Egress Path Of Travel In Revit is crucial for safety and code compliance; TRAVELS.EDU.VN offers solutions to streamline this essential design aspect. Discover how to effectively utilize Revit for designing and analyzing egress paths, ensuring safe and efficient building evacuation strategies. Leveraging tools within Revit can revolutionize your approach to egress design.
1. Understanding Egress Path Requirements in Revit
Designing safe and efficient buildings hinges on a deep understanding of egress path requirements. In Revit, this involves much more than simply drawing lines on a plan. It requires a holistic approach that considers building codes, occupant behavior, and the capabilities of the software. Let’s delve into the critical aspects that shape these requirements:
1.1. Code Compliance: The Foundation of Egress Design
-
International Building Code (IBC): The IBC serves as a baseline for many local building codes in the United States. It dictates minimum widths for corridors, maximum travel distances to exits, and the number and placement of exits based on occupancy type and building size.
-
NFPA 101: Life Safety Code: While not a legal requirement in all jurisdictions, NFPA 101 is a widely recognized standard for life safety. It provides detailed guidance on egress design, including requirements for emergency lighting, signage, and fire protection systems.
-
Local Amendments: It’s crucial to remember that local jurisdictions often amend the IBC and NFPA 101 to address specific regional concerns. Always consult the local building code official to ensure full compliance.
-
Key Considerations:
- Occupancy Type: Different occupancies (e.g., residential, commercial, educational) have varying egress requirements based on their potential hazard levels.
- Building Height and Area: Taller and larger buildings generally require more stringent egress measures.
- Sprinkler Systems: The presence of a sprinkler system can sometimes allow for increased travel distances to exits.
-
Example: In California, egress path width might be slightly different from Texas due to local amendments to the IBC.
1.2. Occupant Behavior: Predicting Evacuation Patterns
-
Human Factors: Understanding how people behave during an emergency is essential for effective egress design. Factors like familiarity with the building, panic, and physical limitations can all impact evacuation speed and efficiency.
-
Agent-Based Modeling: Advanced simulation tools can model occupant behavior during a fire or other emergency. These simulations can help identify potential bottlenecks and areas where egress paths may need to be widened or reconfigured.
-
Common Bottlenecks:
- Doorways: Narrow doorways can create bottlenecks, especially in high-occupancy areas.
- Stairwells: Stairwells can be challenging for people with mobility issues.
- Sharp Turns: Sharp turns in corridors can slow down evacuation speed.
-
Design Strategies:
- Clear Signage: Ensure that exit signs are visible and easy to understand, even in smoky conditions.
- Wide Corridors: Provide ample corridor width to accommodate the expected flow of people.
- Multiple Exits: Offer multiple exit options to prevent overcrowding in any one area.
1.3. Revit’s Role in Egress Analysis
- Path of Travel Tool: Revit’s built-in Path of Travel tool automatically calculates the shortest distance between two points, taking into account obstacles like walls and furniture. This is a valuable tool for verifying code compliance and identifying potential egress issues.
- Custom Families: Create custom Revit families to represent egress components like exit signs, fire extinguishers, and emergency lighting. This will ensure that these elements are accurately represented in your model and can be easily scheduled and tracked.
- Scheduling and Tagging: Use Revit’s scheduling and tagging features to track key egress parameters like travel distance, exit width, and occupancy load. This will help you ensure that your design meets all applicable code requirements.
- Advanced Analysis: Integrate Revit with third-party analysis tools to perform more sophisticated egress simulations. These tools can model occupant behavior, predict evacuation times, and identify potential safety hazards.
- TRAVELS.EDU.VN’s Expertise: TRAVELS.EDU.VN leverages Revit’s capabilities to provide comprehensive egress path analysis, ensuring designs meet safety standards and optimize evacuation efficiency. Contact us at +1 (707) 257-5400 for expert guidance.
2. Setting Up Revit for Egress Path Design
Before diving into the specifics of egress path creation, configuring Revit appropriately is essential for a streamlined and accurate workflow. This involves setting up project parameters, view templates, and custom families tailored to egress design.
2.1. Project Parameters for Egress Data
-
Purpose: Project parameters allow you to add custom data fields to Revit elements, enabling you to track and manage egress-related information effectively.
-
Key Parameters:
- Occupancy Load: Defines the number of people expected to occupy a specific area. This is crucial for calculating required exit widths.
- Travel Distance: Represents the distance a person must travel from any point in a space to reach an exit.
- Exit Width: Specifies the clear width of an exit opening, ensuring it meets code requirements for occupant capacity.
- Egress Component Type: Categorizes elements as exit signs, fire extinguishers, or other egress-related components.
- Fire Resistance Rating: Indicates the fire resistance rating of walls, doors, and other elements along the egress path.
-
Implementation:
- Go to the “Manage” tab and click “Project Parameters.”
- Click “Add” to create a new parameter.
- Define the parameter name, discipline, type of parameter (e.g., number, text, yes/no), and the categories to which it applies (e.g., rooms, doors, walls).
- Choose whether the parameter is an “Instance” parameter (unique to each element) or a “Type” parameter (applies to all elements of a specific type).
2.2. View Templates for Clarity
-
Purpose: View templates allow you to save and apply specific view settings, ensuring consistency and clarity in your egress plans.
-
Essential Settings:
- Visibility/Graphics Overrides: Control the visibility and appearance of different element categories. For example, you might highlight egress paths in a specific color or hide non-essential elements.
- Filters: Create filters to highlight elements based on their egress-related parameters. For instance, you could filter all rooms with an occupancy load exceeding a certain threshold.
- View Scale: Set the appropriate view scale for clear presentation of egress information.
- Annotation Settings: Define the style and size of tags and annotations used to label egress elements.
-
Steps to Create a View Template:
- Create a new view or modify an existing one to display the desired egress information.
- Go to the “View” tab and click “View Templates” > “Create Template from Current View.”
- Name the template and specify which view settings to include.
- Apply the template to other views to maintain consistency.
2.3. Custom Families for Egress Components
-
Purpose: Custom families allow you to create accurate and detailed representations of egress components, ensuring they are correctly modeled and scheduled.
-
Examples:
- Exit Signs: Create families that accurately depict the size, shape, and lighting characteristics of exit signs.
- Fire Extinguishers: Model fire extinguishers with the correct dimensions and placement requirements.
- Emergency Lighting: Develop families for emergency lighting fixtures that include photometric data for accurate lighting analysis.
- Accessible Egress Routes: Design families to indicate accessible routes, including ramps and elevators, ensuring compliance with accessibility standards.
-
Family Creation Tips:
- Use Reference Planes: Use reference planes to define the geometry of the family and ensure it can be easily adjusted.
- Add Parameters: Add parameters to control the size, material, and other properties of the family.
- Include Connectors: Include connectors for electrical or plumbing systems, as needed.
- Test Thoroughly: Test the family in a project environment to ensure it behaves as expected.
-
TRAVELS.EDU.VN Can Help: TRAVELS.EDU.VN can assist in creating custom Revit families tailored to your specific egress design needs. Contact us at 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States, or visit TRAVELS.EDU.VN.
3. Utilizing Revit’s Path of Travel Tool
Revit’s Path of Travel tool is a game-changer for egress analysis, offering automated route calculation and valuable insights into travel distances. However, mastering this tool requires understanding its functionalities, limitations, and best practices.
3.1. Automatic Route Generation
-
Functionality: The Path of Travel tool automatically generates the shortest path between two points in a Revit model, taking into account walls, furniture, and other obstructions.
-
Workflow:
- Go to the “Analyze” tab and click “Path of Travel.”
- Specify the start and end points of the egress path.
- Revit automatically calculates the shortest path, displaying it as a green line.
- The tool also calculates the travel distance and displays it as a tag.
-
Benefits:
- Time Savings: Automates a traditionally time-consuming task.
- Accuracy: Provides accurate travel distance calculations, reducing the risk of errors.
- Code Compliance: Helps verify that travel distances meet code requirements.
3.2. Adjusting and Refining Paths
-
Manual Adjustments: While the Path of Travel tool provides a good starting point, manual adjustments are often necessary to refine the path and ensure it accurately reflects real-world conditions.
-
Common Scenarios:
- Forced Paths: In some cases, occupants may be required to follow a specific path due to security protocols or other factors.
- Obstacles: The tool may not always accurately account for temporary obstacles like furniture or equipment.
- Door Swings: The tool doesn’t automatically consider door swings, which can impact egress path width.
-
Adjustment Techniques:
- Drag and Drop: Drag the path segments to adjust their position.
- Add Vertices: Add vertices to create more complex paths.
- Modify Properties: Modify the path properties to specify the path width and other parameters.
3.3. Analyzing Travel Distances
- Travel Distance Tag: The Path of Travel tool automatically generates a tag that displays the travel distance. This tag can be customized to display other relevant information, such as the occupancy load of the space.
- Scheduling: You can create a schedule to list all of the egress paths in your project, along with their travel distances and other properties. This allows you to quickly identify areas where travel distances may exceed code requirements.
- Color Coding: Use color coding to visually represent travel distances on your plans. For example, you could color-code paths based on their travel distance, with red indicating paths that exceed the maximum allowable distance.
- Worst-Case Scenarios: Analyze travel distances from the most remote points in a space to ensure that all occupants can safely evacuate the building in an emergency.
- TRAVELS.EDU.VN’s Advanced Analysis: TRAVELS.EDU.VN goes beyond basic travel distance analysis, offering comprehensive simulations to model occupant behavior and identify potential egress bottlenecks. Contact us at +1 (707) 257-5400 to learn more.
4. Advanced Egress Modeling Techniques
While Revit’s Path of Travel tool provides a solid foundation, advanced techniques can enhance your egress models, providing more realistic and informative analyses.
4.1. Incorporating Door Swings and Obstacles
-
Door Swings: Door swings can significantly impact egress path width and should be accurately modeled in Revit.
-
Modeling Techniques:
- Swing Direction: Ensure the door swing direction is correctly modeled, swinging in the direction of egress whenever possible.
- Clearance: Provide adequate clearance around doors to accommodate the door swing and allow for easy passage.
- Family Parameters: Use family parameters to control the door swing angle and ensure it meets code requirements.
-
Obstacles: Temporary obstacles like furniture, equipment, and storage can obstruct egress paths and should be considered in your analysis.
-
Strategies:
- Furniture Layout: Plan the furniture layout carefully to minimize obstructions to egress paths.
- Dynamic Elements: Use dynamic Revit families to represent movable obstacles, allowing you to simulate different scenarios.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections to ensure that egress paths are clear of obstructions.
4.2. Modeling Complex Egress Scenarios
-
Multi-Story Buildings: Modeling egress in multi-story buildings requires careful consideration of stairwell locations, fire resistance ratings, and vertical travel distances.
-
Techniques:
- Stairwell Families: Use detailed stairwell families that accurately represent the geometry and fire resistance of the stairwell.
- Vertical Travel Distance: Calculate the vertical travel distance in addition to the horizontal travel distance to ensure code compliance.
- Fire Compartmentation: Model fire compartments to prevent the spread of fire and smoke, providing occupants with a safe refuge area.
-
Assembly Spaces: Assembly spaces like theaters, auditoriums, and stadiums require specialized egress design due to their high occupancy loads and complex layouts.
-
Considerations:
- Multiple Exits: Provide multiple exits to accommodate the large number of occupants.
- Aisles and Cross-Aisles: Design aisles and cross-aisles to facilitate easy movement to exits.
- Panic Hardware: Use panic hardware on exit doors to allow for quick and easy egress.
4.3. Integrating with Fire Simulation Software
-
Advanced Analysis: Integrate your Revit model with fire simulation software to perform advanced egress analysis. This software can model the spread of fire and smoke, simulate occupant behavior, and predict evacuation times.
-
Benefits:
- Identify Bottlenecks: Identify potential bottlenecks in the egress system.
- Optimize Egress Design: Optimize the egress design to improve evacuation efficiency.
- Verify Code Compliance: Verify that the egress design meets all applicable code requirements.
-
Software Options: Popular fire simulation software options include:
- FDS (Fire Dynamics Simulator): A computational fluid dynamics (CFD) model for simulating fire behavior.
- Pathfinder: An agent-based evacuation simulator.
- MassMotion: A pedestrian simulation software.
-
TRAVELS.EDU.VN’s Expertise: TRAVELS.EDU.VN utilizes advanced fire simulation software to provide comprehensive egress analysis, ensuring the safety and well-being of building occupants. Contact us at TRAVELS.EDU.VN for expert consultation.
5. Documenting and Presenting Egress Plans
Creating clear and concise egress plans is crucial for communication with building officials, contractors, and occupants. Revit offers several tools and techniques for effectively documenting and presenting your egress designs.
5.1. Creating Dedicated Egress Plans
-
Purpose: Dedicated egress plans provide a clear and focused view of the egress system, highlighting key elements like exit locations, travel distances, and fire protection features.
-
Essential Elements:
- Exit Locations: Clearly indicate the location of all exits, including doors, stairwells, and exterior exits.
- Travel Distances: Show the travel distance from the most remote point in each space to an exit.
- Occupancy Load: Indicate the occupancy load of each space.
- Fire Resistance Ratings: Highlight the fire resistance ratings of walls, doors, and other fire-rated elements.
- Egress Path Markings: Use clear and consistent markings to indicate the egress paths.
- Accessibility Features: Clearly identify accessible egress routes, including ramps, elevators, and accessible restrooms.
-
Revit Techniques:
- View Templates: Use view templates to control the visibility and appearance of elements in the egress plan.
- Filters: Use filters to highlight specific egress-related elements.
- Color Coding: Use color coding to visually represent different aspects of the egress system.
- Annotation: Use annotations to label key elements and provide additional information.
5.2. Tagging and Scheduling Egress Components
-
Tagging: Tagging egress components allows you to quickly and easily identify and label elements in your model.
-
Custom Tags: Create custom tags to display specific egress-related information, such as the exit width, occupancy load, or fire resistance rating.
-
Scheduling: Scheduling allows you to extract and organize data about egress components, providing a comprehensive overview of the egress system.
-
Schedule Uses:
- Exit Door Schedule: List all exit doors, along with their width, height, fire rating, and hardware.
- Occupancy Load Schedule: List all rooms, along with their area, occupancy load, and required exit width.
- Fire Protection Equipment Schedule: List all fire extinguishers, fire alarms, and other fire protection equipment, along with their location and specifications.
5.3. Exporting and Sharing Egress Information
- PDF Export: Export your egress plans to PDF format for easy sharing and viewing.
- DWG Export: Export your Revit model to DWG format for use in other CAD software.
- BIM Collaboration: Share your Revit model with other stakeholders using BIM collaboration platforms.
- TRAVELS.EDU.VN’s Collaborative Approach: TRAVELS.EDU.VN utilizes BIM collaboration platforms to ensure seamless communication and coordination with all project stakeholders. Contact us at 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States, for a collaborative egress design experience.
6. Best Practices for Egress Path Design in Revit
Following best practices ensures accurate, efficient, and code-compliant egress designs in Revit.
6.1. Start Early in the Design Process
-
Early Integration: Integrate egress design considerations early in the design process, rather than as an afterthought.
-
Benefits:
- Avoid Costly Revisions: Early integration can help avoid costly revisions later in the project.
- Optimize Layout: Optimize the building layout to improve egress efficiency.
- Code Compliance: Ensure code compliance from the outset.
6.2. Collaborate with Stakeholders
-
Teamwork: Collaborate with architects, engineers, fire protection consultants, and building officials to ensure a coordinated and comprehensive egress design.
-
Communication:
- Regular Meetings: Hold regular meetings to discuss egress design issues.
- BIM Collaboration: Use BIM collaboration platforms to share information and coordinate efforts.
- Clear Communication: Communicate clearly and effectively with all stakeholders.
6.3. Stay Up-to-Date with Codes and Standards
-
Continuous Learning: Building codes and standards are constantly evolving. Stay up-to-date with the latest requirements to ensure compliance.
-
Resources:
- ICC (International Code Council): The ICC publishes the International Building Code (IBC) and other related codes.
- NFPA (National Fire Protection Association): The NFPA publishes NFPA 101: Life Safety Code and other fire protection standards.
- Local Building Officials: Consult with local building officials to clarify any questions or concerns.
6.4. Validate Your Design
-
Verification: Validate your egress design using a variety of methods, including:
- Code Review: Conduct a thorough code review to ensure compliance with all applicable requirements.
- Egress Simulation: Perform egress simulations to model occupant behavior and predict evacuation times.
- Third-Party Review: Engage a third-party consultant to review your design and provide feedback.
-
TRAVELS.EDU.VN’s Comprehensive Validation: TRAVELS.EDU.VN offers comprehensive egress design validation services, ensuring your design meets the highest standards of safety and code compliance. Contact us at +1 (707) 257-5400 for a thorough review of your egress plans.
7. Common Challenges and Solutions
Egress path design in Revit can present challenges; understanding them and having solutions is vital.
7.1. Complex Building Geometries
-
Challenge: Complex building geometries, such as curved walls or irregular floor plans, can make it difficult to accurately model egress paths.
-
Solutions:
- Reference Planes: Use reference planes to define the geometry of the building and ensure accurate modeling.
- Path of Travel Tool Adjustments: Manually adjust the paths generated by the Path of Travel tool to account for the complex geometry.
- Advanced Modeling Techniques: Use advanced modeling techniques, such as adaptive components, to create accurate representations of complex building elements.
7.2. Integrating with Existing Models
-
Challenge: Integrating egress design into existing Revit models can be challenging, especially if the models are not well-organized or contain errors.
-
Solutions:
- Model Auditing: Conduct a thorough audit of the existing model to identify any errors or inconsistencies.
- Model Cleanup: Clean up the model by deleting unnecessary elements and correcting any errors.
- Phased Implementation: Implement the egress design in phases to minimize disruption to the existing model.
7.3. Maintaining Accuracy over Time
-
Challenge: Maintaining the accuracy of the egress design over time can be challenging, especially as the building undergoes renovations or modifications.
-
Solutions:
- Regular Model Updates: Update the Revit model regularly to reflect any changes to the building.
- Version Control: Use version control to track changes to the model and ensure that the latest version is always available.
- Training: Provide training to building staff on how to maintain the accuracy of the egress design.
7.4. Addressing Code Interpretation Issues
-
Challenge: Code interpretation can vary, leading to uncertainty in egress design.
-
Solutions:
- Consult with Authorities: Consult with local building officials for clarification on code requirements.
- Document Interpretations: Document all code interpretations and assumptions made during the design process.
- Seek Expert Advice: Engage a qualified fire protection engineer for expert advice on code compliance.
-
TRAVELS.EDU.VN Offers Clarity: TRAVELS.EDU.VN provides expert guidance on code interpretation, ensuring your egress design meets all applicable requirements. Contact us at 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States, for reliable code compliance assistance.
8. The Future of Egress Design in Revit
Egress design in Revit is constantly evolving, with new tools and technologies emerging to improve the process.
8.1. AI-Powered Egress Analysis
-
Artificial Intelligence: AI is being used to automate and improve egress analysis, providing designers with valuable insights and recommendations.
-
Applications:
- Automated Path Generation: AI can automatically generate egress paths based on building layout and occupancy patterns.
- Predictive Analysis: AI can predict occupant behavior during a fire and identify potential bottlenecks in the egress system.
- Code Compliance Checking: AI can automatically check the egress design for compliance with applicable codes and standards.
8.2. Virtual and Augmented Reality
-
Immersive Experience: VR and AR technologies are being used to create immersive experiences that allow designers and building occupants to visualize and evaluate the egress system.
-
Benefits:
- Improved Understanding: VR and AR can improve understanding of the egress system and identify potential issues.
- Enhanced Collaboration: VR and AR can enhance collaboration among stakeholders by providing a shared understanding of the egress design.
- Effective Training: VR and AR can be used to train building occupants on how to evacuate the building in an emergency.
8.3. Integration with Smart Building Systems
-
Connected Technology: Egress design is becoming increasingly integrated with smart building systems, such as fire alarm systems, smoke control systems, and emergency lighting systems.
-
Advantages:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of building conditions can provide valuable information for egress planning.
- Automated Response: Automated responses to fire events can improve evacuation efficiency.
- Enhanced Safety: Integration with smart building systems can enhance the overall safety of the building.
8.4. Data-Driven Design
-
Analysis: Data analysis is playing a larger role in egress design, with designers using data on occupant behavior, fire incidents, and building performance to inform their decisions.
-
Insights:
- Optimized Designs: Data-driven design can lead to more optimized and effective egress systems.
- Improved Safety: Data analysis can help identify potential safety hazards and improve the overall safety of the building.
- Informed Decisions: Designers can make more informed decisions based on data analysis rather than intuition.
-
TRAVELS.EDU.VN Embraces Innovation: TRAVELS.EDU.VN is committed to staying at the forefront of egress design technology, incorporating the latest innovations to provide cutting-edge solutions for our clients. Contact us at +1 (707) 257-5400 to learn more about our innovative approach.
 Revit Egress Path Railing Options
Revit Egress Path Railing Options
9. Egress Design Services at TRAVELS.EDU.VN
TRAVELS.EDU.VN offers expert egress design services, ensuring safety and compliance.
9.1. Comprehensive Egress Path Analysis
-
Our Approach: We conduct thorough egress path analyses using Revit’s advanced tools and industry best practices.
-
Services:
- Travel distance calculations
- Occupancy load analysis
- Exit capacity verification
- Code compliance review
9.2. Custom Egress Modeling
-
Tailored Solutions: We create custom Revit models tailored to your specific building requirements.
-
Modeling Services:
- Accurate representation of building geometry
- Detailed modeling of egress components
- Integration of fire protection systems
9.3. Egress Plan Documentation
-
Clear and Concise Plans: We provide clear and concise egress plans that are easy to understand and use.
-
Documentation Services:
- Dedicated egress plans
- Tagged and scheduled egress components
- PDF and DWG exports
9.4. Egress Design Consultation
-
Expert Guidance: Our experienced egress design consultants provide expert guidance throughout the design process.
-
Consultation Services:
- Code interpretation
- Design review
- Value engineering
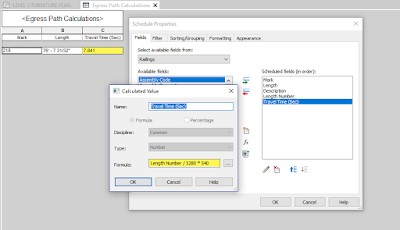 Revit Egress Path Schedule
Revit Egress Path Schedule
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
10.1. What is the Egress Path of Travel in Revit?
The egress path of travel in Revit refers to the route an occupant would take to evacuate a building during an emergency, modeled and analyzed within the Revit software environment. It is vital for ensuring building designs meet safety and code compliance standards.
10.2. How Does Revit Help in Egress Path Design?
Revit provides tools like the Path of Travel tool, custom families, and scheduling features to automate calculations, accurately model egress components, and track relevant parameters, facilitating efficient and compliant egress design.
10.3. What are Key Considerations for Egress Design in Revit?
Key considerations include code compliance (IBC, NFPA 101), occupant behavior, door swings, obstacles, fire resistance ratings, and accurate modeling of building geometry.
10.4. What is the Path of Travel Tool in Revit?
The Path of Travel tool automatically calculates the shortest distance between two points in a Revit model, taking into account walls, furniture, and other obstructions. It helps verify code compliance and identify potential egress issues.
10.5. How Can I Customize Egress Components in Revit?
You can create custom Revit families for egress components like exit signs, fire extinguishers, and emergency lighting. Add parameters to control the size, material, and other properties of the family to meet specific project needs.
10.6. How Do I Analyze Travel Distances in Revit?
Revit’s Path of Travel tool generates a tag displaying the travel distance. You can also create schedules to list all egress paths, along with their travel distances and other properties, allowing you to identify areas where travel distances may exceed code requirements.
10.7. What are Some Advanced Techniques for Egress Modeling in Revit?
Advanced techniques include incorporating door swings and obstacles, modeling complex egress scenarios in multi-story buildings and assembly spaces, and integrating with fire simulation software for comprehensive analysis.
10.8. How Can I Document and Present Egress Plans in Revit?
Create dedicated egress plans that clearly indicate exit locations, travel distances, occupancy loads, and fire resistance ratings. Use tagging and scheduling to organize data about egress components, and export your plans to PDF or DWG format for easy sharing.
10.9. What are the Best Practices for Egress Path Design in Revit?
Best practices include starting early in the design process, collaborating with stakeholders, staying up-to-date with codes and standards, and validating your design using code reviews, egress simulations, and third-party reviews.
10.10. How Can TRAVELS.EDU.VN Help with Egress Design in Revit?
TRAVELS.EDU.VN offers comprehensive egress design services, including egress path analysis, custom egress modeling, egress plan documentation, and expert consultation. Contact us at +1 (707) 257-5400 or visit TRAVELS.EDU.VN for assistance with your project.
Plan your Napa Valley getaway with travels.edu.vn, where expert guidance ensures a safe, enjoyable, and memorable experience. Don’t wait, contact us now at +1 (707) 257-5400 for personalized assistance. Our office is located at 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States.