Which of these has traveled the farthest? Voyager 1, without a doubt, has traveled the farthest, venturing deeper into interstellar space than any other human-made object. TRAVELS.EDU.VN helps you explore the farthest reaches of our knowledge, just like Voyager, by providing curated travel experiences. Consider this your personal invitation to discover unparalleled Napa Valley adventures; our detailed itineraries and individualized service make planning simple.
1. What Makes Voyager 1 The Farthest Traveling Spacecraft?
Although launched after Voyager 2, Voyager 1 is the farthest spacecraft, surpassing even Pioneer 10. This is mainly because of its trajectory and velocity in space.
Launched in 1977, the Voyager program aimed to explore the outer planets. According to NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the Voyager probes exceeded expectations, continuing their mission for over 40 years.
1.1. Velocity And Trajectory Differences
Voyager 1 moves faster than Voyager 2, even though it had fewer gravity assists. According to NASA, Voyager 1 travels at approximately 35,000 miles per hour (61,500 kilometers per hour), while Voyager 2 travels at around 26,100 miles per hour (42,000 kilometers per hour).
 Voyager 1 LaunchThe launch of Voyager 1 marked a milestone in space exploration, symbolizing humanity’s ambition to venture beyond our solar system and seek new knowledge about the universe, and the advancements made since then inspire the innovation at TRAVELS.EDU.VN as we curate exceptional travel experiences.
Voyager 1 LaunchThe launch of Voyager 1 marked a milestone in space exploration, symbolizing humanity’s ambition to venture beyond our solar system and seek new knowledge about the universe, and the advancements made since then inspire the innovation at TRAVELS.EDU.VN as we curate exceptional travel experiences.
| Spacecraft | Launch Date | Speed (mph) | Speed (km/h) | Gravity Assists |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voyager 1 | September 5 | 35,000 | 61,500 | 2 |
| Voyager 2 | August 20 | 26,100 | 42,000 | 4 |
1.2. Crossing The Heliosphere
In 2012, Voyager 1 crossed the heliopause, the edge of the sun’s solar wind, entering interstellar space, 6 years later in 2018 Voyager 2 accomplished this.
1.3. Distance From Earth
Voyager 1 is approximately 14.7 billion miles (23.6 billion kilometers) from Earth. In comparison, Voyager 2 is about 12.2 billion miles (19.6 billion kilometers) away. For perspective, Pluto, the farthest dwarf planet, is only 49.3 AU away at its farthest. Therefore, Voyager 1 is more than three times farther from us than Pluto.
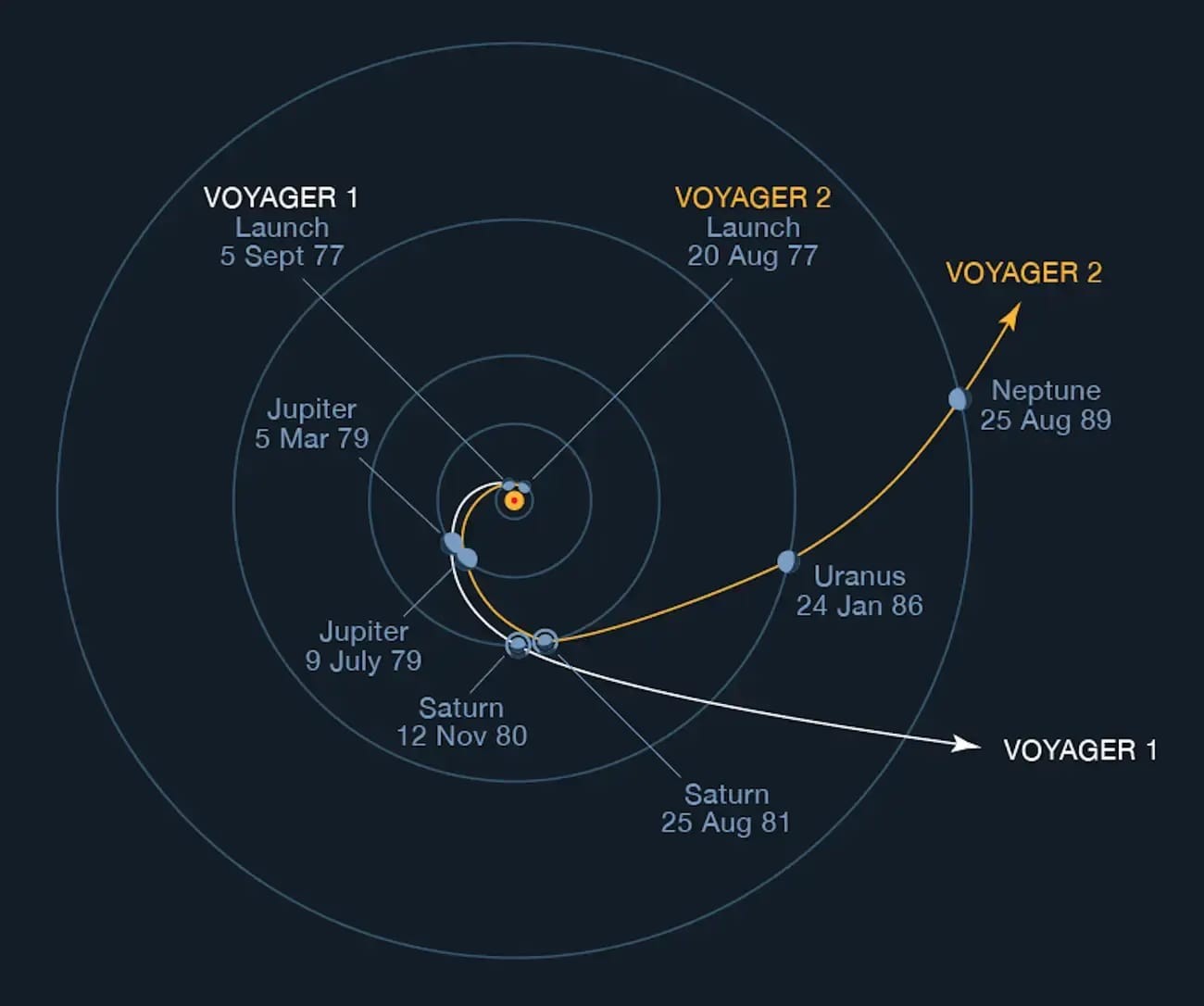 Voyager Probes Flightpath Through Solar System Showing The DifferencesThe flightpath of the Voyager probes showcases their remarkable journey through our solar system, their paths, and how such celestial navigation has provided invaluable insights into the outer reaches of space, much like TRAVELS.EDU.VN navigates you to unique destinations and curated itineraries.
Voyager Probes Flightpath Through Solar System Showing The DifferencesThe flightpath of the Voyager probes showcases their remarkable journey through our solar system, their paths, and how such celestial navigation has provided invaluable insights into the outer reaches of space, much like TRAVELS.EDU.VN navigates you to unique destinations and curated itineraries.
2. What Were The Voyager Spacecrafts Missions?
Launched in 1977, the Voyager probes were initially tasked with a four-year mission to explore the outer solar system. Their primary targets were Jupiter and Saturn.
2.1. Jupiter Encounters
As Voyager 1 approached Jupiter, it made several significant discoveries. According to NASA, these include:
- Discovery of two new moons: Thebe and Metis.
- Discovery of a thin ring around Jupiter.
- Spectacular photos of the Galilean moons.
- Confirmation that Io is an active moon.
2.2. Saturn Encounters
When Voyager 1 reached Saturn, it continued its streak of discoveries. NASA reports that Voyager 1 found:
- The G-ring around Saturn.
- Five new moons.
- Confirmation that Saturn’s main moons are mostly water ice.
- First spacecraft to visit Saturn.
| Planet | Discoveries |
|---|---|
| Jupiter | Two new moons (Thebe and Metis), thin ring |
| Saturn | G-ring, five new moons, water ice composition |
2.3. Solar System Portrait
In 1990, at a distance of 40 AU, Voyager 1 took the first “Solar System portrait” photos. This unique set of images captured all the planets from a single vantage point.
3. How Did The Voyager Spacecrafts Travel So Far?
The Voyager spacecraft’s ability to travel such immense distances is primarily due to the nature of space, where there is little friction to slow down objects.
3.1. Minimal Energy Loss
In space, objects lose very little kinetic energy. This means that once an object is in motion, it tends to stay in motion unless acted upon by an external force.
3.2. Escaping The Sun’s Gravity
As the Voyager probes move farther from the sun, they experience less gravitational pull. Over time, they will require less power to maintain their trajectory.
3.3. Gravity Assists
The planets in our solar system provided valuable “gravity assists,” boosting the speed of the probes and helping them escape the sun’s gravity, similar to how TRAVELS.EDU.VN assists you in discovering the best routes and destinations for your travels.
4. What Is The Future For Voyager 1?
Voyager 1 and 2 will continue to drift through space, eventually encountering the gravity of other stars. However, their current trajectory makes this unlikely.
4.1. Reaching The Oort Cloud
Both probes are headed toward the theoretical Oort Cloud, a vast collection of icy objects at the edge of our solar system. It is estimated that they will reach the Oort Cloud in about 300 years.
4.2. Minimal Risk Of Collision
The vastness of space means that the probes are unlikely to collide with asteroids or comets. According to NASA, even in the asteroid belt, the distance between objects is vast.
4.3. Loss Of Power
From 2025 to 2036, Voyager 1 will gradually lose the ability to power its instruments. Eventually, both probes will be out of range of the Deep Space Network, and their signals will no longer be detectable.
| Timeline | Event |
|---|---|
| 300 years | Reach the Oort Cloud |
| 2025-2036 | Loss of instrument power |
| Future | Signal undetectable by Deep Space Network |
5. What Are Voyager 1’s Key Achievements?
Even as communication with the Voyager probes diminishes, their accomplishments remain significant. Voyager 1’s achievements include:
5.1. Interstellar Pioneer
Voyager 1 is the first spacecraft to successfully cross the sun’s heliosphere and enter interstellar space, marking it as the first human-made object to venture into this region.
5.2. Jupiter Discoveries
When Voyager 1 approached Jupiter, it discovered two new moons, Thebe and Metis, and a thin ring around the gas giant. It also provided detailed images of the Galilean moons, revealing their terrain and confirming that Io is an active moon with large volcanoes.
5.3. Saturn Discoveries
Upon reaching Saturn, Voyager 1 discovered the G-ring and five new moons. It analyzed Saturn’s moons, revealing they are primarily composed of water ice, and was the first spacecraft to visit Saturn.
5.4. First Solar System Portrait
In 1990, Voyager 1 captured the first official Solar System portrait photos from a distance of 40 AU, offering a unique perspective of our planetary neighborhood.
5.5. Extensive Imaging And Data Collection
Voyager 1 took over 67,000 images during its mission and conducted numerous experiments, providing critical information about the planets and our solar system as a whole.
6. What Is Interstellar Space And Why Is It Important?
Interstellar space is the region beyond the influence of a star’s heliosphere, making Voyager 1’s entry into this area a monumental achievement.
6.1. Understanding Interstellar Medium
Venturing into interstellar space allows us to study the interstellar medium (ISM), the matter and radiation that exist between star systems. This study is crucial for understanding the formation and evolution of galaxies.
6.2. Detecting Cosmic Rays
Interstellar space is filled with cosmic rays, high-energy particles that travel at nearly the speed of light. Understanding these rays is essential for protecting future spacecraft and astronauts.
6.3. Studying Magnetic Fields
Interstellar space has magnetic fields that can affect the movement of charged particles. Studying these fields helps scientists understand how they influence the structure of galaxies.
7. What Technologies Did Voyager Use?
The Voyager spacecraft used technologies that were cutting-edge at the time, enabling them to travel vast distances and collect invaluable data, just as TRAVELS.EDU.VN utilizes the latest technologies to enhance your travel planning.
7.1. Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generators (RTGs)
Voyager used RTGs to convert heat from the natural decay of plutonium-238 into electricity. This reliable power source allowed the spacecraft to operate for decades.
7.2. Advanced Imaging System
The imaging system on Voyager included two television cameras, each equipped with different filters to capture detailed images of planets and moons.
7.3. Magnetometers
Magnetometers were used to measure the magnetic fields of planets and the interstellar medium, providing data on the structure and dynamics of these fields.
7.4. Plasma Detectors
Plasma detectors measured the properties of plasma, a superheated state of matter, in the solar wind and interstellar space.
| Technology | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generators (RTGs) | Provided reliable power for long-duration missions |
| Advanced Imaging System | Captured detailed images of planets and moons |
| Magnetometers | Measured magnetic fields of planets and the interstellar medium |
| Plasma Detectors | Measured properties of plasma in the solar wind and interstellar space |
8. How Does The Voyager Mission Relate To Future Space Exploration?
The Voyager mission serves as a foundation for future space exploration, providing invaluable data and inspiring new missions.
8.1. Inspiring Future Missions
The success of the Voyager mission has inspired new missions to explore the outer solar system and beyond, such as the New Horizons mission to Pluto and the Europa Clipper mission to Jupiter’s moon Europa.
8.2. Informing Spacecraft Design
The lessons learned from Voyager have informed the design of future spacecraft, improving their reliability and capabilities for long-duration missions.
8.3. Testing New Technologies
Voyager tested new technologies that have been incorporated into future spacecraft, such as advanced communication systems and power sources.
9. What Impact Did The Voyager Mission Have On Science Education?
The Voyager mission has had a profound impact on science education, inspiring students and the public to learn more about space and the universe.
9.1. Sparking Interest In STEM
The stunning images and discoveries from Voyager have sparked interest in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) among students of all ages.
9.2. Educational Resources
NASA has created numerous educational resources based on the Voyager mission, including lesson plans, videos, and interactive websites.
9.3. Public Engagement
The Voyager mission has engaged the public through media coverage, museum exhibits, and outreach events, increasing awareness of space exploration.
10. How Can I Experience A Journey Similar To The Voyager Mission?
While you can’t travel to interstellar space, you can embark on an unforgettable journey of discovery with TRAVELS.EDU.VN in Napa Valley, where you’ll uncover the beauty and sophistication of one of the world’s premier wine regions.
10.1. Napa Valley: A Terrestrial Voyager Experience
Explore Napa Valley’s rolling vineyards and picturesque landscapes, reminiscent of the vastness and beauty explored by the Voyager spacecraft. Each winery visit is a new discovery, offering unique insights into the art of winemaking.
10.2. Personalized Exploration With TRAVELS.EDU.VN
Just as Voyager’s mission was tailored to uncover specific aspects of our solar system, TRAVELS.EDU.VN offers personalized itineraries designed to meet your interests, whether you’re a wine connoisseur, a gourmet food enthusiast, or an adventure seeker.
10.3. Technological Innovation In Travel
TRAVELS.EDU.VN leverages advanced planning tools to enhance your travel experience, providing real-time updates and interactive maps that guide you through Napa Valley’s hidden gems and iconic landmarks.
10.4. Sustainable and Ethical Travel Practices
In alignment with Voyager’s mission to preserve and understand our environment, TRAVELS.EDU.VN promotes sustainable tourism practices, ensuring that your visit supports local communities and preserves Napa Valley’s natural beauty for future generations.
Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN today at +1 (707) 257-5400 or visit our website at TRAVELS.EDU.VN. Our office is located at 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States.
FAQ: Voyager 1 And Space Exploration
1. How Far Has Voyager 1 Traveled Compared To Other Spacecraft?
Voyager 1 has traveled the farthest compared to any other spacecraft, reaching interstellar space, unlike other missions like Pioneer 10.
2. What Is The Main Reason Voyager 1 Traveled Further Than Voyager 2?
Voyager 1 traveled further due to its higher speed and trajectory, allowing it to reach interstellar space faster than Voyager 2.
3. What Were The Primary Missions Of The Voyager Spacecraft?
The primary missions were to explore Jupiter and Saturn, providing invaluable data and images of these planets and their moons.
4. What Important Discoveries Did Voyager 1 Make During Its Mission?
Voyager 1 discovered new moons around Jupiter and Saturn, captured the first Solar System portrait, and provided detailed images of planetary surfaces.
5. How Did The Voyager Spacecraft Manage To Travel Such Vast Distances?
The spacecraft used gravity assists from planets to increase speed and minimize energy loss in the vacuum of space, enabling long-distance travel.
6. What Is The Future Outlook For The Voyager 1 Spacecraft?
Voyager 1 will continue drifting in interstellar space, eventually losing power but remaining a symbol of human exploration and innovation.
7. What Technologies Enabled Voyager 1 To Operate For So Many Years?
Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generators (RTGs) provided a reliable power source, and advanced imaging systems captured high-quality data over decades.
8. How Did The Voyager Mission Impact Science Education And Public Interest In Space?
The mission sparked interest in STEM fields, provided educational resources, and engaged the public through discoveries and stunning visuals.
9. What Is Interstellar Space, And Why Is It Important To Explore?
Interstellar space is the region beyond a star’s heliosphere. Exploring it helps us understand the interstellar medium, cosmic rays, and magnetic fields, essential for galactic evolution.
10. How Can I Experience A Sense Of Discovery Similar To The Voyager Mission On Earth?
Exploring unique destinations like Napa Valley with travels.edu.vn, offering personalized itineraries and innovative travel planning, provides a terrestrial sense of adventure and discovery.
