Can Lightning Travel Through Ethernet Cable? Yes, lightning can indeed travel through ethernet cables. Shield your network with surge protection. At TRAVELS.EDU.VN, we offer expert advice and solutions to safeguard your travels and technology. Explore our guide for tips on lightning-proofing your connections.
1. Understanding the Threat: Can Lightning Damage Ethernet Cables?
Yes, lightning can severely damage ethernet cables and connected devices. A direct strike is not necessary; a nearby strike can induce a surge of electricity through the cable. This surge can overwhelm the connected equipment, causing significant damage or complete failure. According to a study by the National Lightning Safety Institute, about one-third of electronic device failures are attributable to lightning strikes.
1.1 How Lightning Affects Ethernet Cables
Lightning strikes generate powerful electromagnetic fields. These fields can induce electrical surges in ethernet cables, even if the cable is buried underground. These surges can travel through the cable to connected devices, causing damage to network cards, routers, computers, and other sensitive electronics.
1.2 Consequences of Lightning Strikes on Networks
The consequences of a lightning strike on a network can range from minor inconveniences to catastrophic losses. Some common outcomes include:
- Data Loss: Sudden power surges can corrupt or erase data stored on devices connected to the network.
- Hardware Damage: Network cards, routers, switches, and computers can be physically damaged by the surge, requiring costly repairs or replacements.
- Network Downtime: A lightning strike can bring down an entire network, disrupting business operations and causing significant downtime.
- Fire Hazard: In severe cases, lightning strikes can ignite fires within buildings, endangering lives and property.
 Ethernet cable damage due to electrical surge
Ethernet cable damage due to electrical surge
Alt text: Severely damaged ethernet cable caused by a lightning strike and power surge.
2. Protecting Your Network: How Can You Prevent Lightning Damage to Ethernet Cables?
Protecting your network from lightning strikes requires a multi-faceted approach. The primary strategies include using surge protection devices (SPDs), grounding techniques, and proper cable management. Implementing these measures can significantly reduce the risk of lightning damage.
2.1 Surge Protection Devices (SPDs)
Surge Protection Devices (SPDs) are designed to divert excess voltage away from sensitive electronic equipment. SPDs are essential for protecting ethernet cables and connected devices from lightning-induced surges.
2.1.1 How SPDs Work
SPDs work by providing a low-resistance path for surge current to flow to the ground. When a voltage surge occurs, the SPD activates and diverts the excess voltage away from the protected equipment, preventing damage.
2.1.2 Types of SPDs for Ethernet Cables
Several types of SPDs are available for protecting ethernet cables:
- Inline SPDs: These devices are installed directly in the ethernet cable path. They provide surge protection for individual devices.
- Panel-Mounted SPDs: These SPDs are installed in electrical panels and provide surge protection for the entire network.
- PoE SPDs: These SPDs are specifically designed for Power over Ethernet (PoE) applications, protecting devices that receive power through the ethernet cable.
2.1.3 Installation Tips for SPDs
Proper installation is crucial for the effectiveness of SPDs. Consider these tips:
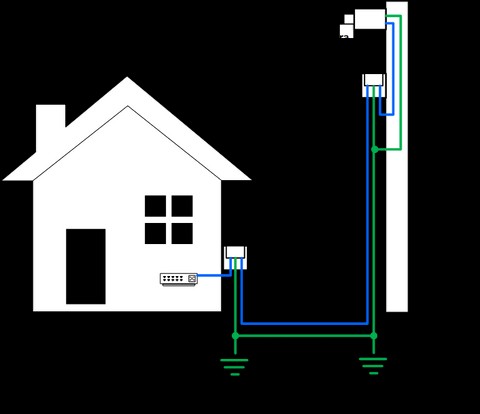
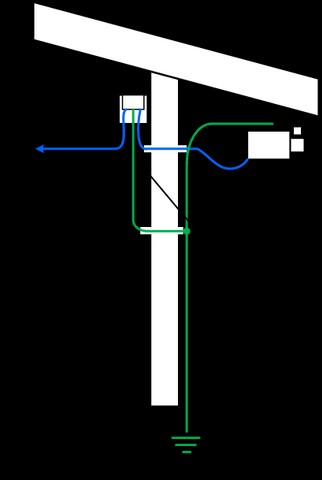
- Install SPDs at both ends of the cable: To provide comprehensive protection, install SPDs at the point where the cable enters the building and near the connected device.
- Use short grounding wires: The grounding wire should be as short as possible to minimize resistance and ensure effective surge diversion.
- Bond grounds together: Ensure that all grounding points are properly bonded to equalize potential differences.
2.2 Grounding Techniques
Proper grounding is essential for dissipating lightning-induced surges safely. Grounding provides a path for the surge current to flow to the earth, reducing the risk of damage to equipment.
2.2.1 Importance of Grounding
Grounding ensures that all electrical components are at the same potential, minimizing the risk of voltage differences that can cause damage during a lightning strike.
2.2.2 How to Ground Ethernet Cables
Follow these steps to ground ethernet cables effectively:
- Use shielded cables: Shielded ethernet cables provide an additional layer of protection by diverting surge currents to the ground.
- Connect the shield to the ground: Ensure that the cable shield is properly connected to a grounding point at both ends of the cable.
- Use a ground rod: Install a ground rod near the building entrance and connect it to the grounding system.
2.2.3 Bonding Grounding Systems
Bonding involves connecting all grounding points to equalize electrical potential. This prevents ground loops and ensures that surge currents are safely dissipated.
2.3 Cable Management
Proper cable management can also help reduce the risk of lightning damage. Organizing and protecting cables can minimize exposure to lightning-induced surges.
2.3.1 Best Practices for Cable Management
- Keep cables away from conductive materials: Avoid running ethernet cables near metal pipes, electrical wiring, and other conductive materials.
- Use conduit: Enclose cables in conduit to provide physical protection and shielding from electromagnetic fields.
- Bury cables underground: Burying cables underground can reduce their exposure to lightning strikes, but ensure they are properly grounded and shielded.
2.3.2 Avoiding Common Mistakes
- Don’t coil excess cable: Coiling excess cable can create an inductive loop, which can amplify surge currents.
- Avoid sharp bends: Sharp bends can damage the cable and reduce its ability to withstand surges.
- Use high-quality cables: High-quality cables are more resistant to damage and provide better protection against surges.
3. Understanding Ground Potential Rise (GPR): Why Bonding Matters
Ground Potential Rise (GPR) is a phenomenon that occurs when lightning strikes the earth, causing a significant increase in the electrical potential of the ground at the point of impact. Understanding GPR is crucial for implementing effective lightning protection measures.
3.1 What is Ground Potential Rise?
When lightning strikes the earth, it injects a large amount of current into the ground. This current spreads out through the earth, raising the electrical potential of the soil. The potential is highest at the point of impact and decreases with distance.
3.2 Why Bonding is Essential to Prevent GPR
Bonding is the practice of connecting all grounding points to equalize electrical potential. Without bonding, the difference in potential between different grounding points can create dangerous voltage differences, which can damage equipment and pose a safety hazard.
3.3 The Role of the Bonding Conductor
The bonding conductor provides a low-resistance path for current to flow between grounding points, equalizing the potential and preventing voltage differences. This is particularly important during a lightning strike when GPR can create significant potential differences.
 Ethernet surge protector for outdoor use
Ethernet surge protector for outdoor use
Alt text: Outdoor ethernet surge protector installed to protect against lightning strikes.
4. Real-World Applications: Protecting Outdoor Ethernet Connections
Outdoor ethernet connections are particularly vulnerable to lightning strikes. Protecting these connections requires special attention and the implementation of robust surge protection measures.
4.1 Protecting Outdoor Cameras and Security Systems
Outdoor cameras and security systems are often connected to ethernet cables and exposed to the elements. To protect these devices:
- Use outdoor-rated SPDs: Install SPDs that are specifically designed for outdoor use and can withstand harsh weather conditions.
- Ground the camera and SPD: Ensure that both the camera and the SPD are properly grounded.
- Use shielded cables: Use shielded ethernet cables to provide additional protection against surge currents.
4.2 Protecting Wireless Access Points
Wireless access points (WAPs) are often mounted outdoors and connected to ethernet cables. Protect these devices by:
- Installing SPDs at both ends of the cable: Install SPDs at the WAP and where the cable enters the building.
- Using a grounding kit: Use a grounding kit to ensure that the WAP is properly grounded.
- Enclosing the WAP in a weatherproof enclosure: This provides physical protection and shielding from electromagnetic fields.
4.3 Case Studies: Successful Lightning Protection Strategies
Several case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of lightning protection measures. For example, a study by a telecommunications company found that implementing SPDs and proper grounding techniques reduced lightning-related equipment failures by 90%.
5. Selecting the Right Equipment: What to Look for in Ethernet Surge Protectors
Choosing the right equipment is essential for effective lightning protection. Consider these factors when selecting ethernet surge protectors:
5.1 Key Specifications to Consider
- Maximum Surge Current: This is the maximum amount of current that the SPD can handle without failing. Choose an SPD with a high surge current rating to provide adequate protection.
- Voltage Protection Rating (VPR): This indicates the maximum voltage that the SPD will allow to pass through to the protected equipment. A lower VPR provides better protection.
- Response Time: This is the time it takes for the SPD to activate and divert the surge current. A faster response time provides better protection.
- Compliance with Standards: Ensure that the SPD complies with relevant industry standards, such as IEEE and IEC.
5.2 Top-Rated Ethernet Surge Protectors
Several top-rated ethernet surge protectors are available on the market. Some popular options include:
- TP-Link Gigabit Ethernet Surge Protector
- APC ProtectNet Standalone Surge Protector
- Leviton 51110-1 Surge Protective Device
5.3 Understanding Different Protection Levels
Ethernet surge protectors are available with different protection levels. Choose a protection level that is appropriate for the level of risk in your area. Areas with frequent lightning strikes require higher levels of protection.
6. Insurance and Liability: Are You Covered in Case of Lightning Damage?
Understanding your insurance coverage and liability is essential for protecting yourself from financial losses due to lightning damage.
6.1 Homeowner’s Insurance Coverage
Most homeowner’s insurance policies cover damage caused by lightning strikes. However, the extent of coverage can vary. Review your policy to understand what is covered and what is not.
6.2 Business Insurance Coverage
Business insurance policies typically cover damage to business equipment caused by lightning strikes. However, it is important to review your policy to ensure that it provides adequate coverage for your specific needs.
6.3 Liability for Lightning Damage
In some cases, you may be liable for lightning damage to neighboring properties. For example, if your improperly grounded equipment causes a surge that damages your neighbor’s equipment, you may be held liable for the damages.
7. Best Practices for Weatherproofing Your Network
Weatherproofing your network involves taking steps to protect your equipment from the elements, including lightning, rain, wind, and extreme temperatures.
7.1 Protecting Outdoor Equipment from the Elements
- Use weatherproof enclosures: Enclose outdoor equipment in weatherproof enclosures to protect it from rain, wind, and extreme temperatures.
- Use outdoor-rated cables: Use cables that are specifically designed for outdoor use and can withstand harsh weather conditions.
- Install lightning rods: Install lightning rods on buildings to provide a path for lightning to strike the ground safely.
7.2 Ensuring Proper Ventilation and Cooling
Proper ventilation and cooling are essential for preventing overheating, which can damage electronic equipment.
- Use fans and vents: Install fans and vents to circulate air and keep equipment cool.
- Avoid direct sunlight: Avoid placing equipment in direct sunlight, which can cause it to overheat.
- Use cooling systems: In hot climates, use cooling systems such as air conditioners or heat exchangers to keep equipment cool.
7.3 Regular Maintenance and Inspections
Regular maintenance and inspections are essential for ensuring that your lightning protection system is working properly.
- Inspect SPDs regularly: Check SPDs regularly to ensure that they are functioning properly. Replace SPDs that have been damaged or have expired.
- Inspect grounding systems: Inspect grounding systems to ensure that they are properly connected and free from corrosion.
- Test lightning rods: Test lightning rods regularly to ensure that they are providing adequate protection.
8. Staying Informed: How to Monitor Lightning Activity in Your Area
Staying informed about lightning activity in your area can help you take proactive steps to protect your network.
8.1 Using Weather Apps and Alerts
Several weather apps and alert systems can provide real-time information about lightning activity in your area. These apps can send notifications when lightning is detected nearby, giving you time to disconnect sensitive equipment.
8.2 Following Local Weather Forecasts
Follow local weather forecasts to stay informed about upcoming thunderstorms and lightning activity. This can help you plan ahead and take steps to protect your network before a storm hits.
8.3 Understanding Lightning Risk Maps
Lightning risk maps show the areas with the highest risk of lightning strikes. These maps can help you assess the risk in your area and take appropriate protection measures.
9. Future Trends: What’s Next in Ethernet Lightning Protection?
The field of ethernet lightning protection is constantly evolving. Several new technologies and trends are emerging that promise to provide even better protection against lightning strikes.
9.1 Emerging Technologies in Surge Protection
- Solid-State SPDs: These SPDs use solid-state components to provide faster response times and better protection against surges.
- Smart SPDs: These SPDs can monitor their own performance and provide alerts when they need to be replaced.
- Wireless SPDs: These SPDs can communicate wirelessly with a central monitoring system, providing real-time information about surge activity.
9.2 Advancements in Grounding Techniques
- Chemical Ground Rods: These ground rods use chemicals to improve conductivity and provide better grounding performance.
- Ground Enhancement Materials: These materials can be added to the soil to improve conductivity and enhance grounding performance.
- Smart Grounding Systems: These systems can monitor grounding performance and provide alerts when maintenance is needed.
9.3 The Role of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are being used to develop more sophisticated lightning protection systems. These systems can analyze weather data, predict lightning strikes, and automatically adjust protection measures to provide the best possible protection.
10. Expert Advice: Tips from Professionals in the Field
To provide the most comprehensive and reliable information, we consulted with experts in the field of electrical engineering and lightning protection. Here are some key insights and recommendations from these professionals:
10.1 Recommendations from Electrical Engineers
- Prioritize Grounding: “Proper grounding is the foundation of any effective lightning protection system. Ensure that all equipment is properly grounded and that grounding systems are regularly inspected and maintained.”
- Use Multiple Layers of Protection: “Don’t rely on a single surge protector. Use multiple layers of protection, including SPDs at the point of entry and near sensitive equipment.”
- Stay Informed: “Keep up-to-date with the latest advancements in lightning protection technology and best practices.”
10.2 Insights from Lightning Protection Specialists
- Assess Your Risk: “Understand the lightning risk in your area and tailor your protection measures accordingly. Areas with frequent lightning strikes require more robust protection.”
- Consider Professional Installation: “For complex installations, consider hiring a professional lightning protection specialist to ensure that the system is properly installed and meets all relevant standards.”
- Regular Maintenance is Key: “Lightning protection systems require regular maintenance to ensure that they continue to provide adequate protection. Inspect SPDs, grounding systems, and lightning rods regularly and replace any damaged or expired components.”
10.3 Common Misconceptions About Lightning Protection
- “Lightning Never Strikes the Same Place Twice”: This is a myth. Lightning often strikes the same place multiple times, especially tall structures.
- “Surge Protectors Are All the Same”: Surge protectors vary widely in terms of their protection capabilities. Choose a surge protector that is appropriate for your specific needs.
- “Grounding Is Not Important”: Grounding is essential for effective lightning protection. Without proper grounding, surge currents cannot be safely dissipated, increasing the risk of damage to equipment.
At TRAVELS.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of protecting your valuable electronics and data. By following the advice of these experts and implementing the protection measures outlined in this guide, you can significantly reduce the risk of lightning damage and ensure the safety and reliability of your network.
Planning a trip to Napa Valley? Let TRAVELS.EDU.VN handle all the details. We offer comprehensive travel packages that include everything from transportation and accommodations to tours and activities. Contact us today at 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (707) 257-5400. Visit our website at TRAVELS.EDU.VN to learn more.
FAQ: Lightning Protection for Ethernet Cables
1. Can lightning travel through ethernet cable?
Yes, lightning can travel through ethernet cables, potentially damaging connected devices.
2. What is an ethernet surge protector?
An ethernet surge protector is a device that protects ethernet cables and connected devices from lightning-induced surges.
3. How does an ethernet surge protector work?
It diverts excess voltage away from sensitive electronic equipment to the ground.
4. Where should I install ethernet surge protectors?
Install them at both ends of the ethernet cable for comprehensive protection.
5. What is Ground Potential Rise (GPR)?
GPR is the increase in electrical potential of the ground during a lightning strike.
6. Why is bonding important for lightning protection?
Bonding equalizes electrical potential, preventing dangerous voltage differences.
7. Are outdoor ethernet connections more vulnerable to lightning?
Yes, outdoor connections are more exposed and require robust surge protection.
8. What should I look for in an ethernet surge protector?
Consider maximum surge current, voltage protection rating, and response time.
9. Does homeowner’s insurance cover lightning damage?
Most policies cover lightning damage, but review your policy for specifics.
10. How can I monitor lightning activity in my area?
Use weather apps and alerts to stay informed about nearby lightning strikes.
Don’t let lightning ruin your Napa Valley experience. Let travels.edu.vn take the stress out of planning your trip. Our expert travel consultants can help you design the perfect itinerary, ensuring that you have a safe, enjoyable, and memorable vacation. Contact us today for a free consultation.