Electricity can travel through mediums, but how does this fascinating phenomenon occur? TRAVELS.EDU.VN unveils the secrets of electromagnetic waves, explaining how they propagate through various substances and even the vacuum of space. Discover the crucial role of electromagnetic radiation in travel and beyond, and let us help you plan an unforgettable trip.
1. Understanding Electromagnetic and Mechanical Waves
Electromagnetic waves and mechanical waves are distinct ways energy travels. Mechanical waves, such as water waves and sound waves, need a medium like air, water, or solid materials to propagate. These waves transfer energy by causing molecules to collide, much like a chain reaction. Sound, for example, cannot travel in the vacuum of space because it lacks a medium.
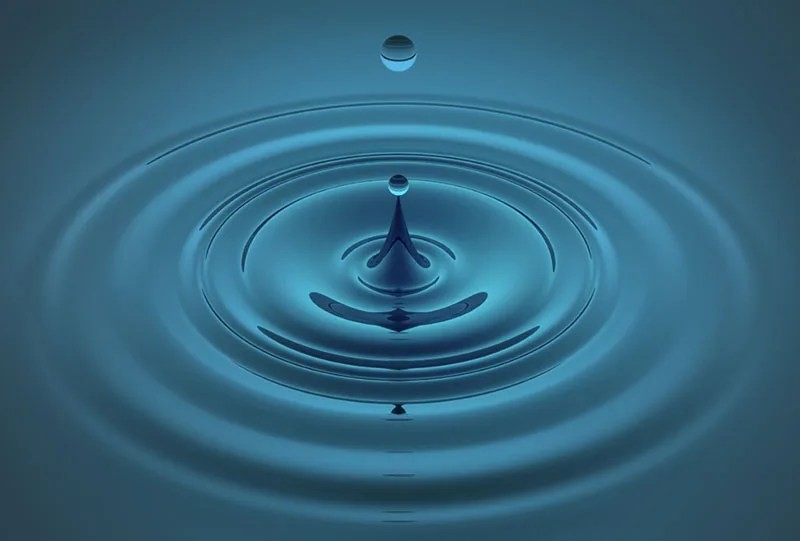 Ripples expanding outward from a drop of water in a still pool, illustrating the propagation of mechanical waves through a medium.
Ripples expanding outward from a drop of water in a still pool, illustrating the propagation of mechanical waves through a medium.
Electromagnetic waves, conversely, don’t need a medium. This critical difference allows them to travel through air, solids, liquids, and even the vacuum of space. This makes possible various aspects of modern technology, including radio communication and the study of distant celestial objects.
2. Delving into Electromagnetic Waves
Static electricity, like that created by rubbing a balloon on hair, demonstrates electrical energy. Magnetism can also be static, like a refrigerator magnet. Electromagnetic waves are formed when a changing magnetic field induces a changing electric field, and vice versa. James Clerk Maxwell, a Scottish scientist, developed a theory in the 1860s and 1870s explaining how these fields couple to form electromagnetic waves, summarized in “Maxwell’s Equations.”
Heinrich Hertz further validated Maxwell’s theories, producing and receiving radio waves. He demonstrated that radio waves travel at the speed of light, proving they are a form of light. The unit of frequency, Hertz (Hz), is named in his honor. This experiment helped unlock the principles behind wireless communication.
3. Waves or Particles? The Dual Nature of Light
Light exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties. Light is composed of photons, discrete packets of energy that carry momentum, have no mass, and travel at the speed of light. Depending on how light is observed, either its wave or particle nature becomes apparent. For instance, diffracting light into a spectrum highlights its wave-like nature, whereas using detectors in digital cameras demonstrates its particle-like behavior.
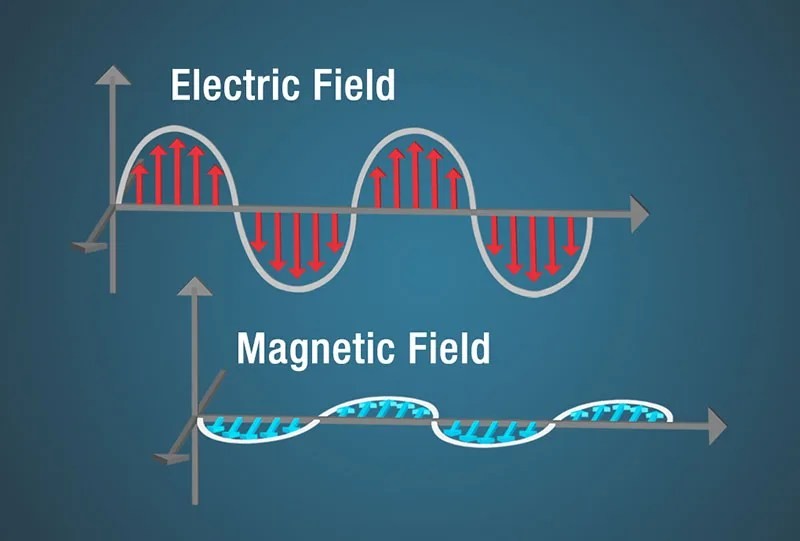 Diagram illustrating an electric field (red) and a magnetic field (blue) oscillating perpendicularly, forming an electromagnetic wave.
Diagram illustrating an electric field (red) and a magnetic field (blue) oscillating perpendicularly, forming an electromagnetic wave.
This dual nature is fundamental to understanding how light interacts with matter and is crucial in technologies like solar panels and medical imaging.
4. Understanding Polarization
Polarization measures the alignment of an electromagnetic field. Consider throwing a Frisbee at a picket fence; it can pass through if aligned correctly but will be blocked otherwise. Similarly, polarized sunglasses eliminate glare by absorbing the polarized portion of light.
Polarization affects how light interacts with different materials and surfaces, influencing the design of everything from camera lenses to communication systems.
5. Describing Electromagnetic Energy
Light, electromagnetic waves, and radiation describe the same phenomenon: electromagnetic energy. This energy can be defined by frequency (Hertz), wavelength (meters), or energy (electron volts). These parameters are mathematically related, allowing for conversions between them. Radio and microwaves are described by frequency, infrared and visible light by wavelength, and X-rays and gamma rays by energy.
Using appropriate units ensures convenient and comprehensible measurement and understanding of electromagnetic energy across the spectrum.
6. Exploring Frequency
Frequency is the number of wave crests passing a point per second, measured in Hertz (Hz). A wave with one cycle per second has a frequency of 1 Hz, and so on. Higher frequency means more cycles passing per second.
Frequency is critical in tuning radios, designing communication systems, and understanding the behavior of electromagnetic radiation.
7. Understanding Wavelength
Wavelength is the distance between successive crests in an electromagnetic wave. Wavelengths vary dramatically, from fractions of the size of an atom to larger than the diameter of the Earth. Shorter wavelengths correspond to higher energy and frequencies.
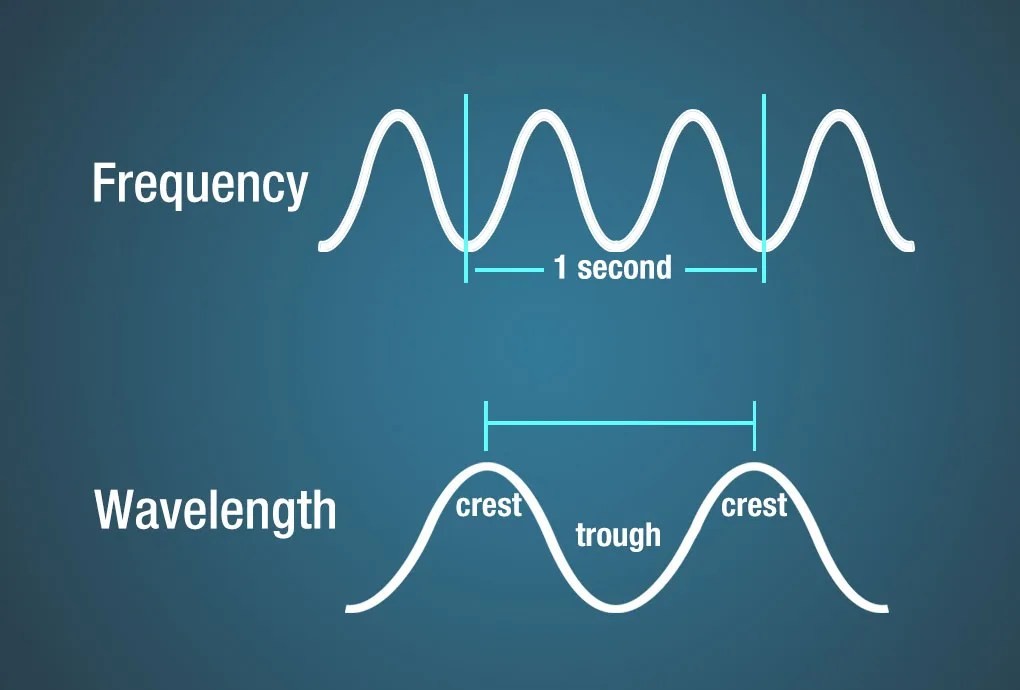 Diagram illustrating frequency as the number of wave crests passing a point per second and wavelength as the distance between crests.
Diagram illustrating frequency as the number of wave crests passing a point per second and wavelength as the distance between crests.
Wavelength is crucial in designing antennas, understanding the interaction of light with matter, and exploring the universe through telescopes.
8. Energy and Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic wave energy is measured in electron volts (eV), representing the kinetic energy needed to move an electron through one volt potential. Energy increases as wavelength shortens. Consider a jump rope: more energy is required to create more waves, thus shortening the wavelength.
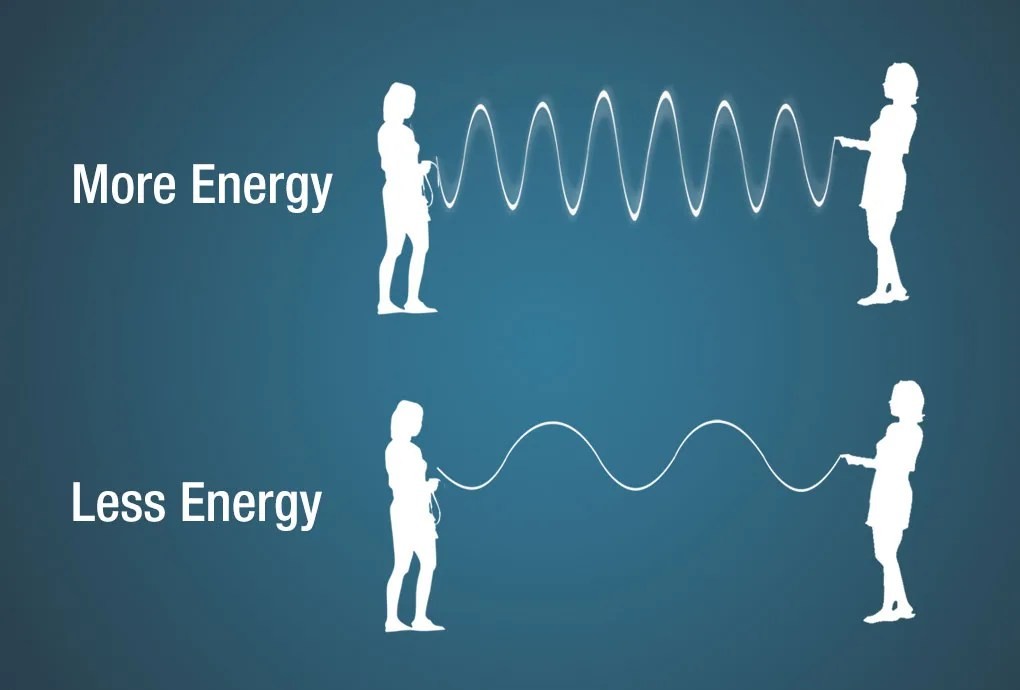 Illustration showing a jump rope with faster movement creating shorter wavelengths and slower movement creating longer wavelengths.
Illustration showing a jump rope with faster movement creating shorter wavelengths and slower movement creating longer wavelengths.
This relationship between energy and wavelength is vital in understanding the electromagnetic spectrum, from low-energy radio waves to high-energy gamma rays.
9. Electricity’s Journey Through Various Mediums
Electricity’s ability to travel through different mediums depends on whether it’s conducted through a material or propagated as electromagnetic radiation. In conductive materials like metals, electrons move freely, allowing electrical current to flow. In contrast, electromagnetic waves don’t need physical contact; they propagate through fields.
9.1. Electricity Through Conductors
Conductors like copper and aluminum are common in electrical wiring because their atomic structure allows electrons to move with minimal resistance. This movement of electrons is what constitutes electrical current.
9.2. Electricity Through Insulators
Insulators like rubber and glass resist the flow of electricity because their electrons are tightly bound to atoms. These materials are used to prevent electrical current from flowing where it’s not needed.
9.3. Electricity Through Semiconductors
Semiconductors like silicon have conductivity between conductors and insulators, making them crucial in electronic devices. Their conductivity can be controlled by adding impurities or applying an electric field.
9.4. Electricity Through Plasma
Plasma, an ionized gas, is an excellent conductor due to the abundance of free electrons. Lightning and the Earth’s ionosphere are examples of plasma conducting electricity.
10. Electromagnetic Radiation in Space
One of the most striking examples of electricity traveling through a medium (or lack thereof) is electromagnetic radiation in space. The sun’s energy reaches Earth as electromagnetic waves, traversing the vacuum of space. This radiation includes visible light, infrared radiation, ultraviolet radiation, and other forms of energy crucial for life on Earth.
10.1. Radio Waves in Space Communication
Spacecraft use radio waves to communicate with Earth, sending data and receiving instructions across vast distances. These waves travel through the vacuum of space without needing a physical medium.
10.2. Microwaves in Satellite Communication
Satellites use microwaves to transmit signals to Earth, essential for television broadcasting, internet access, and weather monitoring. Microwaves can penetrate the atmosphere and travel long distances with minimal loss.
10.3. Infrared Radiation in Remote Sensing
Satellites use infrared radiation to study Earth’s surface temperature, vegetation, and atmospheric conditions. This technology helps monitor climate change and manage natural resources.
10.4. Visible Light in Astronomy
Telescopes capture visible light from distant stars and galaxies, allowing astronomers to study the universe. Analyzing the spectrum of light reveals information about the composition, temperature, and motion of celestial objects.
10.5. Ultraviolet Radiation in Atmospheric Studies
Satellites measure ultraviolet radiation to study the ozone layer and its impact on Earth’s atmosphere. This helps monitor the effects of pollution and protect human health.
10.6. X-rays and Gamma Rays in High-Energy Astrophysics
Space-based observatories detect X-rays and gamma rays from black holes, neutron stars, and other high-energy phenomena. These observations provide insights into the most extreme environments in the universe.
11. Electricity and Travel: A Powerful Connection
Electricity is deeply intertwined with the travel industry. From powering transportation systems to enabling communication and entertainment, electricity makes travel more efficient, convenient, and enjoyable.
11.1. Electric Vehicles and Sustainable Travel
Electric vehicles (EVs) are transforming the transportation sector, offering a sustainable alternative to gasoline-powered cars. EVs reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, contributing to cleaner and healthier travel experiences.
11.2. Electrified Transportation Systems
Trains, subways, and trams rely on electricity to transport passengers within and between cities. These systems provide efficient and reliable mass transit, reducing traffic congestion and promoting sustainable urban development.
11.3. Electricity in Aviation
Airplanes use electricity for navigation, communication, and entertainment systems. Electric propulsion is also emerging as a promising technology for smaller aircraft, potentially revolutionizing regional air travel.
11.4. Electricity in Maritime Transportation
Ships and ferries use electricity for propulsion, lighting, and onboard services. Electric and hybrid propulsion systems are gaining popularity, reducing fuel consumption and emissions in the maritime industry.
11.5. Electricity in Hospitality
Hotels, resorts, and cruise ships rely on electricity for lighting, heating, cooling, and powering appliances. Efficient energy management and renewable energy sources are becoming increasingly important in the hospitality sector.
12. TRAVELS.EDU.VN: Your Guide to Unforgettable Travel Experiences
At TRAVELS.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of electricity in modern travel and strive to provide you with the best possible travel experiences. Whether you’re planning a romantic getaway, a family vacation, or an adventure with friends, we offer a wide range of travel services to meet your needs.
12.1. Napa Valley: A Premier Destination
Napa Valley, located in California, is renowned for its stunning landscapes, world-class wineries, and gourmet cuisine. It’s the perfect destination for wine lovers, foodies, and anyone seeking a relaxing and luxurious escape.
12.2. Why Choose TRAVELS.EDU.VN for Your Napa Valley Trip?
- Expert Knowledge: Our travel experts have in-depth knowledge of Napa Valley and can provide personalized recommendations based on your preferences.
- Curated Experiences: We offer a selection of curated experiences, including wine tours, cooking classes, hot air balloon rides, and spa treatments.
- Exclusive Deals: We have partnerships with top hotels, wineries, and restaurants in Napa Valley, allowing us to offer exclusive deals and discounts.
- Seamless Planning: We handle all the details of your trip, from booking accommodations and transportation to arranging activities and dining reservations.
- 24/7 Support: Our customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you with any questions or concerns.
12.3. Sample Napa Valley Itinerary
Here’s a sample itinerary for a 3-day Napa Valley getaway:
Day 1:
- Arrive in Napa Valley and check into your hotel.
- Visit a renowned winery like Robert Mondavi Winery or Domaine Carneros for a tasting.
- Enjoy a gourmet dinner at The French Laundry or Bouchon Bistro.
Day 2:
- Take a hot air balloon ride over Napa Valley.
- Explore the charming town of Yountville and visit local boutiques.
- Indulge in a spa treatment at a luxury resort.
Day 3:
- Participate in a cooking class at the Culinary Institute of America.
- Visit a smaller, family-owned winery for a more intimate tasting experience.
- Enjoy a farewell dinner at a restaurant with stunning vineyard views.
12.4. Tour Packages and Services Offered at TRAVELS.EDU.VN
TRAVELS.EDU.VN offers a variety of tour packages and services to make your Napa Valley trip unforgettable:
| Package/Service | Description | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Wine Tour | Guided tour of 3-4 wineries with tastings. Includes transportation. | $250-500 |
| Hot Air Balloon Ride | Sunrise hot air balloon ride over Napa Valley with champagne toast. | $300-450 |
| Cooking Class | Hands-on cooking class at a renowned culinary school. | $150-300 |
| Spa Treatment | Relaxing spa treatment at a luxury resort. | $200-400 |
| Custom Itinerary | Personalized itinerary tailored to your interests and budget. | Varies |
| Hotel Booking | Assistance with booking accommodations at top hotels and resorts. | Varies |
| Transportation | Arranging transportation, including airport transfers and private car service. | Varies |
| Dining Reservations | Assistance with making dining reservations at popular restaurants. | Free |
Note: Prices are approximate and may vary depending on availability and seasonality.
12.5. The TRAVELS.EDU.VN Advantage
Booking your Napa Valley trip with TRAVELS.EDU.VN offers several advantages:
- Stress-Free Planning: We handle all the logistics, so you can relax and enjoy your vacation.
- Expert Advice: Our travel experts provide personalized recommendations based on your interests and budget.
- Exclusive Deals: We offer exclusive deals and discounts on hotels, activities, and dining.
- Peace of Mind: We provide 24/7 customer support to assist you with any questions or concerns.
12.6. Ready to Plan Your Napa Valley Getaway?
Don’t wait any longer to experience the beauty and luxury of Napa Valley. Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN today to start planning your unforgettable trip.
Address: 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (707) 257-5400
Website: TRAVELS.EDU.VN
13. Conclusion: Embrace the Wonders of Electricity and Travel
Electricity, in its various forms, is a fundamental force shaping our world and enhancing our travel experiences. From powering our transportation systems to enabling communication and entertainment, electricity makes travel more efficient, convenient, and enjoyable.
At TRAVELS.EDU.VN, we’re passionate about providing you with the best possible travel experiences and helping you explore the world with ease and comfort. Whether you’re interested in the science behind electricity or simply looking for a relaxing getaway, we have something for everyone.
Ready to embark on your next adventure? Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN today and let us help you create memories that will last a lifetime.
14. FAQs About Electricity and Travel
14.1. Can electricity travel through a vacuum?
Yes, electromagnetic waves, which are a form of electricity, can travel through a vacuum. This is how sunlight reaches Earth.
14.2. What is the difference between electromagnetic waves and mechanical waves?
Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium to travel, while mechanical waves do. Sound waves are mechanical, while radio waves are electromagnetic.
14.3. How does electricity power transportation systems?
Electricity powers trains, subways, trams, and electric vehicles. It is also used in aviation and maritime transportation for various onboard systems.
14.4. What are the benefits of electric vehicles for travel?
Electric vehicles reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, contributing to cleaner and healthier travel experiences.
14.5. How does electricity enhance the hospitality industry?
Electricity powers lighting, heating, cooling, and appliances in hotels, resorts, and cruise ships, ensuring comfort and convenience for travelers.
14.6. Why is Napa Valley a popular travel destination?
Napa Valley is renowned for its stunning landscapes, world-class wineries, and gourmet cuisine, making it perfect for wine lovers and those seeking relaxation.
14.7. What types of experiences does TRAVELS.EDU.VN offer in Napa Valley?
TRAVELS.EDU.VN offers wine tours, hot air balloon rides, cooking classes, spa treatments, and custom itineraries in Napa Valley.
14.8. How can TRAVELS.EDU.VN help me plan my Napa Valley trip?
We provide expert knowledge, curated experiences, exclusive deals, seamless planning, and 24/7 support to make your trip unforgettable.
14.9. What is included in a typical Napa Valley wine tour?
A wine tour typically includes guided visits to 3-4 wineries with tastings and transportation.
14.10. How can I contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN to book my trip?
You can contact us via our address: 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States; WhatsApp: +1 (707) 257-5400; or website: TRAVELS.EDU.VN.
We hope this comprehensive guide has illuminated the fascinating relationship between electricity and travel. Contact travels.edu.vn today to plan your next adventure and experience the world in a whole new light.
