Strep throat, while often localized to the throat, can potentially spread to other areas of the body if left untreated. TRAVELS.EDU.VN provides you with reliable information on how strep throat can manifest, its potential complications, and effective strategies for management and prevention, ensuring you stay informed and protected. Understand the interconnectedness of your health and take proactive steps to maintain your well-being with our guidance on systemic strep.
1. Understanding Strep Throat and Its Localized Symptoms
Strep throat is a bacterial infection caused by Group A Streptococcus bacteria. It primarily affects the throat and tonsils. Recognizing the symptoms early is crucial for prompt treatment and preventing further complications.
Common Strep Throat Symptoms
- Sore Throat: A painful sensation, especially when swallowing.
- Fever: Elevated body temperature, typically above 100.4°F (38°C).
- Red and Swollen Tonsils: Inflammation of the tonsils with a red appearance.
- White Patches or Pus: Presence of white or yellowish spots on the tonsils.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Enlarged and tender lymph nodes in the neck.
- Tiny Red Spots: Petechiae, small red spots on the roof of the mouth.
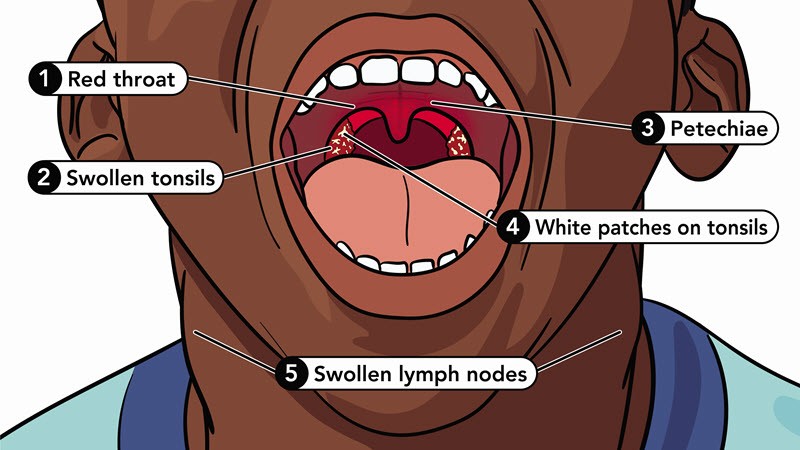 Illustration showcasing the symptoms of strep throat, including swollen tonsils and red spots
Illustration showcasing the symptoms of strep throat, including swollen tonsils and red spots
Less Common Symptoms
- Headache: Pain or discomfort in the head.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Feeling sick to the stomach and possibly throwing up.
- Rash (Scarlet Fever): A fine, red rash that feels like sandpaper.
- Stomach Pain: Abdominal discomfort.
2. How Strep Throat Can Spread Beyond the Throat
While strep throat is initially a localized infection, the bacteria can spread to other parts of the body if not promptly and effectively treated. Understanding the pathways and potential complications is essential for preventing systemic issues.
Mechanisms of Spread
- Direct Extension: The infection can spread directly from the throat to nearby tissues and structures.
- Bloodstream Invasion: In severe cases, the bacteria can enter the bloodstream, leading to widespread infection.
- Immune Response: The body’s immune response to the infection can sometimes cause complications in other organs.
Why Prompt Treatment Matters
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), early antibiotic treatment is crucial to prevent strep throat complications. “Antibiotics can kill the strep bacteria,” the CDC notes, “and reduce the risk of spreading the infection to others.”
3. Potential Complications of Untreated Strep Throat
If left unchecked, strep throat can lead to several serious complications affecting various parts of the body.
Rheumatic Fever
Rheumatic fever is a serious inflammatory condition that can affect the heart, joints, brain, and skin. It is a delayed complication of strep throat, typically occurring 1 to 5 weeks after the initial infection.
- Heart: Rheumatic heart disease, which can cause permanent damage to the heart valves.
- Joints: Painful and swollen joints, often affecting multiple joints.
- Brain: Neurological symptoms, such as Sydenham’s chorea (involuntary movements).
- Skin: Skin rash called erythema marginatum.
The American Heart Association emphasizes the importance of prompt strep throat treatment to prevent rheumatic fever. “Early diagnosis and treatment of strep throat with antibiotics are critical to preventing acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease,” they state.
Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis (PSGN)
PSGN is a kidney disease that can develop after a strep throat infection. It involves inflammation of the glomeruli, which are the filtering units of the kidneys.
- Symptoms: Include blood in the urine, swelling (edema), and high blood pressure.
- Severity: Can range from mild to severe, potentially leading to kidney damage.
The National Kidney Foundation notes that while most people recover fully from PSGN, some may develop chronic kidney disease. “Prompt treatment of strep throat can help reduce the risk of developing post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis,” they advise.
Peritonsillar Abscess
A peritonsillar abscess is a collection of pus that forms behind the tonsils. It occurs when the infection spreads from the tonsils to the surrounding tissues.
- Symptoms: Severe sore throat, difficulty swallowing, fever, and muffled voice.
- Treatment: Often requires drainage of the abscess and antibiotics.
Scarlet Fever
Scarlet fever is a complication of strep throat characterized by a distinctive rash.
- Symptoms: A fine, red rash that feels like sandpaper, typically starting on the neck and chest and spreading to the rest of the body. Other symptoms include a red face and a strawberry tongue (red and swollen).
- Treatment: Antibiotics are used to treat scarlet fever and prevent further complications.
Other Infections
- Ear Infections: Strep bacteria can spread to the middle ear, causing otitis media.
- Sinus Infections: Infection can spread to the sinuses, leading to sinusitis.
- Bacteremia: In rare cases, strep bacteria can enter the bloodstream, causing a systemic infection.
4. Risk Factors for Developing Complications
Certain factors can increase the risk of strep throat spreading to other parts of the body and causing complications.
Age
- Children: Children are more susceptible to strep throat and its complications, especially rheumatic fever and PSGN.
- Adults: Adults can also develop complications, although they are generally less common than in children.
Weakened Immune System
Individuals with a compromised immune system are at higher risk of developing severe complications from strep throat.
- Conditions: HIV/AIDS, diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and cancer.
- Medications: Immunosuppressant drugs, such as those used after organ transplantation.
Delay in Treatment
Delaying or not completing the full course of antibiotic treatment can increase the risk of complications.
Recurrent Infections
People who experience recurrent strep throat infections are at higher risk of developing complications.
5. Diagnosis and Testing for Strep Throat
Prompt and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and preventing the spread of infection.
Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will perform a physical examination to look for signs and symptoms of strep throat, such as:
- Red and swollen tonsils
- White patches or pus on the tonsils
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Fever
Rapid Strep Test
A rapid strep test involves swabbing the back of the throat to collect a sample. The sample is then tested for the presence of Group A Streptococcus bacteria.
- Accuracy: Rapid strep tests are highly specific but may have lower sensitivity.
- Results: Results are typically available within minutes.
Throat Culture
If the rapid strep test is negative but strep throat is still suspected, a throat culture may be performed. This involves swabbing the throat and sending the sample to a laboratory to be cultured for bacteria.
- Accuracy: Throat cultures are more sensitive than rapid strep tests.
- Results: Results typically take 24 to 48 hours.
6. Treatment Options for Strep Throat
The primary treatment for strep throat is antibiotics, which help to kill the bacteria and prevent complications.
Antibiotics
- Penicillin: Penicillin is the most common antibiotic prescribed for strep throat. It is effective and generally well-tolerated.
- Amoxicillin: Amoxicillin is another penicillin-based antibiotic that may be used, especially in children.
- Cephalexin: Cephalexin is a cephalosporin antibiotic that can be used in people who are allergic to penicillin.
- Azithromycin: Azithromycin is a macrolide antibiotic that may be used in people who are allergic to penicillin.
Symptomatic Relief
In addition to antibiotics, several measures can be taken to relieve symptoms of strep throat.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil), can help reduce fever and pain.
- Throat Lozenges: Throat lozenges can soothe a sore throat.
- Warm Liquids: Drinking warm liquids, such as tea or broth, can help relieve throat pain.
- Salt Water Gargles: Gargling with warm salt water can help reduce inflammation and pain in the throat.
- Rest: Getting plenty of rest can help the body fight off the infection.
7. Preventive Measures to Avoid Strep Throat and Its Spread
Preventing strep throat is essential to reduce the risk of infection and its potential complications.
Hygiene Practices
- Handwashing: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after coughing or sneezing and before eating.
- Avoid Sharing: Do not share utensils, cups, or personal items with others.
- Cough Etiquette: Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when coughing or sneezing, and dispose of the tissue properly.
Avoid Close Contact
Avoid close contact with people who have strep throat or other respiratory infections.
Boosting Immune System
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to boost your immune system.
- Adequate Sleep: Get enough sleep to support immune function.
- Stress Management: Manage stress through relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation.
8. Strep Throat and Rheumatic Fever: A Detailed Look
Rheumatic fever is one of the most serious complications of strep throat, particularly affecting children. Understanding this condition is crucial for preventing long-term health issues.
Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Fever
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that occurs as a result of an autoimmune response to strep throat infection. The body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, leading to inflammation in the heart, joints, brain, and skin.
Symptoms of Rheumatic Fever
- Fever: Elevated body temperature.
- Joint Pain: Painful and swollen joints, often affecting multiple joints.
- Carditis: Inflammation of the heart, which can lead to permanent heart damage.
- Sydenham’s Chorea: Neurological symptoms, such as involuntary movements.
- Erythema Marginatum: A skin rash characterized by pink or red rings on the trunk and limbs.
- Subcutaneous Nodules: Small, painless lumps under the skin, typically near joints.
Diagnosis of Rheumatic Fever
The diagnosis of rheumatic fever is based on the revised Jones criteria, which include major and minor manifestations.
- Major Manifestations: Carditis, polyarthritis, Sydenham’s chorea, erythema marginatum, and subcutaneous nodules.
- Minor Manifestations: Fever, arthralgia (joint pain), elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) or C-reactive protein (CRP), and prolonged PR interval on electrocardiogram (ECG).
Treatment of Rheumatic Fever
The treatment of rheumatic fever focuses on reducing inflammation, preventing further heart damage, and managing symptoms.
- Antibiotics: Penicillin is used to eradicate any remaining strep bacteria.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: Aspirin or corticosteroids are used to reduce inflammation.
- Bed Rest: Rest is recommended to reduce the workload on the heart.
- Long-Term Antibiotics: People who have had rheumatic fever may need to take long-term antibiotics to prevent recurrent strep infections and further heart damage.
9. How Strep Throat Affects the Kidneys: Understanding PSGN
Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN) is another significant complication of strep throat, affecting the kidneys.
Pathophysiology of PSGN
PSGN is an inflammatory kidney disease that occurs after a strep throat infection. It involves inflammation of the glomeruli, which are the filtering units of the kidneys. The inflammation is caused by the deposition of immune complexes in the glomeruli.
Symptoms of PSGN
- Hematuria: Blood in the urine, which may cause the urine to appear red or brown.
- Edema: Swelling, typically in the face, hands, and feet.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure.
- Oliguria: Decreased urine output.
Diagnosis of PSGN
The diagnosis of PSGN is based on clinical findings, laboratory tests, and kidney biopsy.
- Laboratory Tests: Urine tests to detect blood and protein, blood tests to measure kidney function and immune markers.
- Kidney Biopsy: In some cases, a kidney biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition.
Treatment of PSGN
The treatment of PSGN focuses on managing symptoms and supporting kidney function.
- Dietary Modifications: Limiting salt and fluid intake to reduce swelling and high blood pressure.
- Medications: Diuretics to reduce fluid retention, antihypertensive medications to control high blood pressure, and corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
- Dialysis: In severe cases, dialysis may be necessary to remove waste products from the blood and support kidney function.
10. Seeking Professional Help and When to Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN
Knowing when to seek medical attention is crucial for managing strep throat and preventing complications.
When to See a Doctor
- Severe Sore Throat: If you have a severe sore throat that makes it difficult to swallow.
- Fever: If you have a fever above 101°F (38.3°C).
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: If you have swollen and tender lymph nodes in the neck.
- Rash: If you develop a rash, especially if it feels like sandpaper.
- Difficulty Breathing: If you have difficulty breathing or swallowing.
Why Choose TRAVELS.EDU.VN for Your Health Information?
At TRAVELS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with accurate, reliable, and up-to-date health information. Our team of experts works diligently to ensure that our content is evidence-based and easy to understand. We strive to empower you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your health.
Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN for Personalized Assistance
If you have any questions or concerns about strep throat or its complications, don’t hesitate to reach out to us. Our knowledgeable and friendly staff are here to help.
- Address: 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (707) 257-5400
- Website: TRAVELS.EDU.VN
We understand that navigating health information can be overwhelming. Let TRAVELS.EDU.VN be your trusted resource for all your health-related needs.
11. Statistics and Impact of Strep Throat in the United States
Understanding the prevalence and impact of strep throat can help individuals and healthcare providers prioritize prevention and treatment efforts.
Prevalence of Strep Throat
- Children: Strep throat is most common in children between the ages of 5 and 15.
- Seasonality: Strep throat is more common during the winter and early spring months.
Impact of Strep Throat Complications
- Rheumatic Fever: Although rare in developed countries, rheumatic fever remains a significant concern in developing countries.
- Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis (PSGN): PSGN can lead to chronic kidney disease in some individuals.
Economic Impact
Strep throat and its complications can result in significant healthcare costs, including doctor visits, diagnostic tests, and medications.
12. The Role of Diet and Nutrition in Recovering from Strep Throat
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in supporting the immune system and promoting healing during and after a strep throat infection.
Foods to Eat
- Soft Foods: Easy-to-swallow foods like soups, yogurt, and mashed potatoes.
- Warm Liquids: Soothing liquids such as herbal teas, broths, and honey-lemon mixtures.
- Nutrient-Rich Foods: Foods high in vitamins and minerals, like fruits and vegetables.
Foods to Avoid
- Acidic Foods: Citrus fruits and juices, which can irritate the throat.
- Spicy Foods: Foods with strong spices that can cause discomfort.
- Hard or Crunchy Foods: Foods that require a lot of chewing, potentially irritating the throat.
Hydration
Staying hydrated is crucial for thinning mucus and soothing the throat. Drink plenty of water, herbal teas, and electrolyte-rich beverages.
13. Complementary and Alternative Therapies for Strep Throat Relief
In addition to conventional medical treatment, some people find relief from strep throat symptoms through complementary and alternative therapies.
Honey
Honey has natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can soothe a sore throat.
Salt Water Gargles
Gargling with warm salt water can help reduce inflammation and pain in the throat.
Herbal Remedies
- Echinacea: Known for its immune-boosting properties.
- Slippery Elm: Can coat and soothe the throat.
- Licorice Root: Has anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties.
Important Note
Always consult with a healthcare provider before using complementary and alternative therapies, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
14. Debunking Common Myths About Strep Throat
It’s important to dispel common misconceptions about strep throat to ensure people have accurate information for prevention and treatment.
Myth 1: Strep Throat is Just a Bad Sore Throat
Fact: Strep throat is a bacterial infection that requires antibiotic treatment, unlike most sore throats caused by viruses.
Myth 2: Strep Throat Only Affects Children
Fact: While more common in children, adults can also contract strep throat.
Myth 3: Strep Throat Always Causes White Spots on the Tonsils
Fact: White spots may be present, but not everyone with strep throat experiences this symptom.
Myth 4: Strep Throat Will Go Away on Its Own
Fact: Strep throat requires antibiotic treatment to prevent complications and spread of infection.
Myth 5: You Can’t Get Strep Throat More Than Once
Fact: It is possible to get strep throat multiple times, especially with frequent exposure to the bacteria.
15. Strep Throat During Pregnancy: Considerations and Precautions
Strep throat during pregnancy requires special consideration to protect the health of both the mother and the baby.
Risks of Untreated Strep Throat
Untreated strep throat during pregnancy can lead to complications, such as:
- Premature Labor: Increased risk of preterm birth.
- Low Birth Weight: Potential for the baby to be born with low birth weight.
- Infection Transmission: Rare but possible transmission of infection to the baby.
Treatment Options
Penicillin and amoxicillin are generally considered safe for use during pregnancy and are effective in treating strep throat.
Precautions
- Consult with a Doctor: Pregnant women should consult with their healthcare provider for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
- Complete Antibiotic Course: It’s crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics to eradicate the infection.
16. The Importance of Completing the Full Course of Antibiotics
Completing the full course of antibiotics is critical for effectively treating strep throat and preventing complications.
Why It Matters
- Eradicates Infection: Completing the course ensures that all the bacteria are killed, preventing the infection from recurring.
- Prevents Resistance: Not finishing the antibiotics can contribute to antibiotic resistance, making future infections harder to treat.
- Reduces Complications: Fully treated strep throat reduces the risk of complications such as rheumatic fever and PSGN.
Potential Consequences of Non-Compliance
- Recurrent Infection: The infection can return if not fully treated.
- Antibiotic Resistance: Bacteria can develop resistance to antibiotics.
- Increased Risk of Complications: Untreated or partially treated strep throat increases the risk of rheumatic fever and PSGN.
17. Strep Throat and Scarlet Fever: Understanding the Connection
Scarlet fever is a complication of strep throat that presents with a distinctive rash and other symptoms.
What is Scarlet Fever?
Scarlet fever is caused by the same bacteria that causes strep throat, Group A Streptococcus. The bacteria produce a toxin that causes the characteristic rash.
Symptoms of Scarlet Fever
- Rash: A fine, red rash that feels like sandpaper, typically starting on the neck and chest and spreading to the rest of the body.
- Red Face: The face may appear flushed.
- Strawberry Tongue: The tongue may be red and swollen, with a coating that makes it look like a strawberry.
- Fever: Elevated body temperature.
- Sore Throat: Pain and discomfort in the throat.
Treatment of Scarlet Fever
Scarlet fever is treated with antibiotics, typically penicillin or amoxicillin. It’s essential to complete the full course of antibiotics to eradicate the infection and prevent complications.
18. Living with Rheumatic Heart Disease: Management and Long-Term Care
Rheumatic heart disease is a serious complication of rheumatic fever that can cause permanent damage to the heart valves.
Management Strategies
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular visits to a cardiologist for monitoring and assessment.
- Medications: Medications to manage symptoms such as heart failure, arrhythmias, and high blood pressure.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Healthy lifestyle choices, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking.
Long-Term Care
- Prophylactic Antibiotics: Long-term antibiotic treatment to prevent recurrent strep infections and further heart damage.
- Valve Repair or Replacement: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace damaged heart valves.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: A program to help people with heart disease improve their health and quality of life.
19. The Future of Strep Throat Research and Prevention
Ongoing research is focused on developing new and improved methods for preventing and treating strep throat.
Vaccine Development
Researchers are working on developing a vaccine for strep throat to prevent infection and reduce the risk of complications.
Improved Diagnostic Tools
Efforts are underway to develop more accurate and rapid diagnostic tests for strep throat.
Antibiotic Stewardship
Strategies to promote the appropriate use of antibiotics and reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance are being implemented.
20. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Strep Throat
1. What is strep throat?
Strep throat is a bacterial infection of the throat and tonsils caused by Group A Streptococcus bacteria.
2. How is strep throat spread?
Strep throat is spread through close contact with infected individuals, typically through respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing.
3. What are the symptoms of strep throat?
Common symptoms include a sore throat, fever, red and swollen tonsils, white patches or pus on the tonsils, and swollen lymph nodes in the neck.
4. How is strep throat diagnosed?
Strep throat is diagnosed through a rapid strep test or throat culture.
5. What is the treatment for strep throat?
Strep throat is treated with antibiotics, typically penicillin or amoxicillin.
6. Can strep throat lead to complications?
Yes, untreated strep throat can lead to complications such as rheumatic fever, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN), and peritonsillar abscess.
7. How can I prevent strep throat?
Preventive measures include frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and practicing good cough etiquette.
8. Is strep throat contagious?
Yes, strep throat is highly contagious.
9. Can adults get strep throat?
Yes, adults can get strep throat, although it is more common in children.
10. What should I do if I think I have strep throat?
Consult a healthcare provider for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
At TRAVELS.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the most comprehensive and reliable information about strep throat and its potential impact on your health. Remember, early detection and proper management are key to preventing serious complications and ensuring a speedy recovery. If you’re planning a trip to Napa Valley and want to ensure your health needs are taken care of, contact us today to learn about our comprehensive travel packages and personalized health support services. Reach out to us at +1 (707) 257-5400 or visit our website at travels.edu.vn to discover how we can make your trip both enjoyable and safe.