Electromagnetic waves travel through various mediums, including a vacuum, because they are self-propagating disturbances in electric and magnetic fields, and at TRAVELS.EDU.VN, we believe understanding this phenomenon opens doors to appreciating the technology that makes modern travel possible. This guide will delve into the fascinating world of electromagnetic radiation, exploring how it travels and its implications for various applications, especially within the realm of travel and communication technologies.
1. What Are Electromagnetic Waves?
Electromagnetic (EM) waves are disturbances that propagate through space by the interaction of electric and magnetic fields. Unlike mechanical waves, like sound waves, which require a medium such as air or water to travel, electromagnetic waves can travel through the vacuum of space. This is because they are self-propagating; a changing electric field generates a magnetic field, and vice versa, allowing the wave to sustain itself without needing any external medium. According to research from Stanford University’s Ginzton Lab, electromagnetic fields are fundamental to understanding wave behavior in both free space and various media.
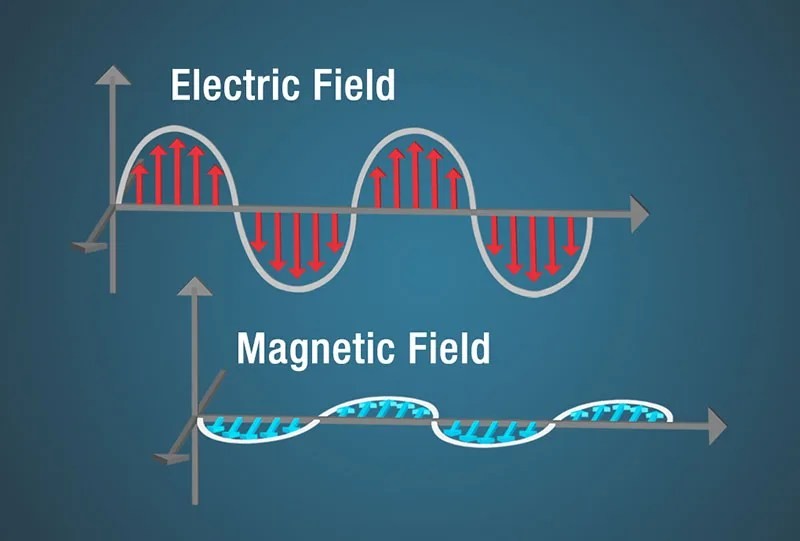 Diagram of an electric field shown as a sine wave with red arrows beneath the curves and a magnetic field shown as a sine wave with blue arrows perpendicular to the electric field.
Diagram of an electric field shown as a sine wave with red arrows beneath the curves and a magnetic field shown as a sine wave with blue arrows perpendicular to the electric field.
1.1 How Electromagnetic Waves Differ From Mechanical Waves
The key difference between electromagnetic and mechanical waves lies in their propagation requirements. Mechanical waves, such as sound or water waves, require a medium to travel. They propagate by causing vibrations in the molecules of the medium. Electromagnetic waves, on the other hand, do not need a medium; they can travel through a vacuum because they are oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. This property is what enables sunlight to reach Earth and allows for wireless communication. The University of Cambridge’s Cavendish Laboratory highlights the significance of understanding these differences for advancements in wireless technology.
1.2 The Role of James Clerk Maxwell in Understanding Electromagnetic Waves
James Clerk Maxwell, a Scottish scientist, developed a comprehensive theory in the 1860s and 1870s that unified electricity and magnetism into a single electromagnetic force. His equations demonstrated that changing electric fields create magnetic fields and vice versa, which allows for the propagation of electromagnetic waves. Maxwell’s work not only explained the nature of light but also predicted the existence of other forms of electromagnetic radiation, such as radio waves. According to a study by MIT’s Electromagnetic Theory Group, Maxwell’s equations are the cornerstone of modern electromagnetics, enabling countless technological innovations.
2. What Mediums Can Electromagnetic Waves Travel Through?
Electromagnetic waves can travel through various mediums, each affecting their speed and behavior differently.
2.1 Vacuum
In a vacuum, such as outer space, electromagnetic waves travel at their maximum speed, which is the speed of light (approximately 299,792,458 meters per second). This is because there are no particles to interact with and slow the wave down.
2.2 Air
Electromagnetic waves can travel through air, although not quite as fast as in a vacuum. The presence of air molecules causes some scattering and absorption, slightly reducing the wave’s speed. However, for most practical purposes, the speed of electromagnetic waves in air is considered to be very close to the speed of light.
2.3 Water
Water affects the propagation of electromagnetic waves more significantly than air. Water molecules can absorb electromagnetic energy, particularly at higher frequencies. This is why radio waves can travel long distances through the air but are quickly attenuated in water.
2.4 Solids
The ability of electromagnetic waves to travel through solids depends on the material’s properties. Some materials, like glass and certain plastics, are transparent to visible light, allowing it to pass through with minimal absorption. Other materials, like metals, are opaque because they absorb or reflect electromagnetic waves.
3. Why Do Electromagnetic Waves Travel Through Different Mediums at Different Speeds?
The speed of electromagnetic waves varies depending on the medium through which they travel due to interactions between the waves and the atoms or molecules of the medium. When an electromagnetic wave enters a medium, it interacts with the electrons of the atoms in that medium. These interactions cause the electrons to oscillate, which in turn generates new electromagnetic waves. The new waves interfere with the original wave, resulting in a change in the wave’s speed.
3.1 Refractive Index Explained
The refractive index of a medium is a measure of how much the speed of light (or any electromagnetic wave) is reduced inside the medium. A higher refractive index indicates a greater reduction in speed. The refractive index depends on the properties of the medium, such as its density and composition.
3.2 How the Medium’s Properties Affect the Speed of Waves
The properties of a medium, such as its density, temperature, and composition, affect how electromagnetic waves propagate through it. For example, denser materials generally have higher refractive indices, which slow down the waves more. Similarly, materials that readily absorb electromagnetic energy will attenuate the waves more quickly.
4. How Do Electromagnetic Waves Propagate?
Electromagnetic waves propagate through a process of self-generation, where changing electric and magnetic fields create each other.
4.1 The Interplay of Electric and Magnetic Fields
An electromagnetic wave consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation. A changing electric field produces a magnetic field, and a changing magnetic field produces an electric field. This continuous cycle allows the wave to propagate through space without needing a medium.
4.2 Wavelength, Frequency, and Energy
Electromagnetic waves are characterized by their wavelength, frequency, and energy. The wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of the wave. The frequency is the number of wave cycles that pass a given point per unit of time, usually measured in Hertz (Hz). The energy of an electromagnetic wave is directly proportional to its frequency; higher frequency waves have more energy.
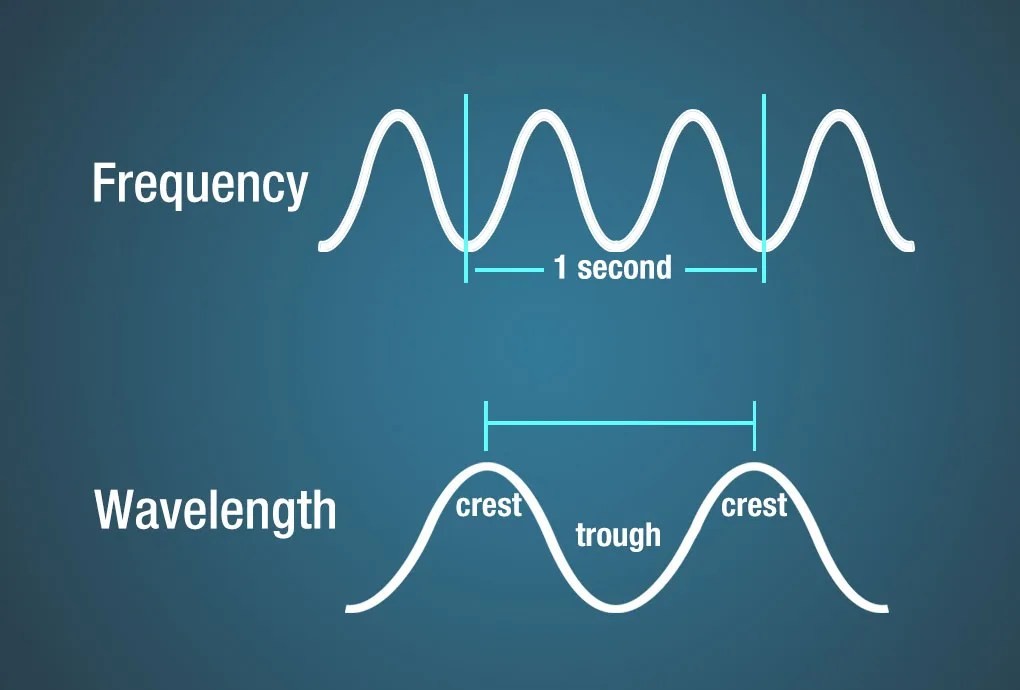 Diagram showing frequency as the measurement of the number of wave crests that pass a given point in a second. Wavelength is measured as the distance between two crests.
Diagram showing frequency as the measurement of the number of wave crests that pass a given point in a second. Wavelength is measured as the distance between two crests.
4.3 The Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all types of electromagnetic radiation, arranged by frequency and wavelength. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each type of electromagnetic radiation has different properties and applications.
5. What Are Some Real-World Examples of Electromagnetic Waves?
Electromagnetic waves are integral to many technologies and natural phenomena that we encounter daily.
5.1 Radio Waves
Radio waves are used for wireless communication, including radio and television broadcasting, mobile phones, and satellite communication. They have long wavelengths and low frequencies, allowing them to travel long distances and penetrate obstacles.
5.2 Microwaves
Microwaves are used in microwave ovens for heating food, as well as in radar systems and satellite communication. They have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than radio waves, which allows them to be focused into narrow beams.
5.3 Infrared Radiation
Infrared radiation is used in remote controls, thermal imaging, and heating applications. It is emitted by warm objects and can be detected by infrared sensors.
5.4 Visible Light
Visible light is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. It is used for illumination, photography, and displays.
5.5 Ultraviolet Radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is used in tanning beds, sterilization, and medical treatments. It has shorter wavelengths and higher energy than visible light, which can cause damage to living tissues.
5.6 X-Rays
X-rays are used in medical imaging to visualize bones and internal organs. They have very short wavelengths and high energy, which allows them to penetrate soft tissues.
5.7 Gamma Rays
Gamma rays are used in cancer treatment and industrial applications. They have the shortest wavelengths and highest energy in the electromagnetic spectrum and are produced by nuclear reactions.
6. What Is the Relevance of Electromagnetic Waves to Travel?
Electromagnetic waves play a crucial role in modern travel, enabling communication, navigation, and safety systems. At TRAVELS.EDU.VN, we leverage these technologies to enhance your travel experiences in Napa Valley.
6.1 Communication Systems
Electromagnetic waves are used in various communication systems that are essential for travel.
6.1.1 Satellite Communication
Satellite communication relies on radio waves to transmit signals between Earth and satellites. This technology is used for GPS navigation, weather forecasting, and global communication.
6.1.2 Mobile Phones
Mobile phones use radio waves to connect to cellular networks, allowing travelers to make calls, send messages, and access the internet.
6.1.3 Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi uses radio waves to provide wireless internet access in hotels, airports, and other public places, enabling travelers to stay connected while on the move.
6.2 Navigation Systems
Electromagnetic waves are fundamental to navigation systems that help travelers find their way.
6.2.1 GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS) uses satellite signals to determine the precise location of a receiver. This technology is used in car navigation systems, mobile phones, and other devices to provide accurate directions.
6.2.2 Radar
Radar systems use radio waves to detect the presence and location of objects. They are used in air traffic control, weather forecasting, and maritime navigation.
6.3 Safety Systems
Electromagnetic waves are used in safety systems that help protect travelers from harm.
6.3.1 Airport Security
Airport security systems use X-rays and other forms of electromagnetic radiation to scan luggage and passengers for prohibited items.
6.3.2 Weather Forecasting
Weather forecasting relies on satellite data and radar systems to monitor weather patterns and predict storms. This information is used to warn travelers of potential hazards and to plan safe routes.
7. How Do Sunglasses Use Polarization to Reduce Glare?
Sunglasses often use polarization to reduce glare by blocking horizontally polarized light, which is a significant component of glare reflected from surfaces like water or roads.
7.1 Understanding Polarization
Polarization refers to the alignment of the electromagnetic field of light waves. Light waves oscillate in various directions, but when light is polarized, its waves are aligned in a specific direction.
7.2 How Polarized Lenses Work
Polarized sunglasses have lenses that contain a special filter that blocks light waves oscillating in a particular direction. Typically, this filter is aligned to block horizontally polarized light. Since glare is often horizontally polarized due to reflection from horizontal surfaces, these sunglasses effectively reduce glare, improving visibility and comfort.
8. TRAVELS.EDU.VN and Napa Valley Travel
At TRAVELS.EDU.VN, we harness the power of electromagnetic wave technology to provide exceptional travel experiences in Napa Valley. From seamless communication to precise navigation, we ensure that your journey is smooth, safe, and enjoyable.
8.1 Utilizing GPS for Napa Valley Tours
Our Napa Valley tours leverage GPS technology to provide accurate and reliable navigation. Whether you are exploring vineyards, scenic routes, or charming towns, our GPS-enabled devices and apps ensure you never lose your way.
8.2 Enhancing Communication with Mobile Technology
We use mobile technology to keep you connected throughout your Napa Valley adventure. Our services include:
- Real-time updates: Receive instant notifications about tour schedules, traffic conditions, and weather alerts.
- 24/7 support: Access our customer support team anytime, anywhere via phone, email, or chat.
- Customized itineraries: Tailor your tour experience with our mobile app, which allows you to adjust your itinerary, book activities, and receive personalized recommendations.
8.3 Ensuring Safety with Advanced Systems
Your safety is our top priority. We utilize advanced safety systems that rely on electromagnetic wave technology to ensure a secure travel experience:
- Weather monitoring: Our weather monitoring systems provide real-time updates on weather conditions in Napa Valley, allowing us to adjust tour plans as needed to avoid hazardous situations.
- Emergency communication: In case of an emergency, our communication systems enable us to quickly contact local authorities and provide assistance.
- Vehicle tracking: Our vehicles are equipped with GPS tracking systems, allowing us to monitor their location and ensure they are on the correct route.
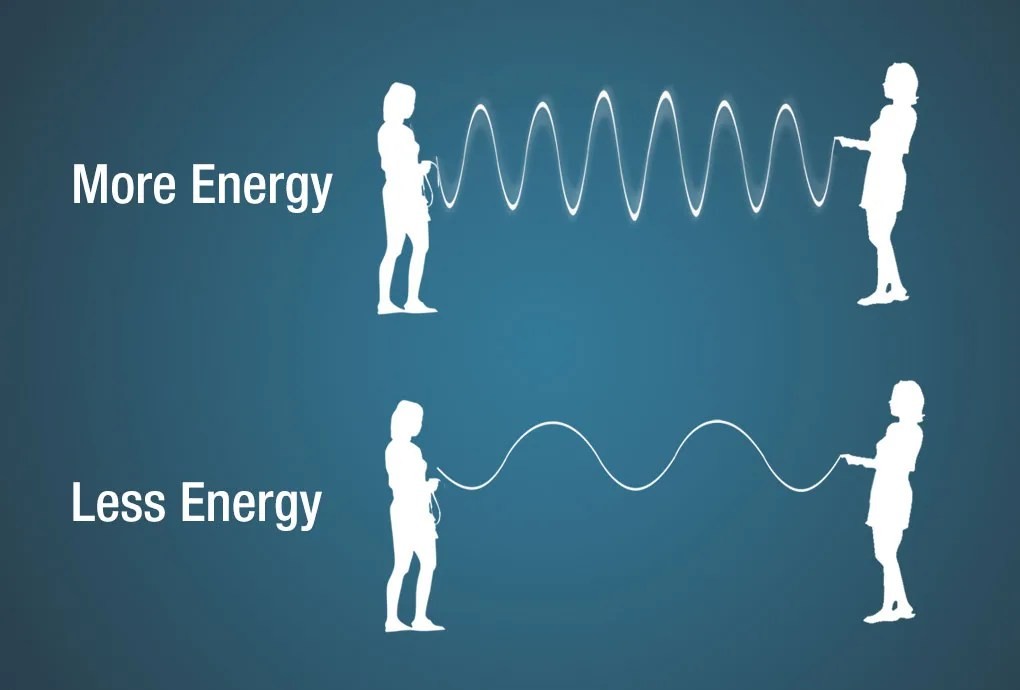 An illustration showing a jump rope with each end being held by a person. As the people move the jump rope up and down very fast – adding MORE energy – the more wave crests appear, thus shorter wavelengths. When the people move the jump rope up and down slower, there are fewer wave crests within the same distance, thus longer wavelengths.
An illustration showing a jump rope with each end being held by a person. As the people move the jump rope up and down very fast – adding MORE energy – the more wave crests appear, thus shorter wavelengths. When the people move the jump rope up and down slower, there are fewer wave crests within the same distance, thus longer wavelengths.
9. Maximizing Your Napa Valley Experience with TRAVELS.EDU.VN
Choosing TRAVELS.EDU.VN for your Napa Valley travel needs ensures a seamless and unforgettable experience. Our expertise in leveraging electromagnetic wave technology, combined with our deep knowledge of the region, sets us apart.
9.1 Benefits of Booking with TRAVELS.EDU.VN
- Time-saving convenience: Let us handle all the details of your trip, from planning your itinerary to booking accommodations and transportation.
- Diverse tour packages: We offer a wide range of tour packages to suit every interest and budget, from wine tasting tours to scenic drives.
- Guaranteed quality: We partner with top-rated hotels, restaurants, and wineries to ensure you receive the highest quality service and experiences.
- Unique experiences: Discover hidden gems and exclusive activities that you won’t find anywhere else.
- Expert support: Our knowledgeable and friendly staff are available to assist you every step of the way, from pre-trip planning to on-site support.
9.2 Tailored Services for Every Traveler
Whether you are a couple seeking a romantic getaway, a group of friends looking for adventure, or a family planning a vacation, TRAVELS.EDU.VN has the perfect tour package for you. We customize our services to meet your specific needs and preferences, ensuring a personalized and memorable experience.
- Romantic Getaways: Enjoy private wine tastings, gourmet dinners, and luxurious accommodations in Napa Valley’s most romantic settings.
- Adventure Tours: Explore the region’s stunning landscapes with hiking, biking, and kayaking tours.
- Family Vacations: Create lasting memories with family-friendly activities, such as visits to local farms, cooking classes, and scenic train rides.
9.3 Up-to-Date Information and Resources
We provide you with the latest information and resources to help you plan your Napa Valley trip:
Note: All prices are estimates and subject to change based on season and availability.
| Service | Description | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Wine Tasting Tour | Visit 3-4 renowned wineries, including tastings and transportation. | $150-300 |
| Hot Air Balloon Ride | Soar over Napa Valley at sunrise for breathtaking views. | $250-400 |
| Gourmet Dinner | Enjoy a multi-course meal at one of Napa Valley’s top restaurants. | $100-200 |
| Hotel Accommodation | Stay in a luxury hotel or charming bed and breakfast. | $200-500 |
| Private Car Service | Travel in style with a private car and driver. | $100-300 |
| Culinary Experiences | Participate in hands-on cooking classes and food tours to experience the rich culinary scene of Napa Valley. | $100-250 |
| Guided Hiking Tours | Explore Napa Valley’s scenic trails with experienced guides, discovering hidden gems and breathtaking vistas. | $75-150 |
| Bicycle Rentals | Rent a bicycle and explore the picturesque countryside at your own pace, with options for electric bikes and guided bike tours. | $50-100 |
| Spa and Wellness Retreats | Indulge in rejuvenating spa treatments and wellness activities at Napa Valley’s premier resorts and spas. | $200-500 |
10. How to Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN for Your Napa Valley Travel Needs
Ready to experience the best of Napa Valley with TRAVELS.EDU.VN? Contact us today to start planning your dream trip.
10.1 Contact Information
- Address: 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (707) 257-5400
- Website: TRAVELS.EDU.VN
10.2 Why Contact Us?
Planning a trip to Napa Valley can be overwhelming, with numerous options for wineries, accommodations, and activities. TRAVELS.EDU.VN simplifies the process by offering expertly curated tour packages and personalized services. Here’s why you should reach out to us:
- Expert Guidance: Our team of travel experts has extensive knowledge of Napa Valley and can provide valuable insights and recommendations to help you create the perfect itinerary.
- Customized Solutions: We tailor our services to meet your specific needs and preferences, ensuring a unique and memorable experience.
- Stress-Free Planning: Let us handle all the details of your trip, from booking accommodations and transportation to arranging wine tastings and activities.
- Exclusive Access: We have established partnerships with top-rated wineries, hotels, and restaurants, giving you access to exclusive experiences and special offers.
- 24/7 Support: Our customer support team is available around the clock to assist you with any questions or concerns you may have before, during, or after your trip.
Don’t wait any longer to start planning your Napa Valley adventure. Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN today and let us help you create a trip of a lifetime. Whether you’re seeking a romantic getaway, a fun-filled family vacation, or an adventurous exploration of the region’s stunning landscapes, we have the perfect tour package for you. Reach out to us via WhatsApp at +1 (707) 257-5400 or visit our website at TRAVELS.EDU.VN to learn more and book your tour. Let us take care of the details so you can relax and enjoy the beauty and charm of Napa Valley.
FAQ About Electromagnetic Waves and Travel
1. What are electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves are disturbances that propagate through space via the interaction of electric and magnetic fields, capable of traveling through a vacuum.
2. How do electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves?
Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium to travel, unlike mechanical waves like sound, which need a medium such as air or water.
3. What mediums can electromagnetic waves travel through?
Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum, air, water, and some solids, each affecting their speed and behavior differently.
4. Why do electromagnetic waves travel at different speeds in different mediums?
The speed of electromagnetic waves varies depending on the medium due to interactions between the waves and the atoms or molecules of the medium, affecting the wave’s speed.
5. How are electromagnetic waves used in travel?
They are used in communication systems (satellite, mobile phones, Wi-Fi), navigation (GPS, radar), and safety systems (airport security, weather forecasting).
6. How does GPS rely on electromagnetic waves for navigation?
GPS uses satellite signals (radio waves) to determine the precise location of a receiver, providing accurate directions for travelers.
7. How do polarized sunglasses reduce glare, and what does polarization mean?
Polarized sunglasses block horizontally polarized light, which is a significant component of glare reflected from surfaces like water or roads. Polarization refers to the alignment of light waves in a specific direction.
8. What are the benefits of booking a Napa Valley tour with TRAVELS.EDU.VN?
Benefits include time-saving convenience, diverse tour packages, guaranteed quality, unique experiences, and expert support.
9. How can I contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN to plan my Napa Valley trip?
You can contact us via address (123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States), WhatsApp (+1 (707) 257-5400), or our website (TRAVELS.EDU.VN).
10. What makes TRAVELS.EDU.VN different from other travel services in Napa Valley?
travels.edu.vn combines expertise in electromagnetic wave technology with deep knowledge of the Napa Valley region, offering seamless communication, precise navigation, and advanced safety systems for an exceptional travel experience.
