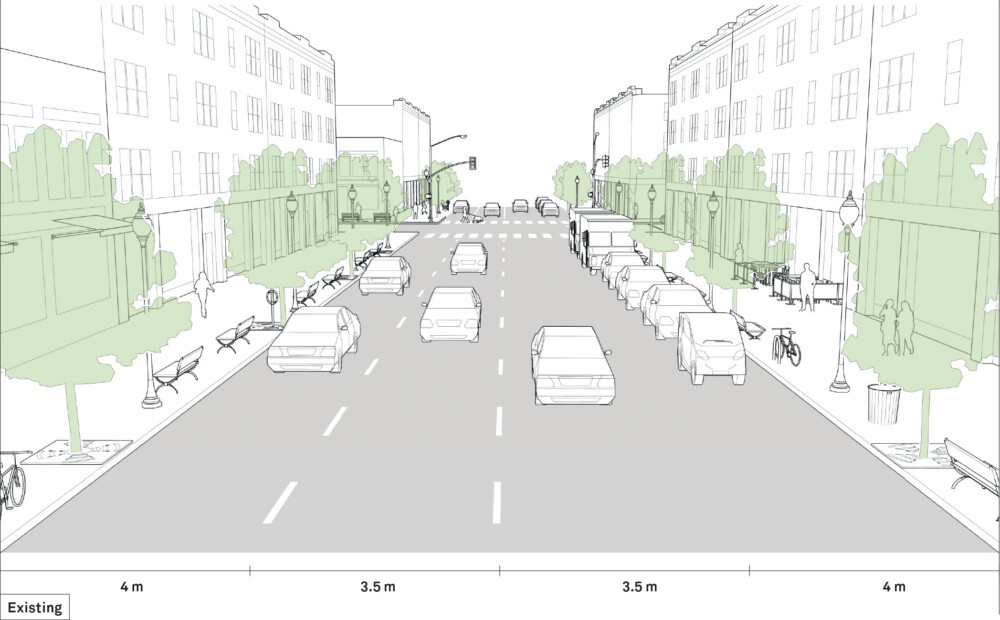
When driving, understanding the dynamics of travel lanes on the roadway is crucial for safety and efficiency. This guide explores the optimal use of travel lanes, focusing on lane width, multi-lane roadways, and parking lane considerations to ensure a smooth and safe journey for all road users.
Wide travel lanes, often favored in high-speed environments, can lead to unintended consequences in urban settings. Research suggests that overly wide lanes don’t necessarily improve traffic flow or safety. Instead, they can encourage speeding during off-peak hours and lane-splitting when traffic is congested. Reducing lane width to 3 meters or less can promote safer driving speeds in urban environments.
Travel Lane Width Optimization
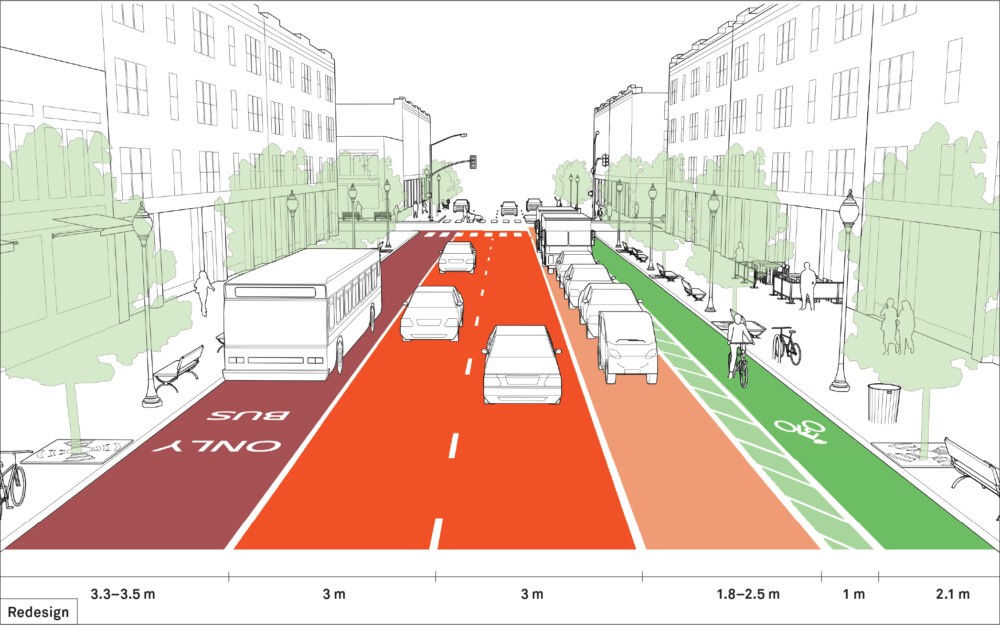
The belief that lane widths less than 3.5 meters decrease traffic flow and capacity is now being challenged by new research. In urban areas, lane widths of 3 meters are appropriate and have a positive impact on street safety without impacting traffic operations. For designated truck or transit routes, a 3.3-meter travel lane in each direction may be used. In some cases, narrower travel lanes of 2.7–3 meters can be effective as through lanes in conjunction with a turn lane.
 A multi-lane road with varying lane widths, highlighting the optimal use of space for different vehicle types.
A multi-lane road with varying lane widths, highlighting the optimal use of space for different vehicle types.
Lanes greater than 3 meters are generally discouraged because they can lead to unintended speeding and double parking, consuming valuable right-of-way at the expense of other modes of transportation. Restrictive policies favoring wide travel lanes are not suitable for constrained urban settings. Narrower lane widths can effectively manage speeds without decreasing safety, and wider lanes do not correlate to safer streets. Wider travel lanes increase exposure and crossing distance for pedestrians, making it essential to consider lane width within the overall street design.
Multi-Lane Roadway Strategies
In multi-lane roadways where transit or freight vehicles are present, providing one wider travel lane is beneficial. This wider lane should ideally be the outside lane, curbside, or next to parking. The inside lanes should continue to be designed at the minimum possible width, at 3 meters or less. This configuration allows larger vehicles to navigate safely while maintaining reasonable speeds in the inner lanes.
Parking Lane Dimensions and Safety
Parking lane widths of 1.8–2.5 meters are recommended. To enhance safety, cities should demarcate parking lanes to indicate to drivers how close they are to parked cars. Clear markings can prevent accidents and ensure that vehicles can park safely without obstructing the travel lanes.
 Vehicles parked in a demarcated parking lane, emphasizing the importance of clear markings for safety and space optimization.
Vehicles parked in a demarcated parking lane, emphasizing the importance of clear markings for safety and space optimization.
Optimizing travel lanes on the roadway requires a balanced approach. Narrower lanes can effectively manage speeds and improve safety in urban environments, while wider lanes may be necessary for specific vehicle types and routes. By understanding and implementing these principles, we can create safer and more efficient roadways for all users.