Light’s speed, a cosmic constant, illuminates our universe, shaping our comprehension of space and time. TRAVELS.EDU.VN unveils the astonishing velocity of light traveling the Earth, opening doors to understanding light speed ramifications. This exploration delves into astronomical distances, the swiftness of electromagnetic radiation, and light’s role.
1. Understanding the Speed of Light
The speed of light, often denoted as c, is a fundamental constant in physics, representing the velocity at which electromagnetic radiation, including light, travels in a vacuum. Its value is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (670,616,629 miles per hour). This speed is not just a measure of how fast light travels, but also a cornerstone of Einstein’s theory of relativity, linking space and time. Understanding light speed implications is key to understanding the universe.
1.1. The Universal Speed Limit
Einstein’s theory of special relativity posits that the speed of light in a vacuum is the maximum speed at which all energy, matter, and information in the universe can travel. This principle has profound implications for our understanding of causality and the structure of spacetime. No object with mass can reach or exceed this speed, as it would require an infinite amount of energy.
1.2. Light Speed and Its Impact on Time and Space
One of the most fascinating aspects of the speed of light is its effect on time and space. According to special relativity, as an object approaches the speed of light, time slows down for that object relative to a stationary observer. This phenomenon, known as time dilation, and the related effect of length contraction, where the length of an object appears to shorten in the direction of motion, are not just theoretical concepts but have been experimentally verified.
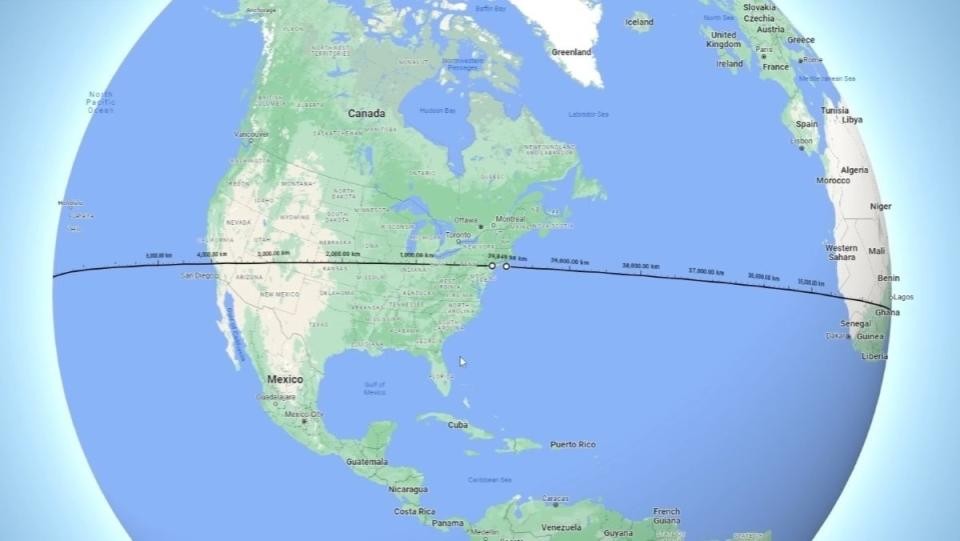
2. How Fast Does Light Travel Around the Earth?
Imagine light racing around the Earth. At its incredible pace, light can circle the Earth multiple times in just one second. To illustrate, let’s calculate how long it takes for light to travel once around the Earth’s circumference, which is approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles).
2.1. The Calculation
To find the time it takes for light to travel around the Earth, we use the formula:
Time = Distance / Speed
Where:
- Distance = 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles)
- Speed of light (c) = 299,792.458 kilometers per second (186,282 miles per second)
Therefore:
Time = 40,075 km / 299,792.458 km/s ≈ 0.134 seconds
This means light can travel around the Earth in approximately 0.134 seconds, a blink of an eye.
2.2. Comparing Light Speed to Other Speeds
To further appreciate how incredibly fast light travels, let’s compare it to other speeds we experience in our daily lives:
- Speed of Sound: The speed of sound in air is about 343 meters per second (767 miles per hour). Light travels almost a million times faster than sound.
- Commercial Airplane: A typical commercial airplane flies at around 900 kilometers per hour (560 miles per hour). Light is more than 745,000 times faster.
- Fastest Train: The Shanghai Maglev, one of the fastest commercial trains, reaches speeds of up to 460 kilometers per hour (286 miles per hour). Light outpaces this train by over 650,000 times.
The scale difference between light speed and these common speeds is staggering, highlighting just how instantaneous light’s journey around the Earth seems to us.
3. Practical Implications and Applications
The speed of light is not just a theoretical concept; it has numerous practical implications and applications in various fields, from communication to astronomy.
3.1. Communication Technology
In modern communication, the speed of light plays a crucial role. Fiber optic cables, which transmit data as light pulses, are used worldwide for internet and telecommunications. The speed at which these light pulses travel determines the latency or delay in data transmission. While fiber optic cables don’t transmit data at the speed of light in a vacuum (due to the refractive index of the glass), they still operate at speeds that are a significant fraction of c, enabling near-instantaneous communication across vast distances.
3.2. Space Exploration and Astronomy
In space exploration and astronomy, the speed of light is a fundamental consideration. The vast distances between celestial objects mean that light takes a significant amount of time to reach us. For example, light from the Sun takes about 8 minutes and 20 seconds to reach Earth, and light from the nearest star system, Alpha Centauri, takes over 4 years. This delay means that when we observe distant stars and galaxies, we are seeing them as they were in the past. Understanding light speed and astronomical distances helps astronomers study cosmic phenomena and the history of the universe.
 An illustration showing a beam of light traveling from the sun to the earth.
An illustration showing a beam of light traveling from the sun to the earth.
3.3. GPS and Satellite Technology
Global Positioning System (GPS) technology relies on the precise timing of signals transmitted from satellites to receivers on Earth. These signals travel at the speed of light, and even small variations in the time it takes for the signals to arrive can lead to significant errors in position calculations. To achieve the accuracy required for GPS, relativistic effects, including time dilation due to the satellites’ motion and gravitational potential, must be taken into account.
4. The Speed of Light in Different Mediums
While we often talk about the speed of light as a constant, it’s important to note that the speed of light (c) refers to the speed in a vacuum. When light travels through a medium other than a vacuum, such as air, water, or glass, it slows down. This reduction in speed is due to the interaction of light with the atoms and molecules of the medium.
4.1. Refractive Index
The extent to which a medium slows down light is characterized by its refractive index (n), which is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the medium:
n = c / v
Where:
- n is the refractive index
- c is the speed of light in a vacuum
- v is the speed of light in the medium
For example, the refractive index of air is approximately 1.0003, which means that light travels slightly slower in air than in a vacuum. The refractive index of water is about 1.33, and for glass, it typically ranges from 1.5 to 1.9.
4.2. Consequences of Light Slowing Down
The slowing down of light in different mediums has several important consequences:
- Refraction: When light passes from one medium to another at an angle, it bends or refracts. This phenomenon is responsible for the way lenses focus light and for the appearance of objects submerged in water.
- Dispersion: The refractive index of a medium can vary depending on the wavelength of light. This effect, known as dispersion, causes different colors of light to bend at different angles when passing through a prism, resulting in the separation of white light into its constituent colors.
- Cherenkov Radiation: When a charged particle travels through a medium faster than the speed of light in that medium (but still slower than c), it emits electromagnetic radiation known as Cherenkov radiation. This effect is similar to a sonic boom and is used in particle detectors.
5. Faster-Than-Light Travel: Science Fiction vs. Reality
The concept of faster-than-light (FTL) travel is a staple of science fiction, appearing in stories like Star Trek (warp drive) and Star Wars (hyperspace). However, according to our current understanding of physics, FTL travel is not possible.
5.1. Challenges to FTL Travel
The primary challenge to FTL travel is Einstein’s theory of special relativity, which states that the speed of light is the universal speed limit. As an object approaches the speed of light, its mass increases, and it requires more and more energy to accelerate further. Reaching the speed of light would require an infinite amount of energy, and exceeding it would violate causality, potentially leading to paradoxes.
5.2. Hypothetical Concepts
Despite these challenges, scientists and theorists have explored hypothetical concepts that might allow for effective FTL travel:
- Wormholes: Wormholes are theoretical tunnels through spacetime that could connect two distant points. While allowed by the equations of general relativity, their existence has not been confirmed, and they would likely require exotic matter with negative mass-energy density to remain open.
- Warp Drive: A warp drive, as depicted in Star Trek, would involve contracting spacetime in front of a spacecraft and expanding it behind, allowing the spacecraft to travel faster than light relative to distant observers without actually exceeding c locally. The feasibility of warp drives is highly speculative and would require enormous amounts of energy.
- Quantum Entanglement: Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon in which two or more particles become linked in such a way that they share the same fate, no matter how far apart they are. Some have speculated that entanglement could be used for instantaneous communication, but this would not allow for the transfer of matter or energy faster than light.
5.3. The Implications of FTL Travel
If FTL travel were possible, it would revolutionize space exploration and our understanding of the universe. It would allow us to reach distant star systems in human lifetimes, explore exoplanets, and potentially make contact with extraterrestrial civilizations. However, it would also raise profound questions about causality, time travel, and the nature of reality.
6. The role of travels.edu.vn in understanding light speed and its applications
TRAVELS.EDU.VN takes pride in providing accurate, accessible, and engaging content about science and technology, including the concept of light speed and its myriad applications. By exploring this topic, we aim to inspire curiosity, foster a deeper understanding of the universe, and encourage readers to appreciate the wonders of scientific discovery.
6.1. Napa Valley: A terrestrial journey at a slower pace
While TRAVELS.EDU.VN explores the cosmos and the speed of light, we also appreciate the beauty and tranquility of terrestrial destinations. Napa Valley, with its rolling vineyards, world-class wineries, and stunning landscapes, offers a unique contrast to the vastness of space. Here, time seems to slow down as you savor the flavors of local wines, indulge in gourmet cuisine, and immerse yourself in the natural beauty of the region.
6.2. Planning your Napa Valley Escape with TRAVELS.EDU.VN
TRAVELS.EDU.VN offers tailored travel services designed to make your Napa Valley experience unforgettable. Whether you’re seeking a romantic getaway, a culinary adventure, or a relaxing escape from the hustle and bustle of everyday life, we can create a customized itinerary to suit your preferences and budget.
6.2.1. Napa Valley Tour Packages
- Wine Tasting Tours: Explore Napa Valley’s renowned wineries with guided tours, private tastings, and exclusive access to some of the region’s most prestigious estates.
| Tour Name | Duration | Price (per person) | Inclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Signature Wine Tour | 6 hours | $299 | Transportation, tastings at 3 wineries, gourmet lunch |
| Exclusive Estate Experience | 8 hours | $499 | Private transportation, tastings at 4 premium wineries, cellar tour, dinner |
| Vineyard Hike & Wine Tour | 7 hours | $349 | Guided hike through vineyards, tastings at 2 wineries, picnic lunch |
- Culinary Experiences: Indulge in Napa Valley’s vibrant food scene with cooking classes, farm-to-table dining experiences, and gourmet food tours.
- Wellness Retreats: Rejuvenate your mind, body, and soul with spa treatments, yoga sessions, and mindfulness workshops amidst the serene landscapes of Napa Valley.
6.2.2. Accommodation Options
TRAVELS.EDU.VN partners with a curated selection of luxury hotels, boutique inns, and charming bed and breakfasts in Napa Valley to provide you with the perfect accommodation for your stay.
| Hotel Name | Star Rating | Average Price (per night) | Amenities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meadowood Napa Valley | 5 stars | $899 | Golf course, spa, Michelin-starred restaurant, private cottages |
| Auberge du Soleil | 5 stars | $799 | Infinity pool, spa, French cuisine, vineyard views |
| The Meritage Resort & Spa | 4 stars | $499 | Wine cave, bowling alley, multiple restaurants, spa |
6.2.3. Transportation Services
TRAVELS.EDU.VN offers a range of transportation options to ensure your comfort and convenience throughout your Napa Valley journey, including private car services, chauffeured limousines, and guided shuttle tours.
6.3. Connect with TRAVELS.EDU.VN for Your Napa Valley Adventure
Ready to experience the magic of Napa Valley? Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN today to start planning your dream escape. Our expert travel consultants will work with you to create a personalized itinerary that exceeds your expectations.
7. Conclusion: Appreciating the speed of light and the beauty of discovery
Understanding the speed of light allows us to appreciate the vastness of the universe, the intricacies of communication technology, and the challenges of space exploration. While faster-than-light travel remains in the realm of science fiction, the pursuit of knowledge and the exploration of new frontiers continue to drive scientific discovery. As we marvel at the speed of light, let us also cherish the beauty and tranquility of destinations like Napa Valley, where we can reconnect with nature and savor the simple pleasures of life.
8. FAQs About the Speed of Light
8.1. What is the exact speed of light?
The speed of light in a vacuum is exactly 299,792,458 meters per second (670,616,629 miles per hour).
8.2. Why is the speed of light important?
The speed of light is a fundamental constant in physics and plays a crucial role in our understanding of space, time, and the universe. It is also essential for various technologies, including communication, astronomy, and GPS.
8.3. Can anything travel faster than light?
According to our current understanding of physics, nothing with mass can travel faster than light.
8.4. Does light travel at the same speed in all mediums?
No, light travels at its maximum speed in a vacuum. When it passes through other mediums, such as air, water, or glass, it slows down.
8.5. How long does it take for light to travel from the Sun to Earth?
It takes approximately 8 minutes and 20 seconds for light to travel from the Sun to Earth.
8.6. What is a light-year?
A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year, which is approximately 9.461 × 10^12 kilometers (5.879 × 10^12 miles).
8.7. How is the speed of light measured?
The speed of light has been measured using various methods, including astronomical observations, laboratory experiments, and precise timing techniques.
8.8. What is the significance of the speed of light in Einstein’s theory of relativity?
In Einstein’s theory of relativity, the speed of light is the universal speed limit and is constant for all observers, regardless of their motion. This principle has profound implications for our understanding of space, time, and causality.
8.9. Could humans ever travel at the speed of light?
According to our current understanding of physics, it is impossible for humans to travel at the speed of light due to the infinite amount of energy required.
8.10. How can TRAVELS.EDU.VN help me plan my next vacation?
TRAVELS.EDU.VN offers expert travel services, personalized itineraries, and exclusive access to destinations around the world. Contact us today to start planning your dream vacation.
Don’t just dream about your perfect Napa Valley getaway – make it a reality with TRAVELS.EDU.VN. Contact us today at +1 (707) 257-5400 or visit our website at TRAVELS.EDU.VN to explore our exclusive tour packages and create a customized itinerary that exceeds your expectations. Let us take care of all the details so you can relax, unwind, and savor every moment of your unforgettable Napa Valley experience. Visit us at 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States. Let travels.edu.vn be your guide to extraordinary adventures.