The space shuttle’s velocity in space is approximately 17,500 miles per hour (28,000 kilometers per hour), allowing it to orbit Earth in roughly 90 minutes, as mentioned on TRAVELS.EDU.VN. This incredible speed is essential for maintaining orbit and conducting various missions. In this article, we will discuss the different aspects of how fast a space shuttle travels in space, delving into the mechanics, mission impact, and historical context.
1. Understanding Space Shuttle Speed
Space shuttles travel at tremendous speeds to maintain their orbit around Earth. So, how fast do they really go? Let’s break down the key aspects:
1.1. Orbital Velocity Explained
Orbital velocity is the speed needed to maintain a stable orbit around a celestial body. For the space shuttle, this speed is approximately 17,500 mph (28,000 km/h). According to NASA, this speed allows the shuttle to circle Earth in about 90 minutes.
1.2. Factors Affecting Speed
Several factors influence a space shuttle’s speed:
- Altitude: Lower orbits require higher speeds. As the shuttle’s altitude increases, its orbital velocity decreases.
- Earth’s Gravity: The stronger the gravitational pull, the faster the shuttle needs to move to avoid being pulled back to Earth.
- Propulsion Systems: The shuttle’s main engines and maneuvering thrusters are crucial for achieving and maintaining its orbital speed.
1.3. The Role of Propulsion
The space shuttle’s main engines are designed to generate enough thrust to escape Earth’s gravity and achieve orbital velocity. These engines, combined with solid rocket boosters (SRBs) during launch, provide the necessary power.
- Main Engines: The three Space Shuttle Main Engines (SSMEs) are responsible for accelerating the shuttle from 3,000 mph to over 17,000 mph in just six minutes.
- Solid Rocket Boosters: SRBs operate in conjunction with the main engines for the first two minutes of flight, providing additional thrust to escape Earth’s gravitational pull.
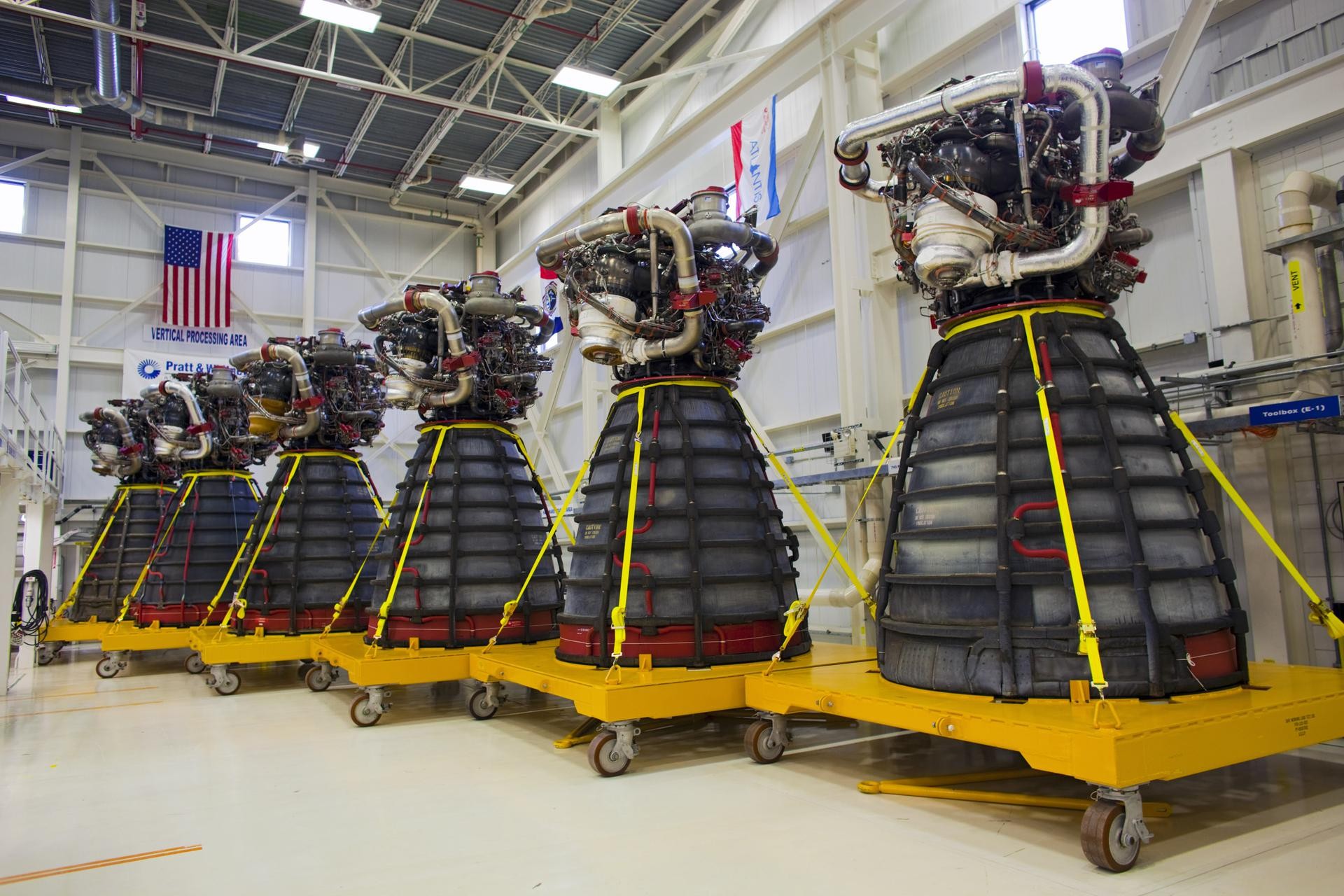 Space Shuttle Main Engines
Space Shuttle Main Engines
Image showing the six Pratt Whitney Rocketdyne space shuttle main engines inside the Engine Shop at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center.
2. Measuring Space Shuttle Speed
Measuring the speed of a space shuttle involves sophisticated technology and precise calculations.
2.1. Doppler Effect and Radar
The Doppler effect, which measures the change in frequency of waves (like radio waves) due to the relative motion between the source and the observer, is used. Radar systems on the ground send signals to the shuttle, and the reflected signals provide data on the shuttle’s speed.
2.2. Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs)
IMUs are devices that use accelerometers and gyroscopes to measure the shuttle’s acceleration and orientation. By integrating these measurements over time, the shuttle’s velocity can be determined.
2.3. Global Positioning System (GPS)
The Global Positioning System (GPS) allows for precise tracking of the shuttle’s location and velocity. Signals from multiple GPS satellites are used to determine the shuttle’s position in three-dimensional space and its speed. Endeavour, for example, was equipped with a three-string global positioning system to improve landing capabilities, allowing landings at any runway long enough to handle the shuttle.
2.4. Ground-Based Tracking
Ground-based tracking stations use telescopes and other instruments to observe the shuttle and calculate its speed based on its position over time.
3. Why is This Speed Necessary?
Maintaining a high speed is crucial for a space shuttle to stay in orbit and perform its missions effectively.
3.1. Counteracting Gravity
The primary reason for the high speed is to counteract Earth’s gravitational pull. Without sufficient speed, the shuttle would be pulled back to Earth.
3.2. Maintaining Orbit
To maintain a stable orbit, the shuttle must continuously travel at a speed that balances the gravitational force pulling it towards Earth and the centrifugal force pushing it away.
3.3. Mission Requirements
The shuttle’s speed is also vital for meeting mission requirements, such as:
- Rendezvous and Docking: High precision is needed to rendezvous and dock with the International Space Station (ISS) or other spacecraft.
- Deployment of Satellites: Satellites need to be deployed at specific speeds and trajectories.
- Scientific Experiments: Certain experiments require precise orbital parameters and speeds.
3.4. Time Efficiency
Traveling at 17,500 mph allows the shuttle to circle Earth in approximately 90 minutes. This speed is essential for conducting experiments and observations that require multiple passes over specific locations.
4. Historical Context of Space Shuttle Speed
The Space Shuttle program, which ran from 1981 to 2011, saw five operational orbiters: Columbia, Challenger, Discovery, Atlantis, and Endeavour. Each orbiter had unique missions and accomplishments.
4.1. Early Missions
The early missions of the Space Shuttle program focused on testing the shuttle’s capabilities and deploying satellites. The speed and precision of the shuttle were critical for these initial successes.
- STS-1 (Columbia): The first flight of the Space Shuttle program demonstrated the safe launch and return of the orbiter and crew.
- STS-6 (Challenger): The maiden voyage of Challenger saw the first spacewalk of the Space Shuttle program and the deployment of the first satellite in the Tracking and Data Relay System constellation.
4.2. Shuttle-Mir Program
The Shuttle-Mir program, which involved docking the space shuttle with the Russian space station Mir, required precise speed and maneuvering capabilities. Atlantis was the pioneer in these missions, flying the first seven missions to dock with Mir.
4.3. International Space Station (ISS)
The construction and maintenance of the International Space Station (ISS) heavily relied on the space shuttle’s speed and cargo capacity. The shuttle delivered vital components, including the U.S. laboratory module Destiny and the Joint Airlock Quest.
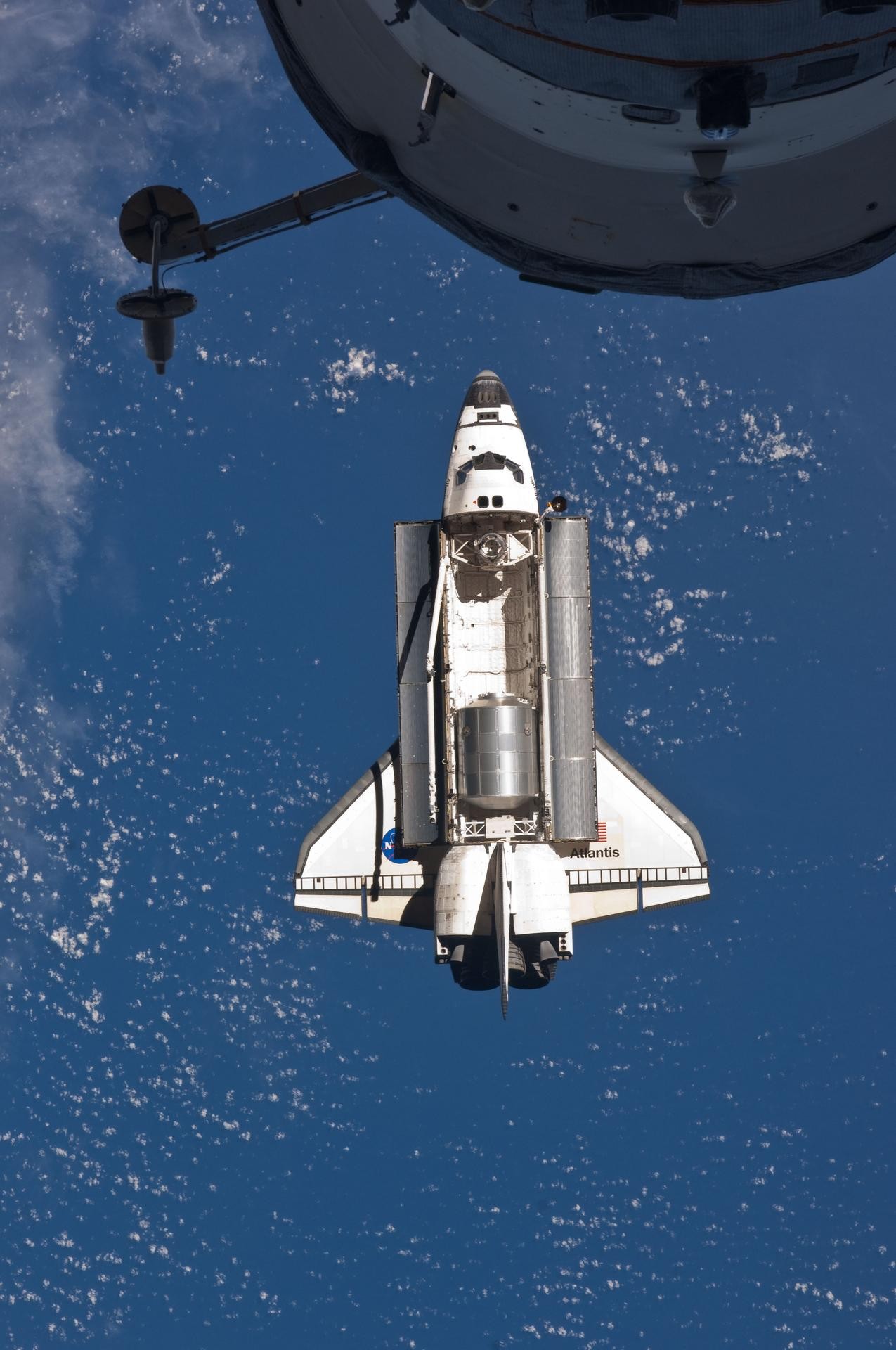 Space Shuttle Atlantis Docking with ISS
Space Shuttle Atlantis Docking with ISS
Image showing the space shuttle Atlantis prior to docking with the International Space Station.
4.4. Final Missions
The final missions of the Space Shuttle program focused on delivering supplies and equipment to the ISS. STS-135, the final mission of Atlantis, delivered over 8,000 pounds of supplies to sustain space station operations.
5. The Impact of Speed on Missions
The speed at which a space shuttle travels has a significant impact on its ability to conduct various missions.
5.1. Satellite Deployment
Deploying satellites into specific orbits requires precise speed control. The shuttle must reach the correct altitude and velocity to ensure the satellite is placed in the intended orbit.
5.2. Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope, carried into space by Discovery during mission STS-31, benefited immensely from the shuttle’s speed and stability. The shuttle’s ability to reach a specific orbit allowed for the accurate deployment of the telescope.
5.3. Scientific Research
Many scientific experiments conducted on the space shuttle required precise orbital parameters. The shuttle’s speed and stability were essential for obtaining accurate data.
5.4. Rescue Missions
In some cases, the space shuttle’s speed was crucial for rescue missions. The ability to quickly reach a specific location in space could be life-saving.
6. Challenges of Maintaining Such High Speed
Maintaining a speed of 17,500 mph in space is not without its challenges.
6.1. Fuel Consumption
Achieving and maintaining such high speeds requires a significant amount of fuel. The space shuttle’s main engines consume liquid propellant at a rate that would drain an average family swimming pool in under 25 seconds.
6.2. Thermal Protection
The extreme speeds generate intense heat due to atmospheric friction during launch and re-entry. The space shuttle’s thermal protection system, including tiles and blankets, is crucial for preventing the shuttle from overheating.
6.3. Orbital Debris
Traveling at high speeds increases the risk of collision with orbital debris. Even small pieces of debris can cause significant damage to the shuttle.
6.4. Physiological Effects on Astronauts
The high speeds and accelerations experienced during launch and re-entry can have significant physiological effects on astronauts, including disorientation and g-force-induced stress.
7. Future of Space Travel and Speed
The Space Shuttle program may be over, but the need for high-speed space travel continues.
7.1. NASA’s Artemis Program
NASA’s Artemis program aims to return humans to the Moon and eventually send them to Mars. These missions will require even faster and more efficient spacecraft.
7.2. Commercial Space Travel
Commercial space companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin are developing new spacecraft capable of high-speed travel to low Earth orbit and beyond.
7.3. Hypersonic Flight
Research into hypersonic flight, which involves traveling at speeds of Mach 5 or higher, could revolutionize air and space travel, enabling faster access to space and quicker travel times on Earth.
7.4. Advanced Propulsion Systems
New propulsion technologies, such as ion drives and nuclear propulsion, could enable spacecraft to reach even higher speeds and travel to distant destinations in our solar system.
8. The Science Behind the Speed
The physics of space travel is complex, involving concepts like orbital mechanics, thermodynamics, and materials science.
8.1. Newton’s Laws of Motion
Newton’s laws of motion are fundamental to understanding how spacecraft move in space. These laws describe how forces affect the motion of objects, including spacecraft.
8.2. Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics plays a crucial role in the design of spacecraft, particularly in managing heat generated by engines and atmospheric friction.
8.3. Materials Science
The materials used in spacecraft must be able to withstand extreme temperatures, pressures, and radiation. Advances in materials science are essential for developing faster and more durable spacecraft.
9. Fun Facts About Space Shuttle Speed
- At 17,500 mph, a space shuttle could travel from New York to Los Angeles in about 10 minutes.
- The space shuttle’s speed is about 25 times the speed of sound.
- Astronauts on the space shuttle experience approximately 16 sunrises and sunsets each day due to their high speed.
- The space shuttle travels faster than a speeding bullet, which typically moves at around 1,700 mph.
10. Planning Your Own Space-Themed Adventure with TRAVELS.EDU.VN
While you might not be able to experience the thrill of space travel just yet, you can still embark on a space-themed adventure with TRAVELS.EDU.VN. Napa Valley, known for its serene landscapes and luxurious experiences, offers a unique blend of relaxation and exploration that mirrors the wonders of space exploration in its own way.
Imagine yourself soaring through the vineyards in a hot air balloon, enjoying panoramic views that stretch as far as the eye can see. The feeling of floating above the world, even if just for a little while, can bring you closer to understanding the freedom and perspective astronauts experience in space.
10.1. Hot Air Balloon Rides Over Napa Valley
Experience the breathtaking views of Napa Valley from above with a hot air balloon ride. As you gently float over the vineyards, you’ll feel a sense of freedom and wonder, much like astronauts in space.
Image depicting hot air ballooning over the scenic Napa Valley.
10.2. Observatory Visits
Take a trip to a local observatory and explore the mysteries of the universe. Learn about stars, planets, and galaxies, and get a glimpse of the cosmos that astronauts travel through.
10.3. Science Museums
Visit science museums to delve into the science behind space travel and learn about the technology that makes it possible. Discover the principles of propulsion, orbital mechanics, and life support systems.
10.4. Space-Themed Events
Check out space-themed events and festivals in your area. These events often feature exhibits, demonstrations, and talks by experts in the field of space exploration.
10.5. Book Your Napa Valley Tour with TRAVELS.EDU.VN
Ready to plan your Napa Valley escape? TRAVELS.EDU.VN offers tailored tour packages that combine luxury, adventure, and unforgettable experiences. Contact us today to create your perfect getaway:
- Address: 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (707) 257-5400
- Website: TRAVELS.EDU.VN
FAQ: Space Shuttle Speed
1. How fast did the space shuttle travel in space?
The space shuttle traveled at approximately 17,500 miles per hour (28,000 kilometers per hour) in space.
2. Why did the space shuttle need to travel so fast?
The high speed was necessary to counteract Earth’s gravitational pull and maintain a stable orbit.
3. How was the speed of the space shuttle measured?
The speed was measured using the Doppler effect, radar, inertial measurement units (IMUs), and the Global Positioning System (GPS).
4. What factors affected the space shuttle’s speed?
Factors affecting the speed included altitude, Earth’s gravity, and the shuttle’s propulsion systems.
5. How long did it take the space shuttle to orbit Earth?
At 17,500 mph, the space shuttle could orbit Earth in approximately 90 minutes.
6. What challenges did the space shuttle face while traveling at high speeds?
Challenges included fuel consumption, thermal protection, orbital debris, and the physiological effects on astronauts.
7. How did the space shuttle’s speed impact its missions?
The speed was crucial for satellite deployment, rendezvous and docking, scientific research, and rescue missions.
8. What is NASA’s next step after the Space Shuttle program?
NASA’s Artemis program aims to return humans to the Moon and eventually send them to Mars.
9. How do commercial space companies like SpaceX contribute to space travel?
Commercial companies are developing new spacecraft capable of high-speed travel to low Earth orbit and beyond.
10. What are some fun facts about the space shuttle’s speed?
At 17,500 mph, a space shuttle could travel from New York to Los Angeles in about 10 minutes, and astronauts experience approximately 16 sunrises and sunsets each day.
Conclusion
The speed at which the space shuttle travels in space is a testament to human ingenuity and technological advancement. This incredible speed, approximately 17,500 mph, is essential for maintaining orbit, conducting missions, and exploring the vastness of space. Whether you’re an avid space enthusiast or simply curious about the wonders of the universe, understanding the science and history behind space shuttle speed offers a fascinating glimpse into the world of space travel.
And while the cosmos may seem distant, TRAVELS.EDU.VN brings the spirit of exploration closer to home with unique travel experiences in Napa Valley. From hot air balloon rides to observatory visits, there are countless ways to embrace the sense of wonder and discovery that defines space exploration.
Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN today and let us help you plan an unforgettable adventure:
- Address: 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (707) 257-5400
- Website: travels.edu.vn