Setting up a GL.iNet travel router involves powering on, connecting to the router’s network, and accessing the web Admin Panel to configure your settings, which TRAVELS.EDU.VN can guide you through. With a travel router, you can secure your connections on public Wi-Fi and create a private network wherever you go. Let’s dive into the setup process so you can safeguard your digital travels, featuring password setup and language preferences.
1. Getting Started: Powering On Your GL.iNet Travel Router
To begin, plug the Micro USB power cable into the power port of your GL.iNet travel router. It’s crucial to use a standard 5V/2A power adapter to prevent any malfunctions. Ensuring the correct power supply will help maintain the longevity and optimal performance of your device. TRAVELS.EDU.VN recommends verifying the power adapter specifications to avoid any power-related issues during your travels.
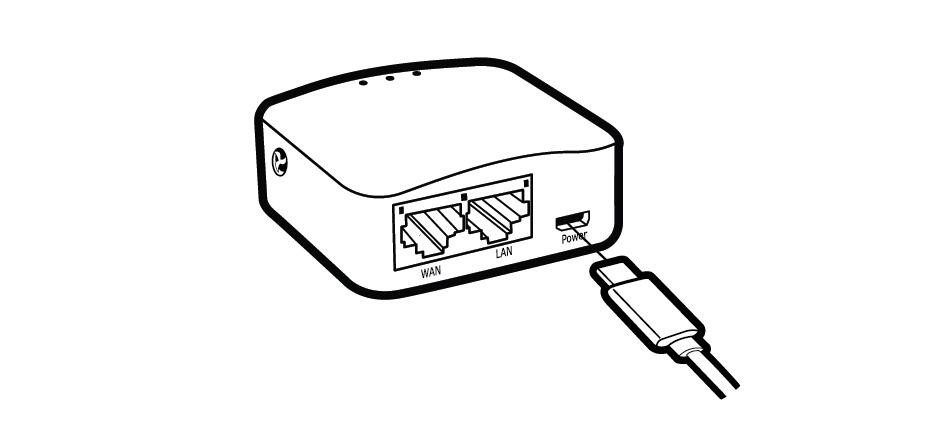 Powering the GL.iNet router using a micro USB cable
Powering the GL.iNet router using a micro USB cable
2. Connecting to Your GL.iNet Travel Router
Once powered on, you can connect to the router either via Ethernet cable or Wi-Fi. Keep in mind that initially, this connection only links your devices to the local area network (LAN) of the router. Accessing the Internet requires completing the setup procedures outlined below and configuring an Internet connection. TRAVELS.EDU.VN emphasizes this step to clarify the difference between LAN and Internet connectivity.
2.1 Connecting via LAN
For a wired connection, use an Ethernet cable to connect your device directly to the LAN port of the router. This method provides a stable and secure connection for the initial setup.
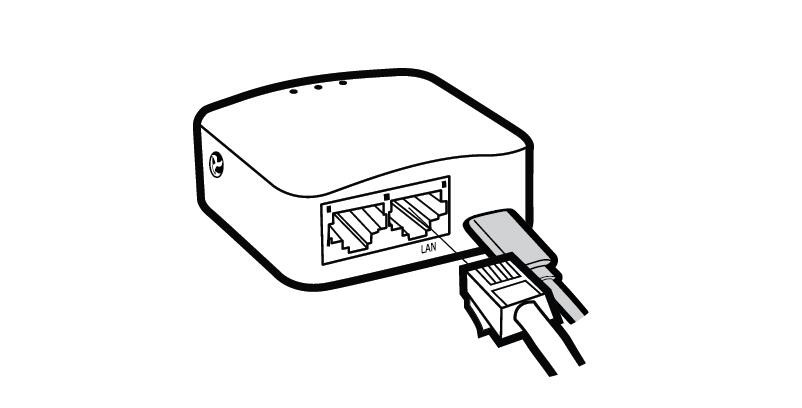 Connecting to the GL.iNet router via an Ethernet cable
Connecting to the GL.iNet router via an Ethernet cable
Note: Some models like GL-AR300M-Lite have only one Ethernet port which functions as WAN by default. In such cases, initial setup must be done via Wi-Fi.
2.2 Connecting via Wi-Fi
Alternatively, you can connect wirelessly by searching for the router’s SSID on your device and entering the default password, which is “goodlife.” The SSID is typically printed on the bottom label of the router and follows formats like GL-MT300N-XXX or GL-AR150-XXX. This wireless setup offers flexibility and convenience, especially when a wired connection isn’t feasible.
3. Accessing the Web Admin Panel
After connecting to the router, open a web browser such as Chrome or Firefox and navigate to http://192.168.8.1. This will direct you to the initial setup of the web Admin Panel, where you can configure various settings for your travel router.
3.1 Language Settings
The first step in the Admin Panel is to select your preferred display language. GL.iNet routers support multiple languages including English, Chinese (Simplified and Traditional), German, French, Spanish, Italian, Japanese, Korean, and Russian. Choosing your language ensures a comfortable and understandable setup process.
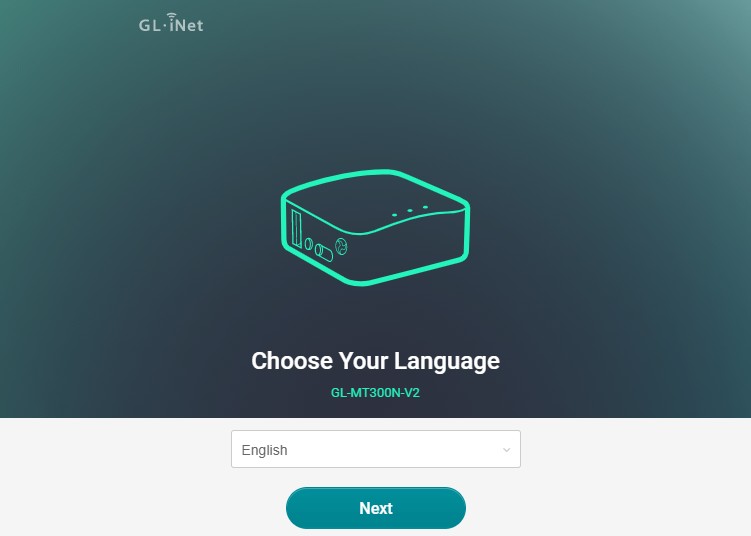 Selecting a language for the GL.iNet router's admin panel
Selecting a language for the GL.iNet router's admin panel
Note: If your browser redirects to LuCI, use http://192.168.8.1/index instead.
3.2 Setting Up the Admin Password
For security reasons, there is no default password for the Admin Panel. You must create your own password, which should be at least 5 characters long. Click “Submit” to proceed after entering your desired password. TRAVELS.EDU.VN reminds users that this password protects the router’s settings and embedded Linux system, separate from your Wi-Fi password.
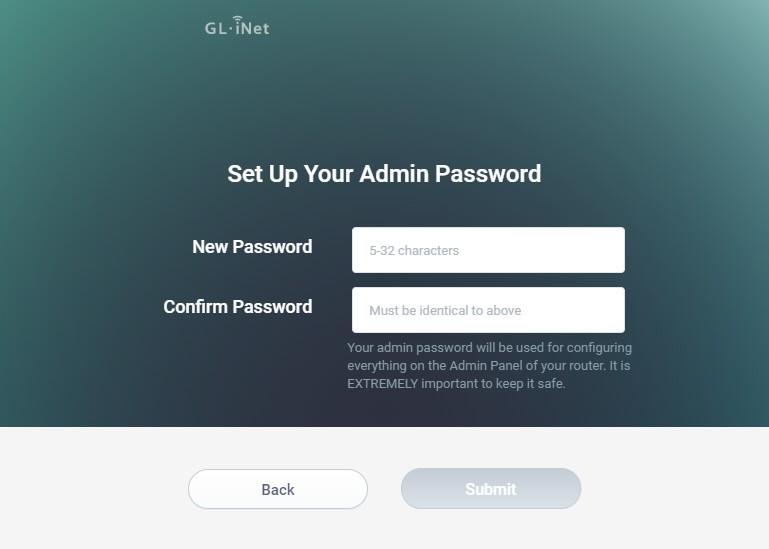 Setting up an admin password for the GL.iNet router
Setting up an admin password for the GL.iNet router
3.3 Exploring the Admin Panel
Once the initial setup is complete, you will access the web Admin Panel, which allows you to monitor the status and manage the settings of your router. This dashboard provides an overview of your network and allows you to customize various features to suit your needs.
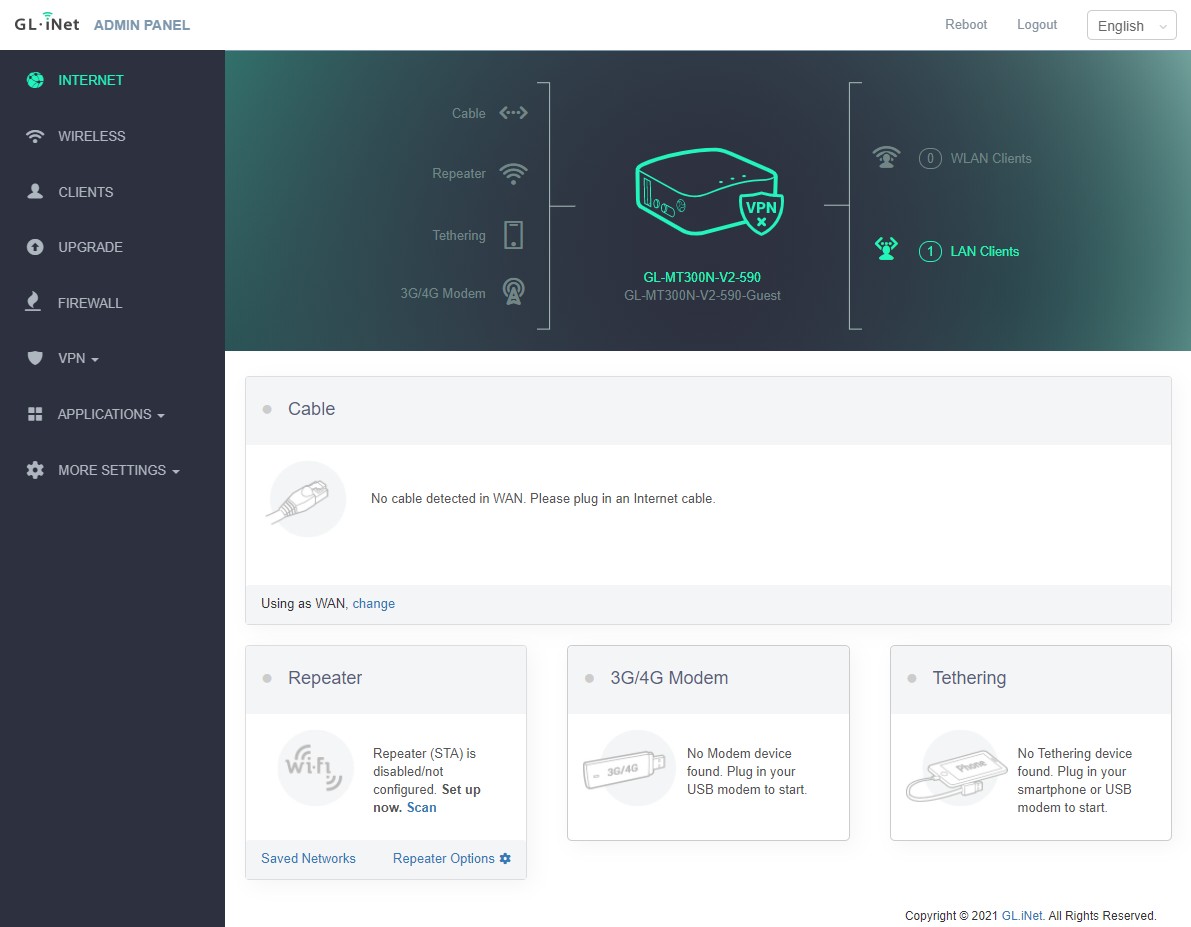 The GL.iNet router's admin panel dashboard
The GL.iNet router's admin panel dashboard
4. Diving Deeper: Advanced GL.iNet Travel Router Configuration
Once you’ve completed the basic setup of your GL.iNet travel router, you can explore advanced configuration options. These settings enable you to fine-tune your router to meet your specific needs, whether you’re focused on security, performance, or customization. TRAVELS.EDU.VN encourages users to explore these advanced features to maximize the benefits of their travel router.
4.1 Setting Up Internet Connection
After setting up the basic configurations, connecting to the internet is crucial. Here’s how to set up different types of internet connections.
4.1.1 Cable Connection
- Access the Internet Settings:
- Navigate to the web Admin Panel of your GL.iNet router.
- Find and click on the “Internet” or “Network” section.
- Select Cable Connection:
- Choose the “Cable” option from the list of available connection types (such as Wi-Fi, Tethering, etc.).
- Configure Interface:
- The interface is usually pre-configured to DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), which automatically obtains an IP address from your ISP (Internet Service Provider).
- If your ISP requires a static IP address, select “Static IP” and enter the necessary IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS server information provided by your ISP.
- Apply Changes:
- Click the “Apply” button to save your settings.
- The router will attempt to establish an internet connection using the configured cable settings.
- Verify Connection:
- Check the status in the Admin Panel to ensure the internet connection is successful.
- You should see an IP address assigned and a “Connected” status.
4.1.2 Wi-Fi Connection
- Access the Internet Settings:
- Open the web Admin Panel of your GL.iNet router.
- Go to the “Internet” or “Network” section.
- Select Wi-Fi Connection:
- Choose the “Wi-Fi” option.
- The router will scan for available Wi-Fi networks.
- Choose Network:
- Select the Wi-Fi network you want to connect to from the list.
- Enter the password for the Wi-Fi network if prompted.
- Apply Changes:
- Click the “Apply” button.
- The router will attempt to connect to the selected Wi-Fi network.
- Verify Connection:
- Check the status in the Admin Panel.
- You should see a “Connected” status and the IP address assigned by the Wi-Fi network.
4.1.3 Tethering Connection
- Connect Your Device:
- Connect your smartphone or USB modem to the GL.iNet router using a USB cable.
- Access the Internet Settings:
- Open the web Admin Panel of your GL.iNet router.
- Navigate to the “Internet” or “Network” section.
- Select Tethering Connection:
- Choose the “Tethering” or “USB Modem” option.
- The router should automatically detect the connected device.
- Configure Settings (if needed):
- Some modems may require additional configuration, such as setting the APN (Access Point Name).
- Consult your mobile carrier for the correct APN settings.
- Apply Changes:
- Click the “Apply” button.
- The router will attempt to establish an internet connection via the tethered device.
- Verify Connection:
- Check the status in the Admin Panel.
- You should see a “Connected” status and the IP address assigned by the tethered device.
4.2 Setting Up VPN (Virtual Private Network)
A VPN encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a server in a location of your choice, providing enhanced security and privacy. Here’s how to set it up:
- Choose a VPN Provider:
- Select a reputable VPN service provider. Some popular options include ExpressVPN, NordVPN, and Surfshark.
- Sign up for an account and obtain the necessary VPN configuration files (usually OpenVPN configuration files).
- Access the VPN Settings:
- In the GL.iNet router’s Admin Panel, navigate to the “VPN” section.
- Configure VPN Client:
- Choose the VPN protocol you want to use (e.g., OpenVPN, WireGuard).
- Upload the VPN configuration file provided by your VPN provider.
- Enter your VPN username and password if required.
- Apply Changes:
- Click the “Apply” button to save your settings.
- The router will attempt to connect to the VPN server.
- Verify Connection:
- Check the status in the VPN section to ensure the VPN connection is successful.
- You can also verify your IP address to confirm that it matches the VPN server location.
4.3 Setting Up a Guest Network
A guest network allows visitors to access the internet without giving them access to your primary network and devices. Here’s how to set it up:
- Access the Guest Network Settings:
- In the GL.iNet router’s Admin Panel, find the “Guest Network” or “Wi-Fi” section.
- Enable Guest Network:
- Turn on the guest network feature.
- Configure Settings:
- Set a unique SSID (network name) for the guest network.
- Choose a password for the guest network.
- Set a limit on the number of connected devices if desired.
- Apply Changes:
- Click the “Apply” button to save your settings.
- The guest network will be created and broadcasted.
- Provide Access:
- Provide the guest network SSID and password to your visitors.
4.4 Setting Up Firewall
Configuring firewall settings on your GL.iNet travel router is essential for protecting your network from unauthorized access and potential threats. Firewalls act as a barrier between your network and the internet, monitoring incoming and outgoing traffic and blocking any suspicious activity.
- Access the Firewall Settings:
- In the GL.iNet router’s Admin Panel, navigate to the “Firewall” or “Security” section.
- Enable the Firewall:
- Ensure that the firewall is enabled. Most GL.iNet routers have the firewall enabled by default, but it’s always a good idea to double-check.
- Configure Firewall Rules:
- Default Policies:
- Set default policies for incoming and outgoing traffic. A common practice is to allow all outgoing traffic while blocking all incoming traffic by default. This helps prevent unauthorized access to your network.
- You can customize these policies based on your specific needs.
- Port Forwarding:
- Configure port forwarding rules to allow specific types of traffic to pass through the firewall.
- For example, if you’re running a web server on your network, you may need to forward port 80 (HTTP) and port 443 (HTTPS) to the server’s IP address.
- Traffic Rules:
- Set up traffic rules to allow or block traffic based on source and destination IP addresses, ports, and protocols.
- This can be useful for blocking access to known malicious websites or restricting access to specific services.
- DMZ (Demilitarized Zone):
- Create a DMZ to expose a specific device on your network to the internet. This should be used with caution, as it can increase the risk of security vulnerabilities.
- Apply Changes:
- Click the “Apply” button to save your settings.
- The firewall will be configured with the new rules.
4.5 Setting Up Dynamic DNS (DDNS)
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) allows you to access your home network remotely, even if your ISP assigns you a dynamic IP address that changes periodically. Here’s how to set it up:
- Choose a DDNS Provider:
- Select a DDNS service provider. Some popular options include DynDNS, No-IP, and DuckDNS.
- Sign up for an account and obtain the necessary DDNS hostname and credentials.
- Access the DDNS Settings:
- In the GL.iNet router’s Admin Panel, navigate to the “DDNS” or “Dynamic DNS” section.
- Configure DDNS Client:
- Choose your DDNS provider from the list.
- Enter your DDNS hostname, username, and password.
- Apply Changes:
- Click the “Apply” button to save your settings.
- The router will attempt to register with the DDNS service.
- Verify Connection:
- Check the status in the DDNS section to ensure the DDNS registration is successful.
- You can also test the DDNS hostname by accessing it from a remote location.
5. Maximizing Your GL.iNet Travel Router: Tips and Tricks
To fully leverage your GL.iNet travel router, consider these tips and tricks that TRAVELS.EDU.VN has compiled to enhance your experience. These suggestions cover security practices, performance optimization, and general usage advice to ensure you get the most out of your device.
5.1 Enhancing Security
- Regular Firmware Updates: Keep your router’s firmware updated to protect against the latest security threats.
- Strong Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for both the Admin Panel and your Wi-Fi networks.
- VPN Usage: Always use a VPN on public Wi-Fi to encrypt your data and protect your privacy.
- Firewall Configuration: Configure the firewall to block unauthorized access and monitor network traffic.
5.2 Optimizing Performance
- Channel Selection: Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app to find the least congested channel for your Wi-Fi network.
- QoS Settings: Configure Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritize traffic for important applications.
- Regular Reboots: Reboot your router periodically to clear its cache and improve performance.
- Antenna Placement: Position the router’s antennas for optimal coverage and signal strength.
5.3 General Usage
- Battery Management: If your router has a battery, manage its usage to prolong its lifespan.
- Travel Case: Use a protective travel case to prevent damage during transit.
- Power Adapter: Carry a compatible power adapter and consider a portable power bank for on-the-go charging.
- Documentation: Keep the router’s documentation handy for quick reference and troubleshooting.
6. Troubleshooting Common GL.iNet Travel Router Issues
Even with a straightforward setup, you might encounter issues. TRAVELS.EDU.VN provides troubleshooting steps for common problems to help you resolve them quickly. These solutions address connectivity issues, password problems, and other typical challenges users face.
6.1 Connectivity Issues
-
Problem: Cannot connect to the router’s Wi-Fi.
- Solution:
- Ensure the router is powered on.
- Verify the Wi-Fi password is correct.
- Check if the device is within the router’s range.
- Reboot the router and try again.
- Solution:
-
Problem: No internet access after connecting to the router.
- Solution:
- Verify the internet connection to the router is active.
- Check the router’s internet settings (e.g., DHCP, Static IP).
- Ensure the router is connected to the correct Wi-Fi network or Ethernet cable.
- Reboot the router and try again.
- Solution:
6.2 Password Problems
-
Problem: Forgot the Admin Panel password.
- Solution:
- Reset the router to its factory settings by pressing and holding the reset button for 10 seconds.
- Reconnect to the router and set up a new Admin Panel password.
- Solution:
-
Problem: Forgot the Wi-Fi password.
- Solution:
- Log in to the Admin Panel using the Admin Panel password.
- Navigate to the Wi-Fi settings and change the Wi-Fi password.
- Solution:
6.3 Firmware Update Issues
-
Problem: Firmware update fails.
- Solution:
- Ensure the router has a stable internet connection.
- Download the firmware file from the official GL.iNet website.
- Upload the firmware file to the router’s Admin Panel.
- Do not interrupt the update process.
- If the update fails, try again or contact GL.iNet support.
- Solution:
6.4 VPN Connection Problems
-
Problem: Cannot connect to the VPN.
- Solution:
- Verify the VPN credentials (username, password) are correct.
- Ensure the VPN configuration file is valid.
- Check the internet connection is stable.
- Try a different VPN server.
- Contact the VPN provider for support.
- Solution:
6.5 Other Issues
-
Problem: Router is overheating.
- Solution:
- Ensure the router is placed in a well-ventilated area.
- Avoid placing the router in direct sunlight or near heat sources.
- Clean the router’s vents to remove any dust or debris.
- If the issue persists, contact GL.iNet support.
- Solution:
-
Problem: Router is not responding.
- Solution:
- Try rebooting the router.
- If the router is still not responding, reset it to its factory settings.
- Contact GL.iNet support for further assistance.
- Solution:
7. Real-World Applications of GL.iNet Travel Routers
Understanding the real-world applications of GL.iNet travel routers can highlight their versatility and usefulness in various scenarios. These devices are not just for travelers; they serve multiple purposes for different users. TRAVELS.EDU.VN explores several practical uses to illustrate the value of these routers.
7.1 Securing Public Wi-Fi
One of the primary applications is securing your connection on public Wi-Fi networks. Whether you’re in a coffee shop, airport, or hotel, public Wi-Fi is often unsecured, making your data vulnerable to hackers. A GL.iNet travel router creates a private, encrypted network, protecting your personal information from potential threats.
7.2 Creating a Mobile Office
For remote workers, a travel router can create a secure and reliable mobile office. You can connect multiple devices to the router and access the internet through a single, secure connection. This is particularly useful when traveling to different locations where the security of the local network is uncertain.
7.3 Enhancing Privacy
Using a VPN in conjunction with a travel router adds an extra layer of privacy. By routing your internet traffic through a VPN server, you can hide your IP address and encrypt your data, preventing websites and third parties from tracking your online activity.
7.4 Bypassing Geo-Restrictions
A travel router can also be used to bypass geo-restrictions and access content that is not available in your current location. By connecting to a VPN server in a different country, you can access streaming services, websites, and other online content as if you were physically located in that country.
7.5 Extending Network Coverage
In situations where the existing Wi-Fi signal is weak, a travel router can be used as a repeater to extend the network coverage. This is particularly useful in large homes, offices, or hotels where the Wi-Fi signal may not reach all areas.
7.6 Creating a Local Network
Travel routers can create a local network for sharing files and resources between devices. This is useful for families or groups traveling together who want to share photos, videos, and other files without relying on the internet.
7.7 Gaming on the Go
Gamers can use travel routers to create a secure and low-latency connection for online gaming. By connecting to a VPN server that is close to the game server, you can reduce lag and improve your gaming experience.
7.8 Setting up Temporary Networks
Travel routers are ideal for setting up temporary networks in locations where internet access is needed for a short period, such as at events, conferences, or pop-up shops.
8. Exploring Alternatives to GL.iNet Travel Routers
While GL.iNet travel routers are popular for their compact size and versatility, several alternatives offer similar functionalities. Understanding these options can help you choose the best device for your specific needs. TRAVELS.EDU.VN reviews some notable alternatives to GL.iNet travel routers, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
8.1 TP-Link Travel Routers
TP-Link offers a range of travel routers known for their ease of use and reliable performance. These routers often come with features like multiple operation modes, allowing them to function as a router, repeater, bridge, or access point.
Pros:
- Easy to set up and use
- Reliable performance
- Multiple operation modes
Cons:
- Fewer advanced features compared to GL.iNet
- Less customization options
8.2 Netgear Nighthawk M1 Mobile Router
The Netgear Nighthawk M1 is a mobile router that provides high-speed internet access via a cellular connection. It supports multiple devices and offers advanced features like parental controls and media streaming.
Pros:
- High-speed internet access
- Supports multiple devices
- Advanced features
Cons:
- Requires a cellular data plan
- More expensive than GL.iNet routers
8.3 HooToo Wireless Travel Router
HooToo travel routers are known for their compact size and affordability. They offer basic features like file sharing, media streaming, and power bank functionality.
Pros:
- Compact and portable
- Affordable
- Built-in power bank
Cons:
- Limited features
- Slower performance compared to GL.iNet
8.4 RAVPower FileHub
The RAVPower FileHub is a versatile device that functions as a wireless travel router, portable NAS, and power bank. It allows you to share files, stream media, and charge your devices on the go.
Pros:
- Multiple functionalities
- Portable
- File sharing capabilities
Cons:
- Slower performance
- Less secure than dedicated routers
8.5 Using a Smartphone as a Hotspot
One alternative to a travel router is using your smartphone as a mobile hotspot. Most smartphones have a built-in hotspot feature that allows you to share your cellular data connection with other devices.
Pros:
- Convenient
- No additional device needed
Cons:
- Drains battery quickly
- May incur additional data charges
- Less secure than a dedicated router
Comparison Table
| Feature | GL.iNet Travel Router | TP-Link Travel Router | Netgear Nighthawk M1 | HooToo Wireless Router | RAVPower FileHub | Smartphone Hotspot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | Moderate | Affordable | Expensive | Affordable | Affordable | Free (with plan) |
| Portability | Excellent | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Ease of Use | Moderate | Excellent | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Excellent |
| Security | High | Moderate | High | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Performance | Good | Good | Excellent | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Battery Life | Varies | N/A | Good | Good | Good | Poor |
| Advanced Features | High | Moderate | High | Low | Low | Low |
9. Understanding the Technical Specifications of GL.iNet Travel Routers
Delving into the technical specifications of GL.iNet travel routers helps you understand their capabilities and limitations. This knowledge is crucial for selecting the right model for your specific needs. TRAVELS.EDU.VN breaks down the key technical aspects of these devices.
9.1 Processor and Memory
The processor and memory of a travel router determine its ability to handle network traffic and run various applications. Higher processing power and more memory generally result in better performance.
- Processor: GL.iNet routers typically use MediaTek or Qualcomm processors, ranging from single-core to dual-core.
- Memory: RAM usually ranges from 64MB to 128MB, while flash storage varies from 16MB to 128MB.
9.2 Wireless Standards
The wireless standards supported by the router determine its compatibility with different devices and networks.
- 802.11ac: The latest standard, offering faster speeds and better range.
- 802.11n: A widely used standard, providing good performance for most devices.
- 802.11g/b: Older standards, still supported for compatibility with older devices.
9.3 Frequency Bands
GL.iNet routers typically support both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency bands.
- 2.4GHz: Offers longer range but is more prone to interference.
- 5GHz: Provides faster speeds but has a shorter range.
9.4 Ports and Interfaces
The ports and interfaces available on the router determine its connectivity options.
- Ethernet Ports: Allow for wired connections to devices or networks.
- USB Ports: Used for connecting USB modems, storage devices, or charging other devices.
- MicroSD Card Slot: Allows for expanding storage capacity.
9.5 Security Protocols
The security protocols supported by the router are crucial for protecting your network and data.
- WPA3: The latest and most secure protocol.
- WPA2: A widely used and secure protocol.
- WPA/WEP: Older protocols, less secure and not recommended.
9.6 VPN Support
GL.iNet routers are known for their extensive VPN support.
- OpenVPN: A popular and secure VPN protocol.
- WireGuard: A modern and fast VPN protocol.
- IPsec: A secure VPN protocol often used in corporate environments.
9.7 Power Consumption
The power consumption of a travel router is an important consideration, especially when using it on the go.
- Power Input: Typically 5V/2A via Micro USB.
- Battery: Some models have a built-in battery for portable use.
10. The Future of Travel Routers: Trends and Innovations
The travel router market is continuously evolving, with new trends and innovations shaping the future of these devices. Understanding these developments can help you make informed decisions when purchasing or using a travel router. TRAVELS.EDU.VN examines the emerging trends and innovations in the travel router industry.
10.1 5G Connectivity
One of the most significant trends is the integration of 5G connectivity into travel routers. 5G offers much faster speeds and lower latency compared to 4G, enabling seamless streaming, gaming, and remote work.
10.2 Enhanced Security Features
Security remains a top priority, with manufacturers adding advanced security features to travel routers. These include:
- Hardware-based encryption: Provides faster and more secure encryption.
- AI-powered threat detection: Detects and blocks malicious traffic in real-time.
- Secure boot: Ensures that only authorized firmware can be loaded on the router.
10.3 Improved User Interface
Manufacturers are focusing on creating more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces for travel routers. This includes:
- Touchscreen displays: Allow for easy navigation and configuration.
- Mobile apps: Enable remote management and monitoring of the router.
- Voice control: Allows you to control the router using voice commands.
10.4 Integration with IoT Devices
Travel routers are increasingly being integrated with IoT (Internet of Things) devices, allowing you to control and manage your smart home devices while on the go.
10.5 Portable Power Solutions
To enhance portability, manufacturers are developing travel routers with improved battery life and more efficient power management. This includes:
- Larger capacity batteries: Provide longer usage times.
- Solar charging: Allows you to charge the router using solar power.
- USB-C charging: Enables faster and more convenient charging.
10.6 Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
SDN is an emerging technology that allows for more flexible and dynamic network management. Travel routers with SDN capabilities can automatically optimize network performance based on real-time conditions.
10.7 Edge Computing
Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving performance. Travel routers with edge computing capabilities can perform tasks like data filtering and analysis locally, without relying on the cloud.
Ready to elevate your travel experience? Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN today at 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States, via Whatsapp at +1 (707) 257-5400, or visit our website at TRAVELS.EDU.VN to explore our exclusive Napa Valley tour packages. Let us handle the details so you can focus on creating unforgettable memories.
FAQ: Setting Up and Using a GL.iNet Travel Router
Here are some frequently asked questions about setting up and using a GL.iNet travel router, compiled by travels.edu.vn, designed to offer additional clarity and support for our readers.
1. What is a GL.iNet travel router?
A GL.iNet travel router is a compact, portable device that creates a secure Wi-Fi network from any internet connection, such as public Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or a USB modem.
2. Why should I use a travel router?
A travel router enhances your online security, protects your data on public Wi-Fi, and allows multiple devices to connect through a single, secure connection.
3. How do I set up a GL.iNet travel router for the first time?
Plug in the router, connect to its Wi-Fi network, access the web Admin Panel via a browser, set a password, and configure your internet connection.
4. Can I use a VPN with a GL.iNet travel router?
Yes, GL.iNet routers support various VPN protocols like OpenVPN and WireGuard, allowing you to encrypt your internet traffic.
5. How do I change the Wi-Fi password on my GL.iNet router?
Log into the web Admin Panel, navigate to the Wi-Fi settings, and update the password.
6. What should I do if I forget my Admin Panel password?
Reset the router to its factory settings by holding the reset button for 10 seconds, then set up a new password.
7. How do I update the firmware on my GL.iNet router?
Download the latest firmware from the official GL.iNet website, log into the Admin Panel, and upload the firmware file.
8. Can I use a GL.iNet travel router to extend my existing Wi-Fi network?
Yes, GL.iNet routers can operate as a repeater to extend the range of your existing Wi-Fi network.
9. How do I set up a guest network on my GL.iNet travel router?
Log into the Admin Panel, go to the Guest Network settings, enable the guest network, set a password, and save the changes.
10. What types of internet connections are supported by GL.iNet travel routers?
GL.iNet routers support Ethernet, Wi-Fi, USB modem (tethering), and some models support cellular connections directly.