Electricity can travel in a vacuum as electromagnetic waves, a phenomenon vital to numerous technologies. TRAVELS.EDU.VN delves into the science behind this, offering insights into electromagnetic radiation, wave properties, and energy transfer. Explore Napa Valley with ease by booking your tour with us today.
1. What Are Electromagnetic Waves and How Do They Propagate?
Electromagnetic waves, unlike mechanical waves, can travel through a vacuum. This is because they don’t require a medium, such as air or water, to propagate. Instead, they are formed by oscillating electric and magnetic fields that generate each other. This self-propagating nature allows them to travel through empty space. According to James Clerk Maxwell’s theory, a changing magnetic field induces a changing electric field, and vice versa, creating electromagnetic waves.
1.1 The Role of Electric and Magnetic Fields
Electromagnetic waves consist of two perpendicular oscillating fields: an electric field and a magnetic field. These fields are interconnected; a change in one induces a change in the other, allowing the wave to propagate through space. This mechanism distinguishes electromagnetic waves from mechanical waves, which require a medium.
1.2 Maxwell’s Equations: The Foundation of Electromagnetic Theory
James Clerk Maxwell’s equations are a set of four fundamental equations that describe the behavior of electric and magnetic fields and their interactions. These equations laid the groundwork for understanding how electromagnetic waves propagate through a vacuum. Maxwell’s work demonstrated that light is a form of electromagnetic radiation.
1.3 Experimental Verification by Heinrich Hertz
Heinrich Hertz validated Maxwell’s theories by producing and detecting radio waves, proving that electromagnetic waves could travel through space. His experiments demonstrated that radio waves have the same velocity as light, confirming that light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. The unit of frequency, Hertz (Hz), is named in his honor.
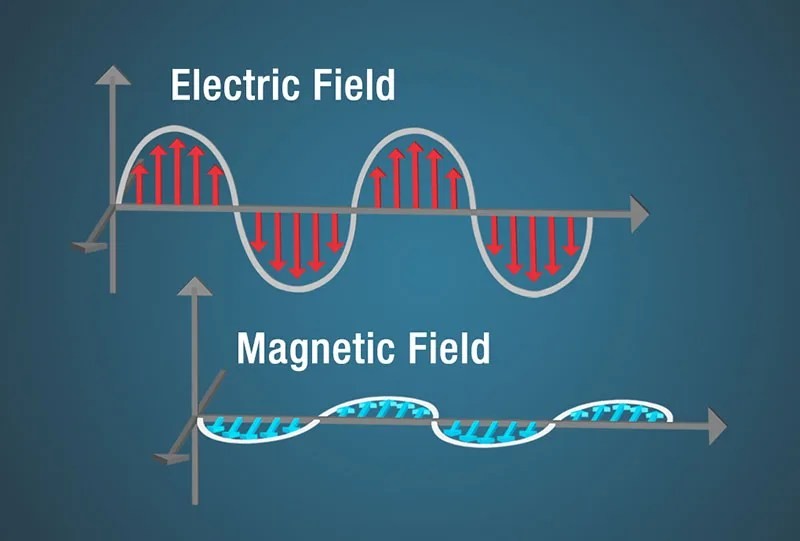 Diagram of electric and magnetic fields forming an electromagnetic wave, the electric field is shown as a sine wave with red arrows beneath the curves and a magnetic field is shown as a sine wave with blue arrows perpendicular to the electric field
Diagram of electric and magnetic fields forming an electromagnetic wave, the electric field is shown as a sine wave with red arrows beneath the curves and a magnetic field is shown as a sine wave with blue arrows perpendicular to the electric field
2. How Do Electromagnetic Waves Differ from Mechanical Waves?
Electromagnetic waves and mechanical waves differ significantly in their propagation mechanisms. Mechanical waves, like sound waves, require a medium to travel, while electromagnetic waves can propagate through a vacuum.
2.1 The Necessity of a Medium for Mechanical Waves
Mechanical waves, such as sound waves and water waves, need a medium (solid, liquid, gas, or plasma) to propagate. These waves transfer energy by causing particles in the medium to vibrate. Without a medium, mechanical waves cannot travel.
2.2 Electromagnetic Waves: Independent of a Medium
Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium. They are generated by oscillating electric and magnetic fields and can travel through the vacuum of space. This is why light from the sun can reach Earth.
2.3 Examples of Mechanical Waves
Common examples of mechanical waves include sound waves, which travel through air, and water waves, which travel through water. These waves rely on the interaction of particles in the medium to transfer energy.
 Ripples in a pool of water, illustrating mechanical waves
Ripples in a pool of water, illustrating mechanical waves
3. What is Electromagnetic Radiation?
Electromagnetic radiation is energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. It encompasses a broad spectrum of frequencies, wavelengths, and energies, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
3.1 The Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum categorizes electromagnetic radiation based on frequency and wavelength. From low-frequency radio waves to high-frequency gamma rays, each type of radiation has unique properties and applications.
3.2 Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation
Electromagnetic radiation exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties. As waves, they have frequency and wavelength. As particles (photons), they carry energy and momentum.
3.3 Uses of Electromagnetic Radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is used in numerous applications, including communication (radio waves), heating (microwaves), medical imaging (X-rays), and astronomy (visible light, infrared, ultraviolet).
4. Can Light Travel Through Space?
Yes, light can travel through space. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation and does not require a medium to propagate. It travels through the vacuum of space from the sun to Earth, enabling vision and supporting life.
4.1 Light as an Electromagnetic Wave
Light consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. These fields allow light to travel through the vacuum of space without the need for a medium.
4.2 The Speed of Light in a Vacuum
The speed of light in a vacuum is a fundamental constant of nature, approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (671 million miles per hour). This speed is the upper limit for the speed of any object in the universe, according to the theory of relativity.
4.3 Implications for Astronomy and Space Exploration
The ability of light to travel through space is essential for astronomy, allowing us to observe distant stars and galaxies. It also enables space exploration, as spacecraft rely on electromagnetic radiation for communication and navigation.
5. Understanding Wavelength and Frequency
Wavelength and frequency are fundamental properties of electromagnetic waves. Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of a wave, while frequency is the number of wave cycles that pass a given point per unit of time.
5.1 Definition of Wavelength
Wavelength is measured in units of length, such as meters or nanometers. Shorter wavelengths correspond to higher-energy radiation, while longer wavelengths correspond to lower-energy radiation.
5.2 Definition of Frequency
Frequency is measured in Hertz (Hz), where 1 Hz is equal to one cycle per second. Higher frequencies correspond to higher-energy radiation, while lower frequencies correspond to lower-energy radiation.
5.3 The Relationship Between Wavelength and Frequency
Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional. The relationship is given by the equation:
c = λν
Where:
c is the speed of light (approximately 299,792,458 m/s)
λ is the wavelength
ν is the frequency
This equation shows that as wavelength increases, frequency decreases, and vice versa, while the speed of light remains constant.
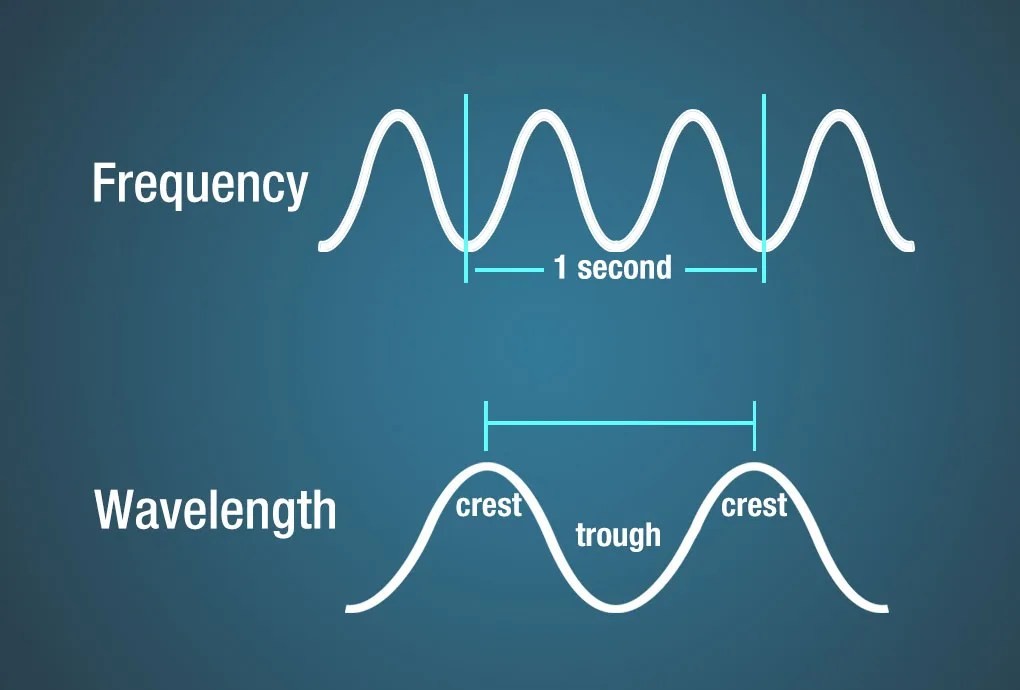 Diagram showing frequency as the measurement of the number of wave crests that pass a given point in a second. Wavelength is measured as the distance between two crests.
Diagram showing frequency as the measurement of the number of wave crests that pass a given point in a second. Wavelength is measured as the distance between two crests.
6. Exploring the Concept of Polarization
Polarization is a property of electromagnetic waves that describes the orientation of the electric field. Light can be polarized in various directions, and understanding polarization is crucial for applications like reducing glare and enhancing imaging.
6.1 What is Polarization?
Polarization refers to the alignment of the electric field in an electromagnetic wave. Light is considered polarized if its electric field oscillates in a single plane.
6.2 Types of Polarization
There are several types of polarization, including:
- Linear Polarization: The electric field oscillates in a single plane.
- Circular Polarization: The electric field rotates in a circle as the wave propagates.
- Elliptical Polarization: The electric field traces an ellipse as the wave propagates.
6.3 Applications of Polarization
Polarization is used in various applications, such as:
- Sunglasses: Polarizing sunglasses reduce glare by blocking horizontally polarized light reflected from surfaces.
- LCD Screens: Liquid crystal displays (LCDs) use polarized light to control the brightness of pixels.
- Photography: Polarizing filters can enhance contrast and reduce reflections in photographs.
7. The Role of Photons in Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic radiation can also be described in terms of particles called photons. Photons are discrete packets of energy that carry momentum and travel at the speed of light.
7.1 What is a Photon?
A photon is a fundamental particle of electromagnetic radiation. It has no mass and carries a specific amount of energy, which is proportional to its frequency.
7.2 Energy of a Photon
The energy of a photon is given by the equation:
E = hν
Where:
E is the energy of the photon
h is Planck’s constant (approximately 6.626 x 10^-34 J·s)
ν is the frequency of the radiation
This equation shows that higher-frequency radiation consists of photons with higher energy.
7.3 Wave-Particle Duality
Light exhibits wave-particle duality, meaning it has both wave-like and particle-like properties. This duality is a fundamental concept in quantum mechanics.
8. Static Electricity and Electromagnetic Waves
Static electricity and electromagnetic waves are related through the movement of electric charges. While static electricity involves stationary charges, the movement or oscillation of these charges can generate electromagnetic waves.
8.1 Static Electricity Explained
Static electricity results from an imbalance of electric charges on the surface of an object. This imbalance can occur through friction, such as rubbing a balloon on hair.
8.2 How Static Electricity Relates to Electromagnetic Waves
When static charges move or discharge, they create changing electric fields. These changing fields can induce magnetic fields, leading to the generation of electromagnetic waves. For example, a spark of static electricity involves a rapid discharge of charges, creating a brief electromagnetic pulse.
8.3 Examples of Static Electricity
Common examples of static electricity include:
- Lightning: A large-scale discharge of static electricity between clouds or between a cloud and the ground.
- Static Cling: The attraction between clothing items due to static charges.
- Hair Standing on End: When a balloon is rubbed against hair, the hair becomes charged and repels itself.
9. The Energy of Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves carry energy, which can be described in terms of frequency, wavelength, or electron volts (eV). The energy of an electromagnetic wave is directly related to its frequency and inversely related to its wavelength.
9.1 Energy Units: Electron Volts (eV)
Energy is often measured in electron volts (eV) in the context of electromagnetic radiation. One electron volt is the amount of kinetic energy gained by an electron when it accelerates through an electric potential difference of one volt.
9.2 Relationship Between Energy, Wavelength, and Frequency
The energy of an electromagnetic wave is related to its wavelength and frequency by the following equations:
E = hν
E = hc/λ
Where:
E is the energy
h is Planck’s constant (approximately 6.626 x 10^-34 J·s)
ν is the frequency
c is the speed of light (approximately 299,792,458 m/s)
λ is the wavelength
These equations show that higher-frequency, shorter-wavelength radiation has higher energy.
9.3 Examples of Energy in the Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Radio Waves: Low energy, long wavelength, low frequency.
- Microwaves: Higher energy than radio waves, shorter wavelength, higher frequency.
- Infrared Radiation: Higher energy than microwaves, shorter wavelength, higher frequency.
- Visible Light: Higher energy than infrared, shorter wavelength, higher frequency.
- Ultraviolet Radiation: Higher energy than visible light, shorter wavelength, higher frequency.
- X-rays: High energy, short wavelength, high frequency.
- Gamma Rays: Highest energy, shortest wavelength, highest frequency.
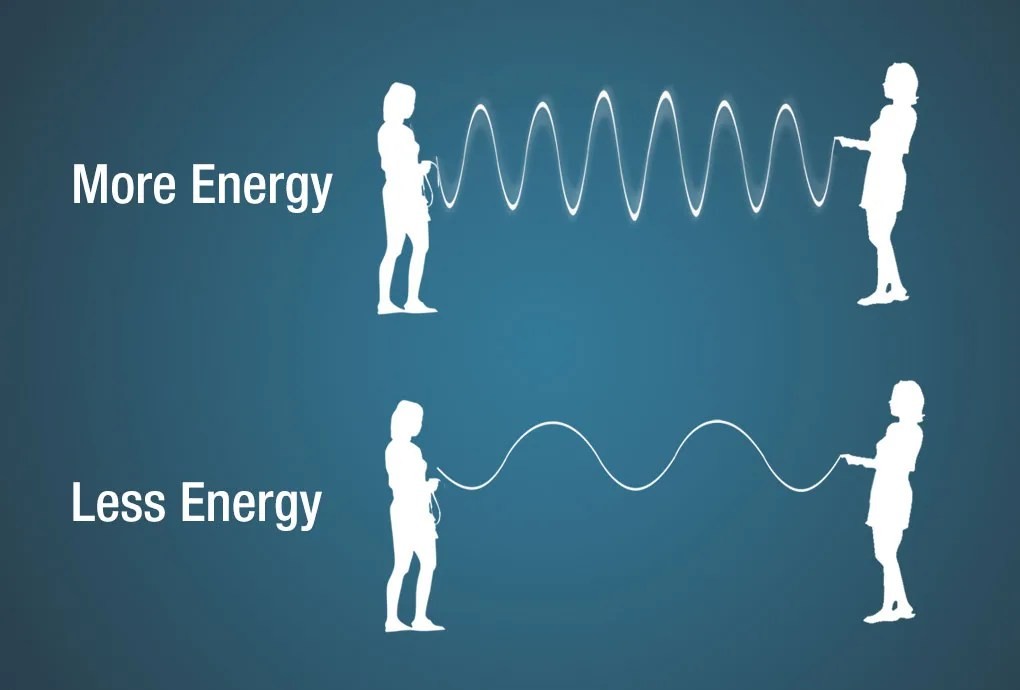 An illustration showing a jump rope with each end being held by a person. As the people move the jump rope up and down very fast – adding MORE energy – the more wave crests appear, thus shorter wavelengths. When the people move the jump rope up and down slower, there are fewer wave crests within the same distance, thus longer wavelengths, illustrating the energy of electromagnetic waves
An illustration showing a jump rope with each end being held by a person. As the people move the jump rope up and down very fast – adding MORE energy – the more wave crests appear, thus shorter wavelengths. When the people move the jump rope up and down slower, there are fewer wave crests within the same distance, thus longer wavelengths, illustrating the energy of electromagnetic waves
10. Traveling Through Napa Valley: A Real-World Application
Understanding electromagnetic waves extends beyond scientific theory; it directly impacts our daily lives, including travel and communication. Consider planning a trip to Napa Valley, where technology powered by electromagnetic waves enhances your experience.
10.1 Utilizing Electromagnetic Waves for Navigation
GPS (Global Positioning System) relies on electromagnetic waves to provide precise location data. Your smartphone or car navigation system receives signals from GPS satellites, allowing you to navigate unfamiliar routes with ease.
10.2 Communication and Connectivity in Napa Valley
Cellular networks use radio waves, a form of electromagnetic radiation, to enable voice and data communication. Whether you’re sharing photos of your vineyard tour or video-calling loved ones, electromagnetic waves keep you connected.
10.3 Enhancing Travel Experiences with Technology
From online booking platforms to digital tour guides, technology powered by electromagnetic waves enhances travel experiences. TRAVELS.EDU.VN leverages these technologies to provide seamless and informative travel services in Napa Valley.
11. How TRAVELS.EDU.VN Enhances Your Napa Valley Experience
TRAVELS.EDU.VN offers exceptional Napa Valley tour packages, leveraging technology and expertise to ensure memorable experiences. Our services are designed to cater to various preferences, ensuring a personalized and seamless travel experience.
11.1 Seamless Booking and Planning
Our online platform provides seamless booking and planning services, allowing you to customize your Napa Valley itinerary with ease. From selecting wineries to arranging transportation, our user-friendly interface simplifies the planning process.
11.2 Curated Tour Packages
TRAVELS.EDU.VN offers curated tour packages that showcase the best of Napa Valley. Whether you’re interested in wine tasting, gourmet dining, or scenic landscapes, our packages are designed to provide unique and unforgettable experiences.
11.3 Expert Guidance and Support
Our team of travel experts provides guidance and support throughout your journey. From recommending hidden gems to addressing logistical concerns, we are committed to ensuring your Napa Valley experience is exceptional.
12. Napa Valley Travel Tips and Recommendations
Planning a trip to Napa Valley requires careful consideration of various factors, including the best time to visit, must-see attractions, and transportation options. Here are some tips and recommendations to enhance your Napa Valley experience.
12.1 Best Time to Visit
The best time to visit Napa Valley is typically during the spring (March-May) and fall (September-November). These seasons offer pleasant weather, vibrant landscapes, and fewer crowds compared to the summer months.
12.2 Must-See Attractions
Napa Valley boasts numerous attractions, including:
- Wineries: Explore renowned wineries such as Domaine Carneros, Castello di Amorosa, and Robert Mondavi Winery.
- Culinary Experiences: Indulge in gourmet dining experiences at Michelin-starred restaurants like The French Laundry and Meadowood.
- Scenic Landscapes: Enjoy breathtaking views of vineyards and rolling hills by taking a hot air balloon ride or driving along the Silverado Trail.
12.3 Transportation Options
Various transportation options are available in Napa Valley, including:
- Car Rental: Renting a car provides flexibility and convenience for exploring the region at your own pace.
- Private Car Service: Hire a private car service for a luxurious and hassle-free travel experience.
- Tour Buses: Join a guided tour bus to visit multiple wineries and attractions without worrying about driving.
13. Ensuring a Sustainable Napa Valley Experience
Sustainable tourism is crucial for preserving the natural beauty and cultural heritage of Napa Valley. Here are some tips for ensuring a responsible and eco-friendly travel experience.
13.1 Supporting Local Businesses
Support local businesses by purchasing locally made products, dining at family-owned restaurants, and staying at boutique hotels. This helps to boost the local economy and preserve the unique character of Napa Valley.
13.2 Reducing Environmental Impact
Minimize your environmental impact by using reusable water bottles, avoiding single-use plastics, and choosing eco-friendly transportation options. Respect the natural environment by staying on marked trails and avoiding littering.
13.3 Respecting Local Culture
Respect local culture by learning about the history and traditions of Napa Valley, engaging with local communities, and adhering to local customs. This fosters a sense of mutual respect and understanding between visitors and residents.
14. Napa Valley Accommodation Options
Napa Valley offers a wide range of accommodation options, from luxurious resorts to cozy bed and breakfasts. Here are some recommendations for finding the perfect place to stay during your visit.
14.1 Luxury Resorts
Indulge in a luxurious stay at renowned resorts such as:
- Meadowood Napa Valley: A world-class resort with elegant accommodations, fine dining, and a championship golf course.
- Auberge du Soleil: A romantic hillside retreat with stunning views, luxurious spa treatments, and gourmet cuisine.
- The Carneros Resort and Spa: A charming resort with cottage-style accommodations, multiple swimming pools, and a farm-to-table restaurant.
14.2 Boutique Hotels
Experience personalized service and unique charm at boutique hotels such as:
- Hotel Yountville: A stylish hotel in the heart of Yountville with luxurious amenities and a central location.
- Bardessono: An eco-friendly hotel in Yountville with sustainable practices, modern design, and a tranquil spa.
- The Napa Valley Lodge: A cozy hotel in Yountville with comfortable accommodations, a heated pool, and a complimentary breakfast.
14.3 Bed and Breakfasts
Enjoy a cozy and intimate stay at bed and breakfasts such as:
- Churchill Manor: A historic mansion in Napa with elegant rooms, a gourmet breakfast, and a beautiful garden.
- The Inn on First: A charming bed and breakfast in Napa with comfortable accommodations, a relaxing atmosphere, and a delicious breakfast.
- Cedar Gables Inn: A Victorian-style bed and breakfast in Napa with luxurious rooms, antique furnishings, and a hearty breakfast.
15. Culinary Delights: Napa Valley’s Food Scene
Napa Valley is renowned for its exceptional culinary scene, offering a diverse range of dining experiences from Michelin-starred restaurants to farm-to-table eateries.
15.1 Michelin-Starred Restaurants
Savor exquisite cuisine at Michelin-starred restaurants such as:
- The French Laundry: A world-renowned restaurant in Yountville offering an unforgettable tasting menu experience.
- Restaurant at Meadowood: A fine-dining restaurant in St. Helena with innovative dishes and impeccable service.
- Kenzo Napa: A Japanese restaurant in Napa serving authentic and refined Kaiseki cuisine.
15.2 Farm-to-Table Eateries
Enjoy fresh, seasonal dishes at farm-to-table eateries such as:
- Farmstead at Long Meadow Ranch: A restaurant in St. Helena showcasing the bounty of Long Meadow Ranch’s organic farm.
- Gott’s Roadside: A casual eatery in St. Helena serving gourmet burgers, fries, and milkshakes using locally sourced ingredients.
- The Girl & The Fig: A French-country restaurant in Sonoma offering rustic dishes made with local produce.
15.3 Wine and Food Pairings
Enhance your culinary experience by indulging in wine and food pairings at:
- Robert Mondavi Winery: A renowned winery in Oakville offering guided tours and wine and food pairing experiences.
- Domaine Carneros: A sparkling wine house in Napa with stunning views and a selection of elegant sparkling wines paired with delectable bites.
- Castello di Amorosa: A medieval-style castle winery in Calistoga offering tours, tastings, and food pairings.
16. Napa Valley Wine Tasting Etiquette
Wine tasting in Napa Valley is a delightful experience, but it’s essential to follow proper etiquette to ensure a respectful and enjoyable visit.
16.1 Making Reservations
Many wineries require reservations for tastings, especially during peak season. Book your tasting appointments in advance to secure your spot and avoid disappointment.
16.2 Arriving on Time
Arrive on time for your tasting appointments to show respect for the winery staff and other guests. If you’re running late, notify the winery as soon as possible.
16.3 Tasting Techniques
Follow proper tasting techniques to fully appreciate the wine:
- Observe: Examine the wine’s color and clarity.
- Swirl: Gently swirl the wine in your glass to release its aromas.
- Smell: Inhale the wine’s aromas, noting the different scents and complexities.
- Taste: Take a small sip of the wine and let it linger on your palate, noting the flavors and textures.
- Savor: Savor the wine’s finish and aftertaste.
16.4 Responsible Consumption
Consume wine responsibly and in moderation. Designate a driver or hire a car service to ensure safe transportation.
17. Understanding E-E-A-T and YMYL in Travel Content
Creating travel content requires adhering to E-E-A-T (Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) and YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) guidelines to provide reliable and accurate information.
17.1 What is E-E-A-T?
E-E-A-T is a set of guidelines used by Google to evaluate the quality of content. It emphasizes the importance of expertise, experience, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness in content creation.
17.2 What is YMYL?
YMYL refers to topics that could potentially impact a person’s money, health, safety, or happiness. Travel content falls under YMYL, as it can influence decisions related to financial investments (travel expenses) and personal safety (travel destinations).
17.3 Implementing E-E-A-T and YMYL in Travel Content
To adhere to E-E-A-T and YMYL guidelines, travel content should:
- Demonstrate Expertise: Provide accurate and informative content based on expert knowledge.
- Share Experience: Include personal experiences and insights to enhance credibility.
- Establish Authoritativeness: Cite reputable sources and references to support claims.
- Build Trustworthiness: Provide transparent and unbiased information to build trust with the audience.
18. Napa Valley Itinerary Ideas
Planning a Napa Valley itinerary can be overwhelming, but here are some ideas to help you create a memorable and enjoyable trip.
18.1 One-Day Itinerary
- Morning: Visit Domaine Carneros for a sparkling wine tasting.
- Afternoon: Explore Castello di Amorosa and enjoy a wine and cheese pairing.
- Evening: Dine at The French Laundry for an unforgettable culinary experience.
18.2 Three-Day Itinerary
- Day 1: Explore Yountville, visit wineries, and dine at a Michelin-starred restaurant.
- Day 2: Drive along the Silverado Trail, visit wineries, and enjoy a hot air balloon ride.
- Day 3: Explore Calistoga, visit mud baths and spas, and dine at a farm-to-table eatery.
18.3 Five-Day Itinerary
- Day 1: Arrive in Napa Valley, check into your hotel, and explore the town of Napa.
- Day 2: Explore Yountville, visit wineries, and dine at a Michelin-starred restaurant.
- Day 3: Drive along the Silverado Trail, visit wineries, and enjoy a hot air balloon ride.
- Day 4: Explore Calistoga, visit mud baths and spas, and dine at a farm-to-table eatery.
- Day 5: Depart from Napa Valley.
19. Understanding Napa Valley Weather Patterns
Napa Valley experiences distinct weather patterns throughout the year, influencing the best time to visit and plan activities.
19.1 Spring (March-May)
Spring in Napa Valley is characterized by mild temperatures, blooming flowers, and lush landscapes. The weather is ideal for outdoor activities such as hiking, biking, and wine tasting.
19.2 Summer (June-August)
Summer in Napa Valley is hot and dry, with temperatures often exceeding 90°F (32°C). This is the peak season for tourism, but it’s essential to stay hydrated and protect yourself from the sun.
19.3 Fall (September-November)
Fall in Napa Valley is considered the harvest season, with vibrant foliage, cooler temperatures, and fewer crowds. This is an excellent time to visit for wine lovers and outdoor enthusiasts.
19.4 Winter (December-February)
Winter in Napa Valley is mild and rainy, with temperatures averaging around 50°F (10°C). While some wineries may have reduced hours, it’s still a great time to visit for a peaceful and less crowded experience.
20. Napa Valley’s Commitment to Sustainability
Napa Valley is committed to sustainable practices in wine production, tourism, and environmental conservation.
20.1 Sustainable Winegrowing Practices
Many wineries in Napa Valley have adopted sustainable winegrowing practices, such as:
- Organic Farming: Using natural methods to cultivate grapes without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers.
- Biodynamic Farming: A holistic approach to farming that emphasizes the interconnectedness of the vineyard ecosystem.
- Water Conservation: Implementing water-saving techniques to reduce water usage in vineyards.
20.2 Environmental Conservation Efforts
Various organizations in Napa Valley are dedicated to environmental conservation, such as:
- Napa County Resource Conservation District: Protecting and restoring natural resources through education, technical assistance, and project implementation.
- Land Trust of Napa County: Conserving open spaces and agricultural lands for future generations.
20.3 Sustainable Tourism Initiatives
Napa Valley encourages sustainable tourism through initiatives such as:
- Green Path Program: Recognizing and promoting businesses that adopt environmentally friendly practices.
- Recycling Programs: Providing recycling opportunities for visitors and residents.
Ready to explore the enchanting Napa Valley? Let TRAVELS.EDU.VN craft the perfect tour for you! Contact us now at +1 (707) 257-5400 or visit our website at TRAVELS.EDU.VN. Our address is 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States. Let us take care of the details while you savor the best of Napa Valley!
FAQ Section
1. Can electromagnetic waves travel through a vacuum?
Yes, electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum because they do not require a medium to propagate. They are formed by oscillating electric and magnetic fields that generate each other.
2. What is the speed of light in a vacuum?
The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (671 million miles per hour).
3. How do electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves?
Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium to travel, while mechanical waves do. Electromagnetic waves are formed by oscillating electric and magnetic fields, while mechanical waves are caused by vibrations in a medium.
4. What is electromagnetic radiation?
Electromagnetic radiation is energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
5. What are the properties of electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves have properties such as frequency, wavelength, energy, and polarization. They exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties.
6. What is wavelength?
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of a wave. It is measured in units of length, such as meters or nanometers.
7. What is frequency?
Frequency is the number of wave cycles that pass a given point per unit of time. It is measured in Hertz (Hz), where 1 Hz is equal to one cycle per second.
8. What is polarization?
Polarization is a property of electromagnetic waves that describes the orientation of the electric field. Light can be polarized in various directions.
9. What is a photon?
A photon is a fundamental particle of electromagnetic radiation. It has no mass and carries a specific amount of energy, which is proportional to its frequency.
10. How can TRAVELS.EDU.VN enhance my Napa Valley experience?
travels.edu.vn offers exceptional Napa Valley tour packages, seamless booking and planning services, curated tour packages, and expert guidance and support to ensure memorable experiences.