries:
- Domaine Carneros: Sparkling wine specialist with stunning chateau.
- Robert Mondavi Winery: Offers tours and tastings focused on education.
- Castello di Amorosa: A 13th-century style Tuscan castle winery.
8.2. Fine Dining and Culinary Experiences
Napa Valley is also a culinary destination, with many world-class restaurants and chefs. Enjoy fine dining experiences that showcase the region’s fresh, local ingredients. Notable restaurants include:
- The French Laundry: A three-Michelin-starred restaurant known for its innovative cuisine.
- Bouchon Bistro: A classic French bistro by chef Thomas Keller.
- Auberge du Soleil Restaurant: Offers stunning views and Mediterranean-inspired cuisine.
8.3. Scenic Beauty and Outdoor Activities
Beyond wine and food, Napa Valley boasts stunning scenery and opportunities for outdoor activities. Explore the rolling hills, vineyards, and forests, and enjoy hiking, biking, and hot air balloon rides. Popular attractions include:
- The Napa Valley Wine Train: A scenic train ride through the vineyards.
- Bothe-Napa Valley State Park: Offers hiking and camping opportunities.
- Robert Louis Stevenson State Park: Features trails with panoramic views.
8.4. Luxurious Accommodations and Spa Retreats
Relax and rejuvenate in Napa Valley’s luxurious accommodations and spa retreats. Enjoy world-class amenities and personalized service in a tranquil setting. Consider these highly-rated accommodations:
- Auberge du Soleil: A luxurious resort with stunning views and a Michelin-starred restaurant.
- Meadowood Napa Valley: Offers a golf course, spa, and fine dining.
- The Carneros Resort and Spa: Features private cottages and a spa.
8.5. Average Costs
| Expense | Average Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Wine Tasting | $50 – $150 per person | Prices vary depending on the winery and tasting options. |
| Fine Dining | $100 – $500 per person | Costs depend on the restaurant and the number of courses. |
| Accommodation | $300 – $1000 per night | Prices vary based on the type of accommodation and the season. |
| Activities | $50 – $300 per person | Costs depend on the activity, such as hot air balloon rides or spa treatments. |
| Transportation | $50 – $200 per day | Includes rental car, taxi, or ride-sharing services. |
| Total (per day) | $550 – $1650 | Estimated total cost per person per day, including wine tasting, fine dining, accommodation, activities, and transportation. Prices can vary based on choices. |
9. TRAVELS.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Creating Unforgettable Experiences
While the stars may be out of reach for now, TRAVELS.EDU.VN can help you plan unforgettable experiences closer to home. From wine tours in Napa Valley to exotic adventures around the world, we offer personalized travel services tailored to your interests and budget.
9.1. Customized Napa Valley Itineraries
TRAVELS.EDU.VN specializes in creating customized Napa Valley itineraries that cater to your specific preferences. Whether you’re a wine connoisseur, a foodie, or an outdoor enthusiast, we can design a trip that exceeds your expectations.
9.2. Expert Travel Planning and Support
Our team of experienced travel professionals provides expert planning and support to ensure a seamless and enjoyable trip. We handle all the details, from booking accommodations and transportation to arranging tours and activities.
9.3. Exclusive Deals and Packages
TRAVELS.EDU.VN offers exclusive deals and packages on Napa Valley accommodations, tours, and activities. Save money and enjoy added value with our special offers.
9.4. 24/7 Customer Service
We provide 24/7 customer service to assist you with any questions or concerns before, during, and after your trip. Our goal is to provide you with peace of mind and ensure that your travel experience is stress-free.
9.5. Personalized Recommendations
Based on your interests and preferences, we provide personalized recommendations for wineries, restaurants, and activities in Napa Valley. Discover hidden gems and off-the-beaten-path experiences that you won’t find in guidebooks.
10. Call to Action: Plan Your Napa Valley Getaway with TRAVELS.EDU.VN
Ready to experience the beauty and charm of Napa Valley? Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN today to start planning your dream getaway. Let us create a customized itinerary that caters to your interests and budget.
Don’t wait, adventure awaits. Contact us today for a free consultation
- Address: 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (707) 257-5400
- Website: TRAVELS.EDU.VN
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Human Travel at the Speed of Light
1. Is it possible for humans to travel at the speed of light?
According to Einstein’s theory of special relativity, it is impossible for objects with mass to reach the speed of light. The energy required to accelerate an object to the speed of light becomes infinite as it approaches that speed.
2. What is time dilation and how does it affect space travel?
Time dilation is a phenomenon predicted by special relativity, where time passes more slowly for a moving object relative to a stationary observer. This effect becomes significant as an object approaches the speed of light. It means that while a journey to a distant star might take hundreds or thousands of years from the perspective of Earth, the occupants of a near-light-speed spacecraft could experience a much shorter duration.
3. What are some of the challenges of accelerating humans to near-light speed?
Some of the challenges include:
- G-forces: The human body can only withstand a limited amount of g-force.
- Radiation exposure: Space is filled with radiation that can damage human cells.
- Life support: Sustaining human life on a long-duration space mission requires advanced life support systems.
- Shielding: Protecting the spacecraft from micrometeoroids and other hazards.
4. What is the twin paradox?
The twin paradox is a thought experiment that illustrates the counterintuitive nature of time dilation. If one twin travels to a distant star at near-light speed and returns to Earth, they will age less than the twin who remained on Earth.
5. What are some alternative approaches to interstellar travel besides near-light-speed travel?
Some alternatives include:
- Generation ships: Spacecraft designed to travel to distant stars over multiple generations.
- Suspended animation: Slowing down the biological processes of the human body to extend lifespan.
- Wormholes and warp drives: Theoretical concepts that could allow faster-than-light travel.
6. How far away is the closest star to our solar system?
The closest star to our solar system is Proxima Centauri, located approximately 4.24 light-years away.
7. What is the Trappist-1 system?
The Trappist-1 system is a star system located about 40 light-years away, home to seven Earth-sized exoplanets, some of which may be habitable.
8. What impact would near-light-speed travel have on society?
It would lead to scientific advancements, economic considerations, ethical considerations, and cultural and philosophical implications.
9. What is the significance of the speed of light?
The speed of light is a fundamental constant in the universe, representing the maximum speed at which information or energy can travel.
10. Can TRAVELS.EDU.VN help me plan a trip to Napa Valley?
Yes, travels.edu.vn specializes in creating customized Napa Valley itineraries that cater to your specific preferences. We offer expert travel planning, exclusive deals, and 24/7 customer service. Let us help you plan your dream Napa Valley getaway.
