The space traveler’s guide to the solar system offers an imaginative and informative journey through our celestial neighborhood, highlighting key features, potential destinations, and the latest scientific findings. TRAVELS.EDU.VN helps you explore the solar system from the comfort of Earth, using the collective knowledge to deliver the best possible virtual tours. By understanding our solar system, you appreciate space tourism opportunities, astrotourism, and celestial exploration.
1. Why Is A Space Traveler’s Guide To The Solar System Important?
A space traveler’s guide to the solar system is crucial because it provides a comprehensive overview of our celestial environment, detailing each planet’s unique characteristics, potential challenges, and opportunities for future exploration. According to NASA, the solar system comprises not only the familiar planets but also countless asteroids, comets, and moons, each holding valuable clues about the formation and evolution of our cosmic neighborhood.
Understanding the solar system helps inform and inspire future space missions. According to a 2023 report by the Space Foundation, investments in space exploration have consistently yielded significant returns, driving innovation in various fields, including materials science, telecommunications, and robotics.
2. What Are The Main Components Of A Space Traveler’s Guide To The Solar System?
A space traveler’s guide to the solar system typically includes detailed information about each planet, their moons, significant asteroids, and comets. It covers aspects such as atmospheric conditions, surface features, potential resources, and the challenges and opportunities for future human or robotic exploration.
2.1 Planets
Each planet in our solar system offers unique attractions and challenges:
| Planet | Key Features | Potential Attractions | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury | Closest to the sun, heavily cratered, extreme temperature variations | Observing solar transits, exploring ancient volcanic landscapes | Extreme temperatures, lack of atmosphere |
| Venus | Dense atmosphere, scorching temperatures, volcanic landscapes | Studying the greenhouse effect, observing unique cloud formations | Toxic atmosphere, extreme heat, high pressure |
| Earth | Only known planet to support life, diverse ecosystems, abundant water | Diverse landscapes, oceans, and rich biodiversity | Environmental concerns, limited space for expansion |
| Mars | Rusty surface, evidence of past water, potential for past life | Exploring canyons and polar ice caps, searching for evidence of past life, and paving the way for future Mars colonization | Thin atmosphere, radiation exposure, extreme temperature variations |
| Jupiter | Largest planet, giant storms, numerous moons | Observing the Great Red Spot, exploring the Galilean moons (Io, Europa, Ganymede, Callisto) | Intense radiation belts, extreme pressure |
| Saturn | Prominent rings, numerous moons, including Titan with its dense atmosphere | Viewing the stunning rings, exploring Titan’s hydrocarbon lakes and potential for unique life forms | Extreme cold, toxic atmosphere on Titan |
| Uranus | Tilted axis, faint rings, icy composition | Observing the unique axial tilt, exploring the icy moons | Extreme cold, faint rings |
| Neptune | Deep blue color, strong winds, distant and icy | Studying the dynamic atmosphere, observing the Great Dark Spot (now gone), exploring the moon Triton with its potential for cryovolcanism | Extreme cold, long travel times |
2.2 Moons
Moons are fascinating destinations, each with unique geological and environmental features.
- Europa (Jupiter): Covered in ice with a potential subsurface ocean, making it a prime target in the search for extraterrestrial life.
- Titan (Saturn): Features a dense atmosphere, hydrocarbon lakes, and rivers, offering insights into potential prebiotic chemistry.
2.3 Asteroids And Comets
These celestial bodies provide insights into the early solar system:
- Asteroid Belt: Located between Mars and Jupiter, contains a vast number of asteroids, including Ceres, the largest asteroid, now classified as a dwarf planet.
- Kuiper Belt: Beyond Neptune, a region containing icy bodies, including Pluto, Eris, and Makemake.
- Comets: Icy bodies that release gas and dust as they approach the sun, creating spectacular displays.
3. How Has Space Exploration Shaped Our Understanding Of The Solar System?
Space missions have revolutionized our understanding of the solar system. For example, the Voyager missions provided unprecedented views of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, while the Cassini-Huygens mission offered detailed insights into Saturn and its moon Titan.
- Voyager Missions: Launched in 1977, these missions provided the first detailed images of the outer planets.
- Cassini-Huygens Mission: Explored Saturn and its moons from 2004 to 2017, offering detailed data about Titan’s atmosphere and liquid hydrocarbon lakes.
- Mars Rovers (Spirit, Opportunity, Curiosity, Perseverance): These rovers have uncovered evidence of past water on Mars, paving the way for future human missions. According to a 2021 study in Nature Geoscience, data from the Curiosity rover suggests that Mars once had a habitable environment.
A view of the Martian landscape with rover tracks. Alt text: Mars Curiosity Rover exploring Mount Sharp’s northeast rim.
4. What Are The Challenges Of Space Travel Within The Solar System?
Space travel presents numerous challenges, including:
- Distance: The vast distances between planets require long travel times, necessitating advanced propulsion systems and life support.
- Radiation: Exposure to cosmic radiation poses significant health risks to astronauts.
- Extreme Temperatures: Planets like Mercury and Uranus experience extreme temperature variations, requiring robust spacecraft and protective gear.
- Resource Availability: Providing sufficient resources for long-duration missions requires in-situ resource utilization (ISRU) techniques.
5. What Technologies Are Being Developed To Overcome These Challenges?
To overcome the challenges of space travel, several innovative technologies are being developed:
- Advanced Propulsion Systems: Ion drives and nuclear propulsion systems aim to reduce travel times.
- Radiation Shielding: Advanced materials and magnetic fields are being researched to protect astronauts from radiation.
- ISRU Technologies: Developing systems to extract and utilize resources like water and minerals from extraterrestrial bodies.
- Closed-Loop Life Support Systems: Recycling air, water, and waste to minimize the need for resupply missions.
6. How Can Space Tourism Become A Reality In The Solar System?
While still in its infancy, space tourism within the solar system could become a reality through:
- Suborbital Flights: Companies like Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin offer suborbital flights, providing brief periods of weightlessness and views of Earth from space.
- Orbital Hotels: Concepts for orbital hotels are being developed to provide tourists with extended stays in space.
- Lunar Tourism: As lunar bases are established, tourism to the moon could become feasible, offering unique experiences such as lunar exploration and stargazing.
7. What Are The Ethical Considerations For Space Exploration And Tourism?
Ethical considerations for space exploration and tourism include:
- Planetary Protection: Preventing contamination of extraterrestrial environments with terrestrial microbes.
- Resource Utilization: Ensuring sustainable use of space resources to avoid exploitation.
- Space Debris: Managing and mitigating space debris to prevent collisions and maintain safe access to space.
- Equity and Access: Ensuring that the benefits of space exploration and tourism are accessible to all, not just a privileged few.
8. How Can I Learn More About Space Exploration And The Solar System?
You can expand your knowledge through various resources:
- NASA and ESA Websites: Provide up-to-date information on missions, discoveries, and educational resources.
- Astronomy Magazines: Publications like Sky & Telescope and Astronomy offer in-depth articles and stunning imagery.
- Documentaries: Documentaries such as Cosmos: A Spacetime Odyssey and The Planets offer engaging visual and narrative explorations of the cosmos.
- Books: Titles like “The Grand Tour: A Traveler’s Guide to the Solar System” by Ron Miller and William K. Hartmann provide accessible and visually appealing introductions to planetary science.
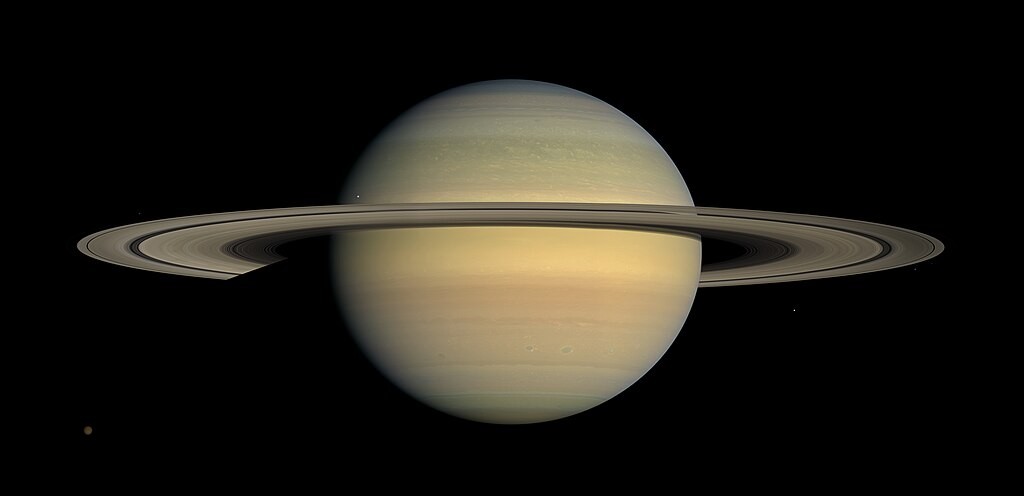 Saturn with its rings
Saturn with its rings
Saturn with its stunning rings, captured during equinox. Alt text: Rings of Saturn at equinox.
9. What Are The Potential Destinations For Future Space Travelers?
Future space travelers could explore a variety of destinations:
- Mars: The Red Planet offers opportunities for geological exploration, searching for signs of past life, and potentially establishing a permanent human presence.
- Europa: Jupiter’s moon Europa, with its potential subsurface ocean, is a prime target for astrobiological research.
- Titan: Saturn’s moon Titan, with its dense atmosphere and hydrocarbon lakes, provides a unique environment for studying prebiotic chemistry.
- The Moon: Establishing lunar bases could facilitate scientific research, resource utilization, and serve as a stepping stone for deeper space exploration.
10. How Is TRAVELS.EDU.VN Contributing To Space Education And Inspiration?
TRAVELS.EDU.VN plays a vital role in space education and inspiration by:
- Providing Educational Content: Offering articles, guides, and resources that explain complex topics in an accessible manner.
- Virtual Tours: Creating virtual tours of the solar system, allowing users to explore planets and moons from the comfort of their homes.
- Highlighting Space Tourism Opportunities: Showcasing potential space tourism experiences, from suborbital flights to lunar expeditions.
11. What New Discoveries Are Expected In The Next Decade That Will Change Our Guide To The Solar System?
The next decade promises exciting discoveries that could reshape our understanding of the solar system:
- Europa Clipper Mission: Scheduled to launch in 2024, this mission will study Europa’s potential habitability by investigating its subsurface ocean.
- James Webb Space Telescope (JWST): Will provide unprecedented views of exoplanets and distant galaxies, enhancing our understanding of planetary systems beyond our own.
- Ongoing Mars Exploration: Continued exploration by rovers and orbiters will provide more insights into Mars’ past and present habitability.
12. What Role Do Private Companies Play In Advancing Space Exploration?
Private companies play a crucial role in advancing space exploration by:
- Developing Launch Capabilities: Companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin are developing reusable rockets, reducing the cost of access to space. According to a 2022 report by Morgan Stanley, the global space economy could reach $1 trillion by 2040, driven by innovations in launch technology and space-based services.
- Providing Space Tourism Services: Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin are pioneering space tourism, making space accessible to private citizens.
- Developing Space Habitats: Companies like Bigelow Aerospace are developing inflatable space habitats for future orbital and lunar settlements.
13. What Should I Pack For A Trip To Mars?
Packing for a trip to Mars requires careful consideration:
- Space Suit: A pressurized suit to protect against the thin atmosphere and extreme temperatures.
- Radiation Shielding: Garments or materials to minimize exposure to cosmic radiation.
- Life Support Systems: Equipment to provide breathable air, water, and food.
- Tools and Equipment: For conducting scientific experiments, maintaining habitats, and exploring the Martian surface.
14. How Can I Prepare For A Career In Space Exploration?
Preparing for a career in space exploration involves:
- Education: Pursuing degrees in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields.
- Internships: Gaining experience through internships at NASA, ESA, or private space companies.
- Research: Participating in research projects related to space exploration, such as astrobiology, planetary science, or aerospace engineering.
15. What Role Does International Collaboration Play In Space Exploration?
International collaboration is essential for space exploration due to:
- Sharing Resources: Pooling financial and technical resources to undertake ambitious missions.
- Sharing Knowledge: Combining expertise from different countries to enhance scientific understanding.
- Promoting Peace: Fostering cooperation and goodwill among nations through shared goals.
The International Space Station (ISS) is a prime example of successful international collaboration, involving contributions from the United States, Russia, Canada, Japan, and the European Space Agency.
16. What Are The Key Differences Between Exploring The Inner And Outer Solar System?
Exploring the inner and outer solar system presents different challenges and opportunities:
- Inner Solar System: Characterized by rocky planets, higher temperatures, and proximity to the sun. Challenges include dealing with extreme heat and radiation.
- Outer Solar System: Features gas giants, icy moons, and greater distances from the sun. Challenges include extreme cold, long travel times, and weaker sunlight.
17. How Do Scientists Study Objects In The Solar System Without Traveling There?
Scientists use various techniques to study objects in the solar system remotely:
- Telescopes: Ground-based and space-based telescopes gather data on planetary atmospheres, surfaces, and compositions.
- Spectroscopy: Analyzing the light emitted or reflected by objects to determine their chemical composition and physical properties.
- Radar: Bouncing radio waves off objects to map their surfaces and measure their distances.
18. What Is Astrobiology And How Does It Relate To Exploring The Solar System?
Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe. It relates to exploring the solar system by:
- Searching For Habitable Environments: Identifying planets and moons with conditions that could support life.
- Looking For Biosignatures: Detecting chemical or physical indicators of past or present life.
- Understanding The Limits Of Life: Studying extremophiles on Earth to understand how life can survive in extreme environments.
19. How Can Students Get Involved In Space Exploration?
Students can get involved in space exploration through:
- Science Clubs: Participating in science clubs and organizations that focus on astronomy, robotics, and space exploration.
- Competitions: Joining competitions such as the FIRST Robotics Competition and the Science Olympiad.
- Educational Programs: Enrolling in educational programs and summer camps offered by NASA, ESA, and universities.
Astronaut during a spacewalk, with Earth visible in the background. Alt text: Astronaut performing an EVA in space.
20. How Will Future Discoveries About Exoplanets Change Our Understanding Of Our Own Solar System?
Future discoveries about exoplanets will revolutionize our understanding of our solar system by:
- Providing Context: Helping us understand how common or unique our solar system is in the context of other planetary systems.
- Testing Theories: Providing new data to test theories about planet formation and evolution.
- Identifying Potential Habitable Worlds: Increasing the chances of finding life beyond Earth.
21. How Is The Search For Extraterrestrial Life Influencing Space Exploration?
The search for extraterrestrial life is a major driver of space exploration, influencing:
- Mission Design: Designing missions to explore potentially habitable environments.
- Technology Development: Developing new technologies to detect biosignatures and explore extreme environments.
- International Collaboration: Fostering collaboration among nations to pursue this ambitious goal.
22. What Are The Implications Of Finding Life Elsewhere In The Solar System?
The discovery of life elsewhere in the solar system would have profound implications:
- Scientific: Revolutionizing our understanding of biology, evolution, and the origin of life.
- Philosophical: Challenging our view of humanity’s place in the universe.
- Technological: Driving the development of new technologies for space exploration and resource utilization.
23. How Do Robotic Missions Contribute To Preparing For Human Missions To Other Planets?
Robotic missions play a critical role in preparing for human missions by:
- Reconnaissance: Providing detailed information about planetary surfaces, atmospheres, and potential hazards.
- Technology Testing: Testing new technologies and systems in the harsh environments of other planets.
- Resource Assessment: Identifying potential resources that could be used by future human missions.
24. What Are Some Of The Most Surprising Facts About The Solar System That Most People Don’t Know?
Surprising facts about the solar system include:
- Venus rotates backwards: Unlike most planets, Venus rotates in the opposite direction.
- Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is shrinking: This massive storm has been raging for centuries but is gradually decreasing in size.
- Enceladus has saltwater geysers: Saturn’s moon Enceladus has geysers that spew saltwater into space, indicating a subsurface ocean.
- There are more moons than planets: The total number of known moons in the solar system exceeds the number of planets.
25. What Should Future Space Travelers Be Aware Of When Visiting Different Planets?
Future space travelers should be aware of:
- Radiation exposure: Taking precautions to minimize exposure to cosmic radiation.
- Extreme temperatures: Wearing appropriate protective gear to withstand extreme heat or cold.
- Atmospheric conditions: Understanding the composition and pressure of planetary atmospheres.
- Potential hazards: Being aware of potential hazards such as meteoroid impacts, volcanic activity, and toxic substances.
Embark on an extraordinary journey with TRAVELS.EDU.VN, your ultimate space traveler’s guide to the solar system. Explore the cosmos from the comfort of your home and prepare for future adventures among the stars.
Are you ready to start your cosmic journey? Contact us at 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States or via Whatsapp at +1 (707) 257-5400, or visit our website at TRAVELS.EDU.VN for exclusive space tourism packages.
FAQ: Your Space Travel Questions Answered
1. What is the best time to travel to Mars?
The best time to travel to Mars is during a launch window that occurs approximately every 26 months when Earth and Mars are aligned to minimize travel time and fuel consumption.
2. How long does it take to travel to Jupiter?
A trip to Jupiter typically takes around 6 to 8 years, depending on the spacecraft’s trajectory and propulsion system.
3. Can humans breathe on Titan?
No, humans cannot breathe on Titan. Titan has a dense atmosphere, but it is primarily composed of nitrogen and methane, lacking oxygen.
4. What is the cost of a space tour with TRAVELS.EDU.VN?
The cost of a space tour with travels.edu.vn varies depending on the destination and duration. Contact us for customized packages and pricing.
5. Are there any hotels on the Moon?
Currently, there are no hotels on the Moon. However, several companies are planning to develop lunar habitats for future tourism.
6. What kind of training is required for space travel?
Space travel requires extensive training, including physical conditioning, survival training, and familiarization with spacecraft systems.
7. Is it safe to travel through the asteroid belt?
Traveling through the asteroid belt is relatively safe, as the asteroids are widely dispersed. Spacecraft can navigate through the belt with minimal risk of collision.
8. What are the biggest challenges of living on Mars?
The biggest challenges of living on Mars include radiation exposure, extreme temperatures, thin atmosphere, and the lack of readily available water and resources.
9. How do astronauts get water in space?
Astronauts get water in space through recycling systems, which purify and reuse water from various sources, including urine and condensation.
10. What should I wear on a trip to Venus?
A trip to Venus would require a specialized, highly heat-resistant and pressurized suit to protect against the extreme temperatures and toxic atmosphere.