Electromagnetic waves, a fascinating form of energy, are pivotal for various aspects of modern life, and at TRAVELS.EDU.VN, we aim to enlighten you on this topic and inspire your next Napa Valley adventure. Understanding how electromagnetic radiation propagates through space, carrying energy and momentum, is key to appreciating technologies like radio communication, medical imaging, and the very light that allows us to see the stunning vineyards of Napa Valley. Explore the intricacies of electromagnetic wave propagation with us and discover how to plan your dream wine country getaway.
1. Understanding Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves are a type of energy that travels through space. Unlike mechanical waves, such as sound waves, electromagnetic waves do not require a medium to propagate; they can travel through the vacuum of space. These waves are produced by the acceleration of charged particles. When a charged particle accelerates, it creates oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation. This interplay of electric and magnetic fields sustains the wave and allows it to travel vast distances.
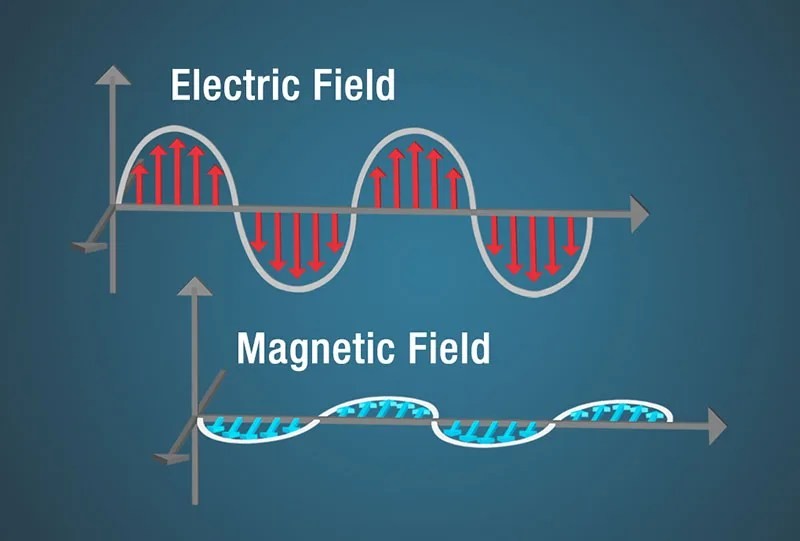 Diagram of an electromagnetic wave showing oscillating electric and magnetic fields
Diagram of an electromagnetic wave showing oscillating electric and magnetic fields
2. The Nature of Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves exhibit a dual nature, behaving as both waves and particles. This concept, known as wave-particle duality, is a fundamental aspect of quantum mechanics. As waves, they possess properties like wavelength, frequency, and amplitude. As particles, they are composed of discrete packets of energy called photons. This duality is crucial in understanding how electromagnetic waves interact with matter.
3. Maxwell’s Equations and Electromagnetic Wave Propagation
James Clerk Maxwell’s equations are a set of four fundamental laws that describe the behavior of electric and magnetic fields. These equations demonstrate that a changing magnetic field induces an electric field, and vice versa. This relationship is the foundation of electromagnetic wave propagation.
Maxwell’s equations predict that electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light (approximately 299,792,458 meters per second) in a vacuum. This speed is a fundamental constant of nature, often denoted as c.
4. Key Properties of Electromagnetic Waves
Understanding electromagnetic waves involves understanding their fundamental properties: frequency, wavelength, and energy.
4.1. Frequency and Wavelength
The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is the number of wave cycles that pass a given point per second, measured in Hertz (Hz). The wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of the wave, typically measured in meters. Frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional, related by the equation:
c = fλ
Where:
- c is the speed of light
- f is the frequency
- λ is the wavelength
This means that higher frequency waves have shorter wavelengths, and lower frequency waves have longer wavelengths.
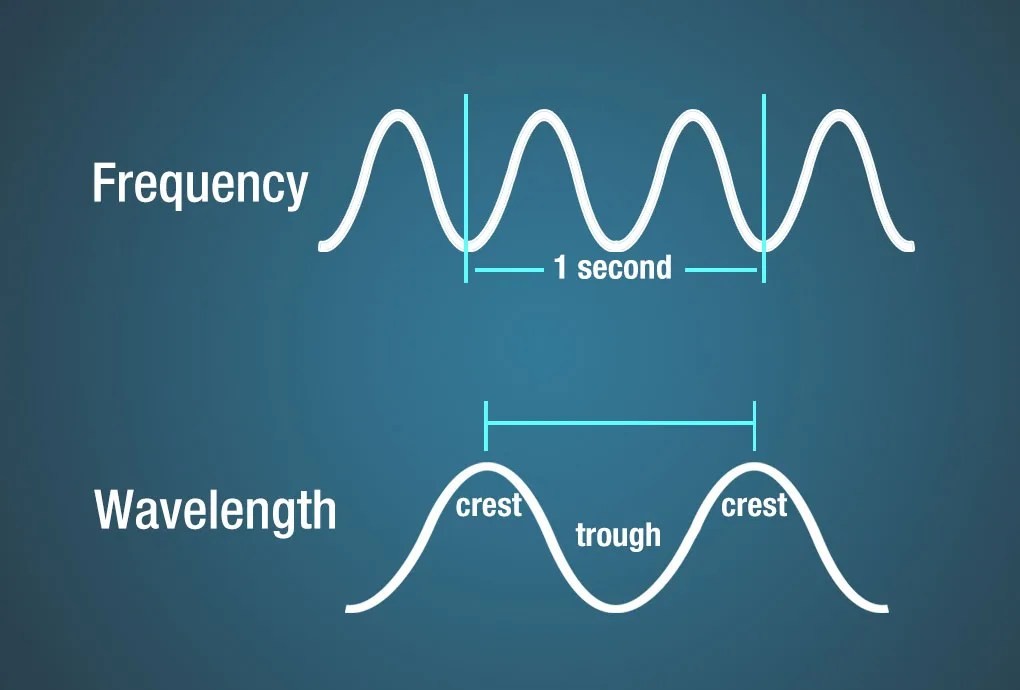 Diagram illustrating wavelength and frequency of a wave
Diagram illustrating wavelength and frequency of a wave
4.2. Energy
The energy of an electromagnetic wave is directly proportional to its frequency. This relationship is described by Planck’s equation:
E = hf
Where:
- E is the energy of the wave
- h is Planck’s constant (approximately 6.626 x 10^-34 joule-seconds)
- f is the frequency
This means that higher frequency waves, such as gamma rays and X-rays, carry more energy than lower frequency waves, such as radio waves and microwaves.
4.3. Polarization
Polarization refers to the orientation of the electric field in an electromagnetic wave. In unpolarized light, the electric field oscillates in random directions. Polarized light, on the other hand, has its electric field oscillating in a single plane. This property is used in various applications, such as sunglasses that reduce glare and LCD screens.
5. The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Comprehensive Overview
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses the entire range of electromagnetic radiation, from low-frequency radio waves to high-frequency gamma rays. Different regions of the spectrum have different properties and applications.
5.1. Radio Waves
Radio waves have the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are used for communication, broadcasting, and radar systems. Radio waves are further divided into different bands, such as:
- AM Radio: Amplitude Modulation, used for long-distance broadcasting.
- FM Radio: Frequency Modulation, offering higher quality audio for local broadcasting.
- Television: Utilizes radio waves to transmit audio and video signals.
- Mobile Communication: Cell phones use radio waves to communicate with cell towers.
5.2. Microwaves
Microwaves have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than radio waves. They are used in microwave ovens for heating food, as well as in radar systems and satellite communication.
- Microwave Ovens: Use microwaves to excite water molecules in food, generating heat.
- Radar Systems: Emit microwaves to detect the location and speed of objects.
- Satellite Communication: Microwaves are used to transmit signals between satellites and ground stations.
5.3. Infrared Radiation
Infrared (IR) radiation has wavelengths shorter than microwaves and longer than visible light. It is often associated with heat and is used in thermal imaging, remote controls, and fiber optic communication.
- Thermal Imaging: Detects infrared radiation emitted by objects to create images based on temperature.
- Remote Controls: Use infrared signals to control electronic devices.
- Fiber Optic Communication: Transmits data using infrared light through optical fibers.
5.4. Visible Light
Visible light is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that the human eye can detect. It ranges from red light (longest wavelength) to violet light (shortest wavelength). Visible light is essential for vision and is used in lighting, displays, and photography.
- Lighting: Incandescent, fluorescent, and LED lights emit visible light for illumination.
- Displays: Computer screens, televisions, and mobile devices use visible light to display images.
- Photography: Captures visible light to create images.
5.5. Ultraviolet Radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation has shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than visible light. It is emitted by the sun and can cause sunburn and skin cancer. UV radiation is also used in sterilization, tanning beds, and medical treatments.
- Sterilization: UV light kills bacteria and viruses, making it useful for sterilizing equipment and surfaces.
- Tanning Beds: Emit UV radiation to darken the skin.
- Medical Treatments: Used to treat skin conditions like psoriasis.
5.6. X-Rays
X-rays have very short wavelengths and high frequencies. They can penetrate soft tissues but are absorbed by denser materials like bone. X-rays are used in medical imaging to diagnose fractures and other conditions.
- Medical Imaging: X-rays create images of bones and internal organs.
- Security Screening: Used in airports to scan luggage for prohibited items.
5.7. Gamma Rays
Gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are produced by nuclear reactions and radioactive decay. Gamma rays are used in cancer treatment, sterilization, and industrial imaging.
- Cancer Treatment: Gamma rays are used to kill cancer cells in radiation therapy.
- Sterilization: Used to sterilize medical equipment and food.
- Industrial Imaging: Used to inspect welds and other materials for defects.
The following table summarizes the electromagnetic spectrum:
| Region | Wavelength Range | Frequency Range | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radio Waves | > 1 mm | < 300 GHz | Communication, broadcasting, radar |
| Microwaves | 1 mm – 1 m | 300 MHz – 300 GHz | Microwave ovens, radar, satellite communication |
| Infrared | 700 nm – 1 mm | 300 GHz – 430 THz | Thermal imaging, remote controls, fiber optic communication |
| Visible Light | 400 nm – 700 nm | 430 THz – 750 THz | Vision, lighting, displays, photography |
| Ultraviolet | 10 nm – 400 nm | 750 THz – 30 PHz | Sterilization, tanning beds, medical treatments |
| X-Rays | 0.01 nm – 10 nm | 30 PHz – 30 EHz | Medical imaging, security screening |
| Gamma Rays | < 0.01 nm | > 30 EHz | Cancer treatment, sterilization, industrial imaging |
6. How Electromagnetic Waves Travel
Electromagnetic waves travel through space via self-propagation. The changing electric field creates a changing magnetic field, which in turn creates a changing electric field, and so on. This continuous generation of electric and magnetic fields allows the wave to propagate through space without needing a medium. The speed at which these waves travel depends on the properties of the medium through which they are passing. In a vacuum, electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light.
7. The Role of Electromagnetic Waves in Daily Life
Electromagnetic waves play a crucial role in many aspects of daily life. From communication to medicine, these waves are essential for modern technology.
7.1. Communication
Radio waves and microwaves are used for wireless communication, including cell phones, Wi-Fi, and satellite communication. These waves allow us to transmit information over long distances quickly and efficiently.
7.2. Medicine
X-rays and gamma rays are used in medical imaging and cancer treatment. X-rays help doctors diagnose fractures and other conditions, while gamma rays are used to kill cancer cells.
7.3. Technology
Infrared radiation is used in remote controls and thermal imaging. Visible light is used in lighting, displays, and photography. Ultraviolet radiation is used in sterilization and medical treatments.
8. Visiting Napa Valley: A Sensory Experience Amplified by Electromagnetic Waves
Now, let’s bring this discussion closer to home, or rather, closer to your next vacation destination: Napa Valley. While you might not immediately connect electromagnetic waves with wine tasting, consider how these waves contribute to the experiences you’ll enjoy.
8.1. The Warmth of the Sun (Infrared Radiation)
The sun, a primary source of electromagnetic radiation, bathes the vineyards in Napa Valley with warmth. This infrared radiation is crucial for grape ripening, influencing the sugar content and overall quality of the grapes. As you stroll through a vineyard, feel the sun’s warmth on your skin – that’s infrared radiation at work.
8.2. The Colors of the Valley (Visible Light)
Visible light allows you to appreciate the vibrant colors of Napa Valley. The lush green vineyards, the golden hues of the setting sun, and the rich colors of the wines themselves are all thanks to the interaction of visible light with the environment. Capture these moments with your camera, using visible light to create lasting memories.
8.3. Communication and Navigation (Radio Waves)
From using your smartphone to navigate the winding roads of Napa Valley to staying connected with friends and family, radio waves are essential for modern travel. GPS systems rely on radio waves from satellites to pinpoint your location, ensuring you never miss a hidden gem.
8.4. The Internet and Information (Microwaves)
Accessing information about wineries, restaurants, and attractions in Napa Valley is made possible by microwaves. Wi-Fi and cellular data rely on microwaves to transmit data, allowing you to research and plan your itinerary on the go.
9. Planning Your Napa Valley Getaway with TRAVELS.EDU.VN
At TRAVELS.EDU.VN, we understand that planning a memorable trip can be overwhelming. That’s why we offer comprehensive travel services to help you create the perfect Napa Valley experience.
9.1. Tailored Itineraries
We work with you to design a personalized itinerary that matches your interests and budget. Whether you’re a wine connoisseur, a foodie, or an outdoor enthusiast, we can create a trip that you’ll never forget.
9.2. Exclusive Access
TRAVELS.EDU.VN provides access to exclusive wineries, restaurants, and accommodations in Napa Valley. Enjoy private wine tastings, gourmet meals, and luxurious stays that are not available to the general public.
9.3. Expert Guidance
Our team of travel experts is available to answer your questions and provide recommendations. We can help you choose the best time to visit, the top attractions to see, and the most delicious wines to taste.
9.4. Stress-Free Planning
Let us take care of all the details, from booking flights and hotels to arranging transportation and activities. With TRAVELS.EDU.VN, you can relax and enjoy your trip without worrying about the logistics.
9.5. Booking Services
| Service | Description | Average Price |
|---|---|---|
| Wine Tour | Guided tour of Napa Valley’s best wineries, including tastings and vineyard visits. | $200 – $500 per person |
| Gourmet Dining | Reservations at top-rated restaurants, featuring local cuisine and wine pairings. | $100 – $300 per person |
| Luxury Accommodation | Stays at premium hotels and resorts, offering exceptional amenities and service. | $300 – $1000 per night |
| Transportation | Private car service and airport transfers, ensuring a comfortable and convenient travel experience. | $100 – $300 per day |
| Hot Air Balloon Ride | Experience Napa Valley from a unique perspective with a hot air balloon ride over the vineyards. | $300 – $500 per person |
10. Call to Action: Start Planning Your Napa Valley Adventure Today
Ready to experience the magic of Napa Valley? Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN today to start planning your dream getaway. Let us create a personalized itinerary that showcases the best of this world-renowned wine region.
Don’t wait any longer—your perfect Napa Valley adventure awaits.
Contact us:
- Address: 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (707) 257-5400
- Website: TRAVELS.EDU.VN
Napa Valley Vineyard under the sun
11. Addressing Your Concerns: Why Choose TRAVELS.EDU.VN?
We understand that you might have some concerns about booking a trip, especially when entrusting your vacation to a travel agency. Here’s how TRAVELS.EDU.VN addresses those concerns:
11.1. Difficulty in Finding Suitable Packages
We offer a wide range of customizable packages to suit different tastes and budgets. Our team takes the time to understand your preferences and create a personalized itinerary that meets your specific needs.
11.2. Time-Consuming Planning Process
Planning a trip can be time-consuming and stressful. With TRAVELS.EDU.VN, you can save time and effort by letting us handle all the details. We take care of everything from booking flights and hotels to arranging transportation and activities.
11.3. Concerns About Service Quality and Reliability
We partner with reputable wineries, restaurants, and accommodations in Napa Valley to ensure the highest quality of service. Our team is dedicated to providing a seamless and memorable travel experience.
11.4. Desire for Unique and Memorable Experiences
We specialize in creating unique and memorable experiences that go beyond the typical tourist attractions. From private wine tastings to hot air balloon rides, we offer a range of exclusive activities that will make your trip unforgettable.
11.5. Need for Up-to-Date and Useful Information
We provide detailed and up-to-date information about Napa Valley, including the best time to visit, the top attractions to see, and the most delicious wines to taste. Our team is always available to answer your questions and provide recommendations.
12. The Benefits of Booking with TRAVELS.EDU.VN
Choosing TRAVELS.EDU.VN for your Napa Valley trip comes with numerous benefits:
- Save Time and Effort: Let us handle all the planning and logistics.
- Access Exclusive Experiences: Enjoy private wine tastings, gourmet meals, and luxurious accommodations.
- Personalized Service: We tailor your itinerary to match your interests and budget.
- Expert Guidance: Our team is available to answer your questions and provide recommendations.
- Stress-Free Travel: Relax and enjoy your trip knowing that everything is taken care of.
13. Testimonials: Hear from Our Satisfied Customers
- “TRAVELS.EDU.VN made our Napa Valley trip unforgettable. The personalized itinerary and exclusive access to wineries were amazing!” – John and Sarah, New York
- “I couldn’t have planned a better trip myself. The team at TRAVELS.EDU.VN took care of every detail, and we had a truly stress-free vacation.” – Emily, Los Angeles
- “The expert guidance and recommendations from TRAVELS.EDU.VN were invaluable. We discovered hidden gems in Napa Valley that we would have never found on our own.” – Michael and Jessica, Chicago
14. Understanding User Search Intent: Why Are You Here?
Let’s address why you might be searching for information on “How Do Electromagnetic Waves Travel.” Understanding the intent behind your search helps us provide the most relevant and helpful information. Here are five possible search intents:
- Educational Purposes: You’re a student or researcher seeking to understand the fundamental principles of electromagnetic wave propagation.
- Technical Application: You’re an engineer or technician working with technologies that utilize electromagnetic waves and need to understand their behavior.
- General Curiosity: You’re simply curious about how these invisible waves work and their role in the world around you.
- Troubleshooting: You’re experiencing issues with a device that relies on electromagnetic waves (e.g., Wi-Fi, cell phone) and want to understand potential causes.
- Travel Planning: You’re planning a trip (perhaps to Napa Valley!) and want to understand the technologies that make modern travel possible (e.g., GPS, communication).
15. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Electromagnetic Waves
1. What are electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves are a form of energy that travels through space as oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
2. How do electromagnetic waves travel through a vacuum?
Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium to travel. They propagate through space via self-propagation, where a changing electric field creates a changing magnetic field, and vice versa.
3. What is the speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum?
Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, which is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second.
4. What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum is the entire range of electromagnetic radiation, from low-frequency radio waves to high-frequency gamma rays.
5. What are some examples of electromagnetic waves?
Examples include radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
6. How are electromagnetic waves used in communication?
Radio waves and microwaves are used for wireless communication, including cell phones, Wi-Fi, and satellite communication.
7. How are electromagnetic waves used in medicine?
X-rays and gamma rays are used in medical imaging and cancer treatment.
8. What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength of an electromagnetic wave?
Frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional, related by the equation c = fλ, where c is the speed of light, f is the frequency, and λ is the wavelength.
9. What is the energy of an electromagnetic wave?
The energy of an electromagnetic wave is directly proportional to its frequency, described by Planck’s equation: E = hf, where E is the energy, h is Planck’s constant, and f is the frequency.
10. What is polarization of an electromagnetic wave?
Polarization refers to the orientation of the electric field in an electromagnetic wave. Polarized light has its electric field oscillating in a single plane.
16. Conclusion: Embrace the Wonders of Science and Travel with TRAVELS.EDU.VN
Understanding how electromagnetic waves travel opens up a world of possibilities, from appreciating the science behind everyday technologies to enhancing your travel experiences. As you plan your next adventure, consider the role of electromagnetic waves in making it possible.
And when it comes to planning your Napa Valley getaway, trust TRAVELS.EDU.VN to create a personalized and unforgettable experience. Contact us today and let us help you explore the beauty and wonder of this world-renowned wine region. We are located at 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States, you can reach us via Whatsapp at +1 (707) 257-5400, or visit our website at travels.edu.vn.