What Type Of Wave Can Travel Through A Vacuum? Electromagnetic waves are the answer, and they are more than just light. Understanding their nature opens doors to grasping the universe’s most fundamental processes. TRAVELS.EDU.VN helps you explore the fascinating world of electromagnetic radiation, from radio waves to gamma rays, and how these waves connect us to the cosmos. Discover the science behind these waves and their impact on our everyday lives, empowering you with knowledge and fueling your curiosity about the universe. Let’s delve into the intricacies of electromagnetic waves, their properties, and their profound implications.
1. Understanding Electromagnetic and Mechanical Waves
Waves are a fundamental way energy travels, and they come in two primary forms: mechanical and electromagnetic. Let’s break down the key differences.
-
Mechanical Waves: These waves require a medium, whether solid, liquid, gas, or plasma, to propagate. Think of ripples in a pond or sound traveling through the air. The energy is transferred through the medium by causing molecules to vibrate or bump into each other. Without a medium, mechanical waves cannot exist.
-
Electromagnetic Waves: This is the type of wave we’re focusing on. Unlike mechanical waves, electromagnetic waves do not need a medium to travel. They can propagate through the vacuum of space, allowing sunlight to reach Earth and radio signals to connect us across vast distances.
The defining characteristic is the need for a medium. Mechanical waves are disturbances that travel through something, while electromagnetic waves are disturbances that are something – specifically, oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
2. The Nature of Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves are a fascinating combination of electricity and magnetism.
2.1 Electricity and Magnetism Intertwined
Consider static electricity, like the kind that makes your hair stand on end. Magnetism, too, can be static, like a refrigerator magnet. However, the real magic happens when these fields change. A changing magnetic field creates a changing electric field, and vice versa. This interlinked dance forms electromagnetic waves.
2.2 Maxwell’s Equations: The Foundation
In the 1860s and 1870s, James Clerk Maxwell, a Scottish physicist, revolutionized our understanding of electromagnetism. He developed a set of equations, now known as Maxwell’s Equations, that elegantly describe the relationship between electricity and magnetism and how they couple to form electromagnetic waves. These equations are a cornerstone of modern physics.
2.3 Hertz’s Confirmation
Following Maxwell’s theoretical work, Heinrich Hertz, a German physicist, experimentally verified the existence of electromagnetic waves, specifically radio waves. He demonstrated that these waves traveled at the speed of light, confirming Maxwell’s theory and paving the way for wireless communication. The unit of frequency, Hertz (Hz), is named in his honor.
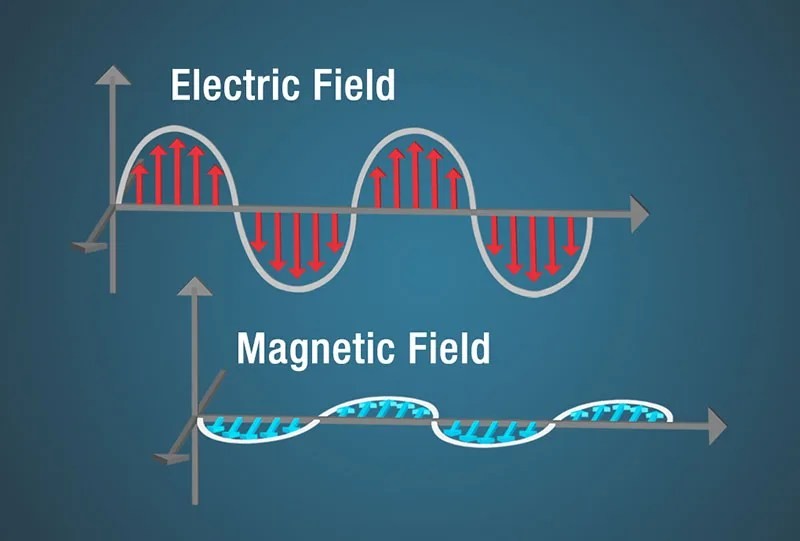 Diagram illustrating electromagnetic waves, showing electric and magnetic fields oscillating perpendicularly.
Diagram illustrating electromagnetic waves, showing electric and magnetic fields oscillating perpendicularly.
3. Waves and Particles: The Duality of Light
Light, a form of electromagnetic radiation, exhibits a fascinating duality: it behaves as both a wave and a particle.
3.1 Photons: Packets of Energy
Light is composed of discrete packets of energy called photons. These photons have no mass, carry momentum, and travel at the speed of light.
3.2 Wave-Particle Duality
The wave-particle duality principle states that all light, and indeed all matter, exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties. Which property is observed depends on how the light is measured. For example, diffracting light through a prism to create a spectrum reveals its wave-like nature.
3.3 Detectors and the Particle Nature
Digital cameras, on the other hand, use detectors that respond to individual photons. When a photon strikes the detector, it releases electrons, which are then used to create an image. This reveals the particle-like nature of light.
4. Polarization: Aligning Electromagnetic Fields
Polarization is a property of electromagnetic waves that describes the alignment of the electric field.
4.1 Vertical Polarization
In vertically polarized light, the electric field oscillates in a vertical direction.
4.2 Filtering Light
Polarizing sunglasses utilize this property to reduce glare. They absorb light that is polarized in a particular direction, blocking reflected light from surfaces like water or roads. This is analogous to trying to throw a Frisbee through a picket fence – it will only pass through if aligned correctly.
5. Describing Electromagnetic Energy: Frequency, Wavelength, and Energy
The terms light, electromagnetic waves, and radiation all refer to the same phenomenon: electromagnetic energy. This energy can be described in terms of frequency, wavelength, or energy. These three quantities are mathematically related, meaning that if you know one, you can calculate the other two.
5.1 Frequency (Hertz)
Frequency refers to the number of wave crests that pass a given point in one second. It is measured in Hertz (Hz), where 1 Hz represents one cycle per second. Radio waves and microwaves are typically described in terms of frequency.
5.2 Wavelength (Meters)
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of a wave. Infrared and visible light are often described in terms of wavelength, measured in meters.
5.3 Energy (Electron Volts)
Energy is another way to characterize electromagnetic radiation. It is often used for X-rays and gamma rays and is measured in electron volts (eV). An electron volt is the amount of kinetic energy an electron gains when moving through an electric potential difference of one volt.
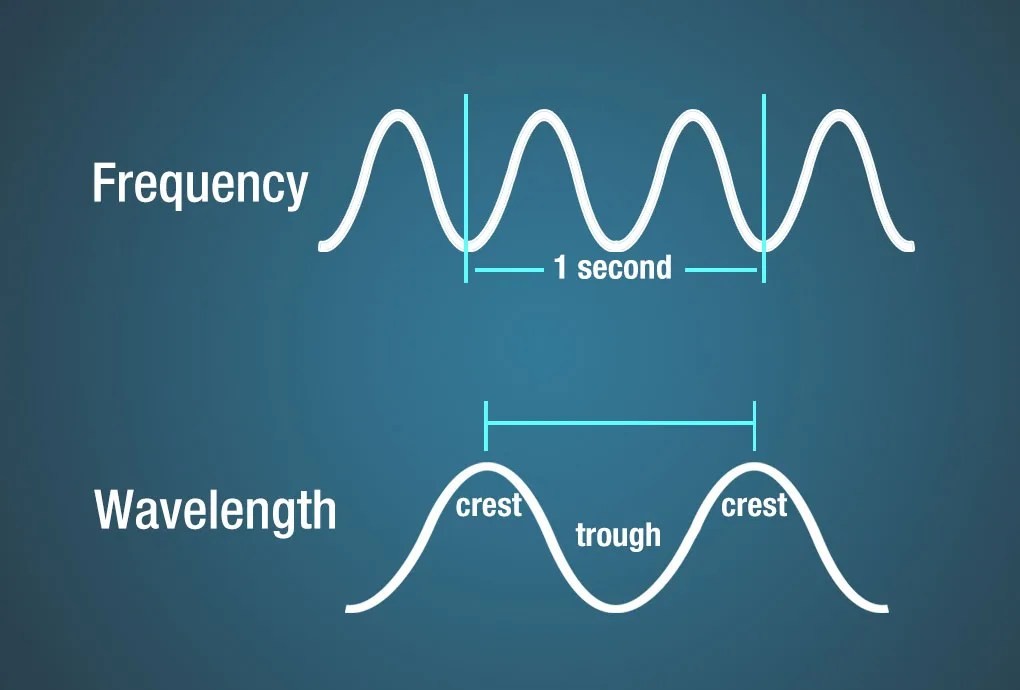 Diagram showing frequency and wavelength of a wave.
Diagram showing frequency and wavelength of a wave.
6. The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Wide Range of Waves
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses a vast range of frequencies, wavelengths, and energies. From radio waves with long wavelengths to gamma rays with short wavelengths, each part of the spectrum has unique properties and applications.
6.1 Radio Waves
Radio waves have the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are used for communication, broadcasting, and radar.
6.2 Microwaves
Microwaves have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than radio waves. They are used for microwave ovens, satellite communication, and radar.
6.3 Infrared Radiation
Infrared radiation has wavelengths shorter than microwaves but longer than visible light. It is associated with heat and is used in thermal imaging and remote controls.
6.4 Visible Light
Visible light is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that the human eye can detect. It includes all the colors we see, from red to violet.
6.5 Ultraviolet Radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation has shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than visible light. It can cause sunburns and skin damage, but it is also used in sterilization and medical treatments.
6.6 X-rays
X-rays have very short wavelengths and high energies. They can penetrate soft tissues and are used in medical imaging.
6.7 Gamma Rays
Gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths and highest energies in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are produced by nuclear reactions and are used in cancer treatment and sterilization.
7. How Electromagnetic Waves Travel Through a Vacuum
The ability of electromagnetic waves to travel through a vacuum is a key difference from mechanical waves. This arises from the way they are generated and sustained.
7.1 Self-Propagating Fields
Electromagnetic waves are created by accelerating charged particles. When a charged particle accelerates, it creates a changing electric field. This changing electric field, in turn, creates a changing magnetic field. This continuous generation of one field by the other allows the wave to propagate, or travel, through space without needing a medium.
7.2 Energy Transport
As the electric and magnetic fields oscillate, they carry energy with them. This is how electromagnetic waves transport energy across vast distances, such as from the sun to the Earth.
7.3 The Speed of Light
Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light, which is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (often rounded to 300,000 kilometers per second). This speed is constant in a vacuum and is one of the fundamental constants of the universe.
8. Applications of Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves have revolutionized numerous aspects of our lives. Here are some key applications:
8.1 Communication
Radio waves and microwaves are essential for wireless communication, including radio, television, cell phones, and satellite communication.
8.2 Medicine
X-rays and gamma rays are used for medical imaging and cancer treatment. Ultraviolet radiation is used for sterilization.
8.3 Astronomy
Astronomers use telescopes to observe electromagnetic radiation from distant stars and galaxies, providing insights into the universe.
8.4 Remote Sensing
Infrared radiation is used for thermal imaging, allowing us to see heat signatures.
8.5 Industry
Microwaves are used for heating and drying in various industrial processes.
9. The Importance of Studying Electromagnetic Waves
Understanding electromagnetic waves is crucial for several reasons:
9.1 Technological Advancement
Electromagnetic waves are the foundation of many technologies we rely on daily. Studying them helps us develop new and improved technologies.
9.2 Understanding the Universe
Electromagnetic radiation is our primary source of information about the universe. By studying it, we can learn about distant stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects.
9.3 Medical Applications
Electromagnetic waves play a vital role in medical diagnostics and treatments, helping us improve healthcare.
9.4 Environmental Monitoring
Remote sensing technologies that use electromagnetic radiation help us monitor the environment and understand climate change.
10. Exploring Napa Valley with TRAVELS.EDU.VN
Now that we’ve explored the science of waves, let’s shift our focus to a different kind of wave – the wave of relaxation and enjoyment that awaits you in Napa Valley. TRAVELS.EDU.VN is your gateway to unforgettable Napa Valley experiences.
10.1 Why Choose Napa Valley?
Napa Valley is renowned for its stunning vineyards, world-class wineries, and exceptional culinary scene. It’s the perfect destination for couples, friends, and anyone seeking a luxurious and memorable getaway.
10.2 Challenges of Planning a Napa Valley Trip
Planning the perfect Napa Valley trip can be overwhelming. With so many wineries, restaurants, and activities to choose from, it’s easy to feel lost and uncertain. You might struggle with:
- Finding accommodations that fit your budget and preferences.
- Selecting the best wineries to visit based on your taste.
- Arranging transportation between wineries.
- Making reservations at popular restaurants.
- Discovering hidden gems and unique experiences.
- Staying within your budget while still enjoying a luxurious trip.
- Keeping up to date on the latest prices for tours, hotels and flights.
10.3 How TRAVELS.EDU.VN Simplifies Your Trip
TRAVELS.EDU.VN eliminates the stress of planning and ensures a seamless, unforgettable Napa Valley experience. We offer:
- Curated Packages: We design a variety of tour packages tailored to different interests and budgets. Whether you’re seeking a romantic escape, a culinary adventure, or a wine connoisseur’s dream, we have the perfect package for you.
- Expert Recommendations: Our team of Napa Valley experts provides personalized recommendations on the best wineries, restaurants, and activities based on your preferences.
- Hassle-Free Bookings: We handle all the bookings for accommodations, transportation, winery tours, and restaurant reservations, saving you time and effort.
- Exclusive Access: We offer exclusive access to some of Napa Valley’s most sought-after wineries and experiences.
- Detailed Information: We provide detailed information about each destination, including history, wine profiles, and insider tips.
- Comprehensive Support: Our team is available to assist you throughout your trip, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable experience.
- Competitive Pricing: We offer competitive pricing on all our packages and services, ensuring you get the best value for your money.
10.4 Sample Napa Valley Packages with TRAVELS.EDU.VN
Here are a few examples of the exceptional experiences you can enjoy with TRAVELS.EDU.VN. Note that pricing can vary based on time of year and availability.
| Package Name | Description | Price (per person) |
|---|---|---|
| Romantic Napa Escape | Three nights in a luxurious boutique hotel, private wine tasting at two premium wineries, gourmet dinner at a Michelin-starred restaurant, and a couples massage. | $1,500 – $2,500 |
| Napa Wine Adventure | Two full-day guided tours of Napa Valley’s top wineries, including tastings and behind-the-scenes access, plus a picnic lunch amidst the vineyards. | $800 – $1,200 |
| Culinary Delights Tour | Cooking class with a renowned Napa Valley chef, a tour of a local farmer’s market, wine pairing dinner at a farm-to-table restaurant, and a visit to a chocolate factory. | $1,000 – $1,800 |
10.5 Featured Napa Valley Destinations
With TRAVELS.EDU.VN, explore the best that Napa Valley has to offer:
- Domaine Carneros: Sparkling wine house offering beautiful views and tours.
- Robert Mondavi Winery: Iconic winery with exceptional tastings and educational experiences.
- The French Laundry: World-renowned Michelin-starred restaurant offering an unforgettable dining experience.
- Castello di Amorosa: Authentic 13th-century Tuscan castle and winery.
- Calistoga: Quaint town known for its mud baths and hot springs.
10.6 Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN Today
Ready to experience the magic of Napa Valley? Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN today to start planning your dream trip. Our expert team is ready to help you create an unforgettable experience.
Contact Information:
- Address: 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (707) 257-5400
- Website: TRAVELS.EDU.VN
Don’t let the complexities of planning hold you back. Let TRAVELS.EDU.VN handle the details, so you can focus on creating memories that will last a lifetime.
FAQ About Electromagnetic Waves
Here are some frequently asked questions about electromagnetic waves:
-
What is an electromagnetic wave?
An electromagnetic wave is a form of energy that travels through space as oscillating electric and magnetic fields. -
How are electromagnetic waves different from mechanical waves?
Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum, while mechanical waves require a medium. -
What is the speed of an electromagnetic wave in a vacuum?
The speed of an electromagnetic wave in a vacuum is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (the speed of light). -
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all types of electromagnetic radiation, from radio waves to gamma rays. -
What are some applications of electromagnetic waves?
Applications include communication, medicine, astronomy, and remote sensing. -
What is frequency?
Frequency is the number of wave crests that pass a given point in one second, measured in Hertz (Hz). -
What is wavelength?
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of a wave. -
What is energy in the context of electromagnetic waves?
Energy is a measure of the amount of energy carried by an electromagnetic wave, often measured in electron volts (eV). -
How do electromagnetic waves travel through space?
Electromagnetic waves travel through space by the continuous generation of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. -
Why are electromagnetic waves important?
Electromagnetic waves are essential for technology, understanding the universe, medical applications, and environmental monitoring.
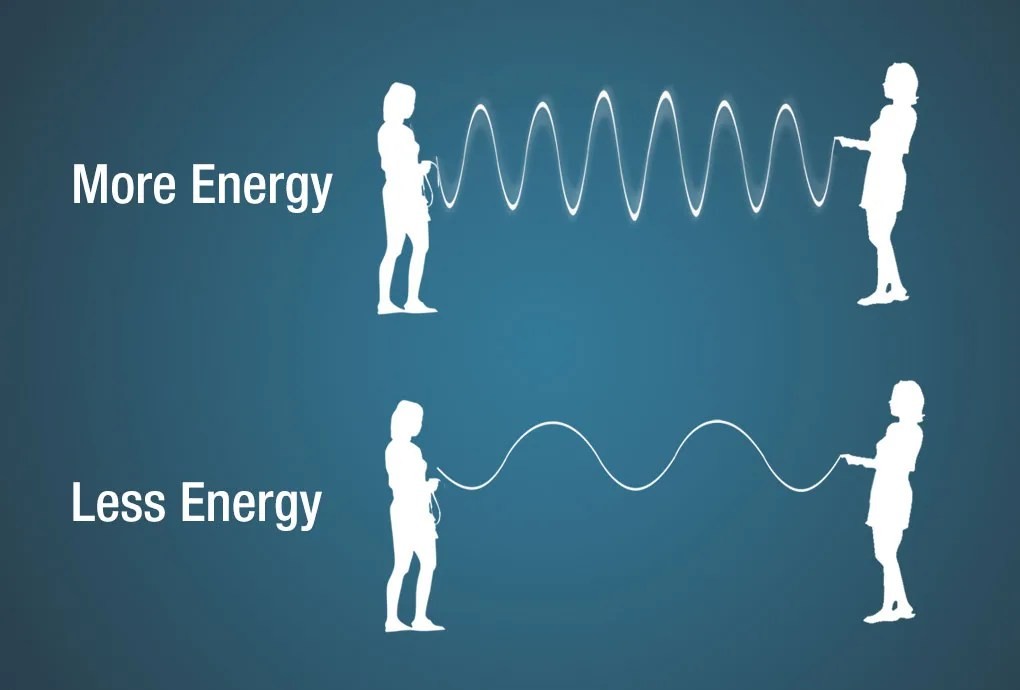 Illustration showing how more energy is needed for shorter wavelengths.
Illustration showing how more energy is needed for shorter wavelengths.
Conclusion: Embrace the Waves
From the invisible waves that power our technology to the rolling hills of Napa Valley, waves surround us. Understanding the science behind electromagnetic waves opens up a world of knowledge, while experiencing the beauty and relaxation of Napa Valley creates memories that last a lifetime. Let TRAVELS.EDU.VN be your guide to both. Contact us today to start planning your Napa Valley adventure and discover the perfect blend of science and serenity.
Ready for Your Dream Napa Valley Getaway?
Don’t wait any longer to experience the best of Napa Valley. Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN now for personalized recommendations and hassle-free bookings. Our team is standing by to help you plan an unforgettable trip!
- Address: 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (707) 257-5400
- Website: TRAVELS.EDU.VN
Let travels.edu.vn transform your travel dreams into reality. We look forward to welcoming you to Napa Valley!