Are you curious about how far dolphins travel and their fascinating movements? Dolphins are known for their intelligence and social behavior, but their travel habits are equally impressive. TRAVELS.EDU.VN explores the distances these marine mammals cover and the factors influencing their journeys. Discover the incredible world of dolphin travel, migratory patterns, and navigational skills.
1. What is the Average Distance Dolphins Travel Daily?
Dolphins can travel an average of 40 to 100 miles (64 to 161 kilometers) daily, depending on the species and their environment. These distances are influenced by their need to find food, mating opportunities, and suitable habitats.
Dolphins are highly mobile creatures, and their daily travels are a testament to their adaptability and resourcefulness. According to research from the Sarasota Dolphin Research Program, bottlenose dolphins, for example, exhibit varied movement patterns, with some remaining in a localized area while others undertake extensive journeys. This behavior is closely linked to prey availability and environmental conditions. The capacity to cover such distances underscores their physical endurance and navigational prowess, making them one of the ocean’s most dynamic inhabitants.
2. Which Factors Influence How Far Dolphins Travel?
Several factors influence the distances dolphins travel, including food availability, breeding season, water temperature, and threats from predators or human activities. Migratory species may travel thousands of miles each year.
The life of a dolphin is one of constant motion, driven by the necessities of survival and reproduction. TRAVELS.EDU.VN emphasizes that food availability is a primary driver, with dolphins following schools of fish across vast distances. During breeding season, they may travel to specific locations to find mates. Water temperature also plays a crucial role, as dolphins prefer certain temperature ranges. The presence of predators, such as sharks, can force dolphins to relocate to safer areas. Human activities, like fishing and boat traffic, can also disrupt their movements, leading them to seek quieter, less disturbed habitats.
3. How Do Dolphins Navigate Over Long Distances?
Dolphins use a combination of echolocation, magnetic fields, and visual cues to navigate over long distances. Echolocation allows them to create a “sound map” of their surroundings, while sensitivity to magnetic fields helps them maintain direction.
Navigating the vast expanse of the ocean requires exceptional skills, and dolphins possess a unique suite of tools to guide their journeys. According to a study published in the “Journal of Experimental Biology,” dolphins can detect subtle changes in the Earth’s magnetic field, aiding in orientation and navigation. Additionally, their acute eyesight allows them to recognize landmarks and track the position of the sun and stars. Echolocation, however, remains their most reliable navigational tool, enabling them to “see” through murky waters and locate prey from considerable distances.
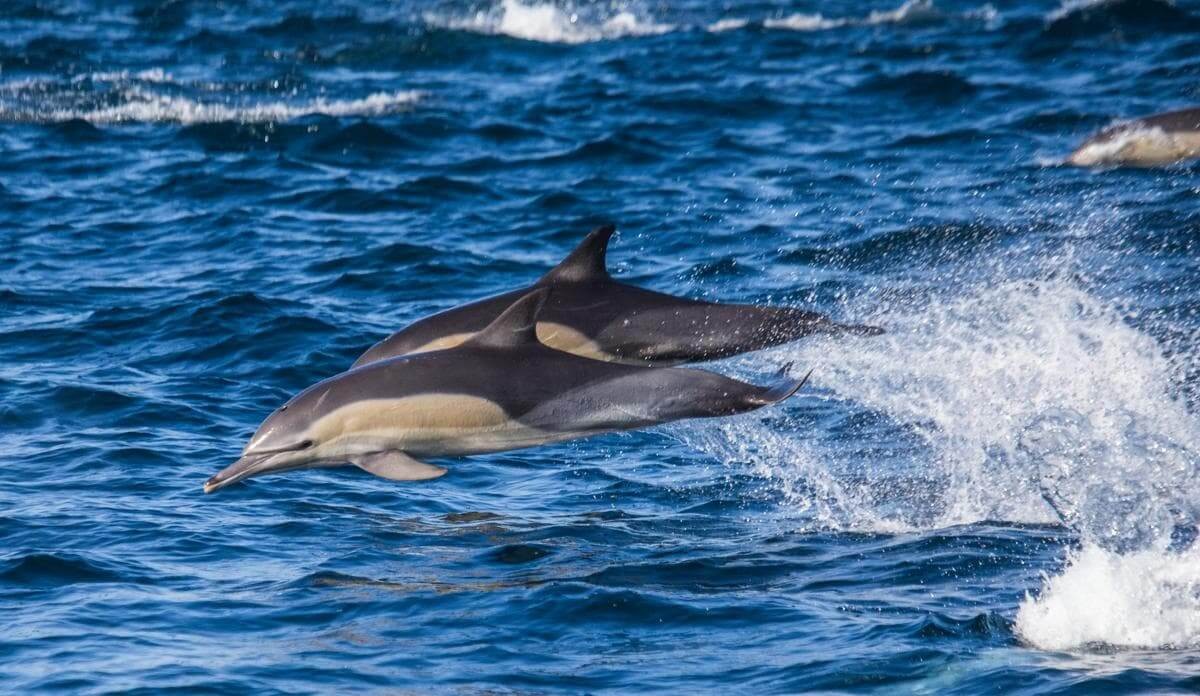 Dolphin echolocation in action
Dolphin echolocation in action
Caption: Common dolphins use echolocation to navigate and hunt, bouncing sound waves off objects to create a “sound map” of their environment.
4. Do All Dolphin Species Travel the Same Distances?
No, different dolphin species have varying travel habits. Smaller dolphins, like the Commerson’s dolphin, may stay within a limited range, while larger species, such as killer whales (orcas), can travel thousands of miles during migration.
TRAVELS.EDU.VN explains that the size, habitat, and social structure of a dolphin species significantly influence its travel patterns. Commerson’s dolphins, known for their striking black and white markings, typically inhabit coastal waters and exhibit localized movements. In contrast, killer whales, the largest members of the dolphin family, undertake long-distance migrations to find food and breeding grounds. These variations in travel behavior highlight the diverse adaptations within the dolphin family.
5. What Are Some Examples of Dolphin Migration Patterns?
Some dolphin species, like the humpback dolphin, migrate seasonally between feeding and breeding grounds. Other species, like the bottlenose dolphin, may exhibit more localized movements depending on resource availability.
Dolphin migration patterns are often driven by the changing seasons and the availability of food. Humpback dolphins, for example, migrate along coastlines to take advantage of seasonal prey abundance. Bottlenose dolphins, on the other hand, may remain in a specific area if resources are plentiful, but will travel to find new food sources or breeding opportunities when necessary. According to the World Wildlife Fund, understanding these migration patterns is crucial for effective conservation efforts.
6. How Does Climate Change Affect Dolphin Travel?
Climate change can significantly impact dolphin travel by altering water temperatures, prey distribution, and ocean currents. These changes can force dolphins to travel farther to find food or suitable habitats, increasing their energy expenditure and stress levels.
TRAVELS.EDU.VN notes that rising ocean temperatures can disrupt the distribution of fish populations, forcing dolphins to travel greater distances to find food. Changes in ocean currents can also affect their ability to navigate and find suitable habitats. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), these climate-related changes pose a significant threat to dolphin populations worldwide.
7. What Role Do Pods Play in Dolphin Travel?
Dolphins often travel in pods, which provide protection from predators, facilitate cooperative hunting, and aid in navigation. Pod size and composition can vary depending on the species and their environment.
Traveling in pods offers numerous advantages for dolphins. Larger groups provide increased protection from predators, such as sharks, and allow for more effective cooperative hunting strategies. Pods also facilitate the transmission of knowledge and skills, including navigation techniques, from older to younger members. According to research from the Marine Mammal Center, social bonds within pods are crucial for the survival and well-being of dolphins.
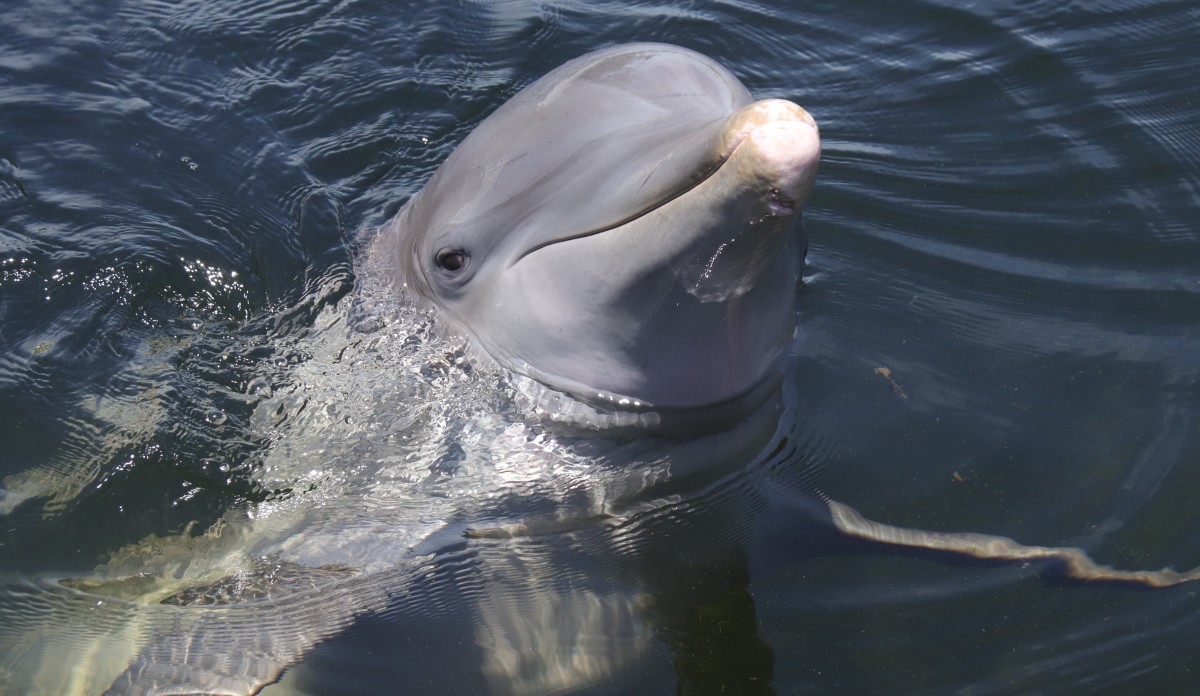 Dolphins traveling in a pod
Dolphins traveling in a pod
Caption: A pod of bottlenose dolphins swim together, demonstrating the social bonds and cooperative behavior that aid in their travels.
8. How Do Researchers Track Dolphin Movements?
Researchers use various methods to track dolphin movements, including satellite tagging, photo-identification, and acoustic monitoring. These techniques provide valuable data on dolphin travel patterns, habitat use, and population dynamics.
Satellite tagging involves attaching a small transmitter to a dolphin’s dorsal fin, allowing researchers to track its movements in real-time. Photo-identification uses unique markings on dolphins’ bodies to identify and track individuals over time. Acoustic monitoring involves deploying underwater microphones to record dolphin vocalizations, providing insights into their distribution and behavior. According to the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, these tracking methods are essential for understanding and protecting dolphin populations.
9. What Are the Conservation Implications of Dolphin Travel?
Understanding dolphin travel patterns is crucial for effective conservation efforts. Protecting key habitats, mitigating human threats, and establishing marine protected areas can help ensure dolphins have the resources and space they need to thrive.
TRAVELS.EDU.VN emphasizes that protecting critical habitats, such as feeding and breeding grounds, is essential for dolphin conservation. Mitigating human threats, such as entanglement in fishing gear and pollution, can reduce mortality rates and improve dolphin health. Establishing marine protected areas can provide dolphins with safe havens from human activities, allowing them to travel and forage without disturbance. According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), collaborative efforts are needed to address the challenges facing dolphin populations worldwide.
10. Where Can I Learn More About Dolphin Travel and Conservation?
You can learn more about dolphin travel and conservation by visiting marine research centers, aquariums, and conservation organizations. Online resources, such as the websites of TRAVELS.EDU.VN, NOAA, and WWF, also provide valuable information.
Visiting marine research centers and aquariums can provide firsthand insights into dolphin behavior and conservation efforts. Conservation organizations offer opportunities to support dolphin research and protection initiatives. Online resources, like TRAVELS.EDU.VN, provide comprehensive information on dolphin travel patterns, threats, and conservation strategies. Stay informed and get involved to help protect these amazing marine mammals.
11. How do dolphins use echolocation for navigation?
Dolphins use echolocation by emitting clicks and listening for the echoes to create a mental “sound map” of their surroundings. This helps them navigate in low visibility conditions and locate prey.
Echolocation is a sophisticated sensory mechanism that allows dolphins to “see” with sound. TRAVELS.EDU.VN explains that dolphins emit a series of clicks that bounce off objects in their environment. By analyzing the returning echoes, dolphins can determine the size, shape, distance, and density of objects. This ability is particularly useful in murky waters or at night, where visibility is limited. Echolocation enables dolphins to navigate complex underwater environments and locate prey with remarkable precision.
12. What is the role of the Earth’s magnetic field in dolphin navigation?
Some studies suggest that dolphins can sense the Earth’s magnetic field, using it as a compass for long-distance navigation. This sense complements their echolocation and visual cues.
The ability to detect magnetic fields provides dolphins with an additional navigational tool, particularly over vast distances where other cues may be scarce. According to research published in “Current Biology,” some marine mammals possess cells containing magnetite, a magnetic mineral, which may enable them to sense the Earth’s magnetic field. This sense, combined with echolocation and visual cues, allows dolphins to maintain direction and navigate effectively during long migrations.
 A map illustrating dolphin migration routes
A map illustrating dolphin migration routes
Caption: A map illustrating typical dolphin migration routes, showcasing the distances and destinations these marine mammals travel annually.
13. Do dolphins have a preferred swimming speed when traveling long distances?
Dolphins typically swim at a cruising speed of 5 to 7 miles per hour (8 to 11 kilometers per hour) when traveling long distances, conserving energy while still covering significant ground.
Maintaining an optimal swimming speed is crucial for dolphins to conserve energy during long journeys. According to a study in the “Journal of Marine Biology,” dolphins adjust their swimming speed based on factors such as water temperature, current, and the presence of predators. By maintaining a cruising speed of 5 to 7 mph, dolphins can efficiently cover large distances while minimizing energy expenditure. This balance is essential for their survival and success in the marine environment.
14. How do dolphins adapt to different water temperatures during their travels?
Dolphins have several adaptations to cope with varying water temperatures, including a thick layer of blubber for insulation and the ability to regulate blood flow to conserve heat in cold water or dissipate heat in warm water.
TRAVELS.EDU.VN highlights that dolphins are well-equipped to handle a range of water temperatures. A thick layer of blubber provides insulation, helping them maintain a stable body temperature in cold waters. Additionally, dolphins can regulate blood flow to their extremities, reducing heat loss in cold conditions or increasing heat dissipation in warm conditions. These physiological adaptations enable dolphins to thrive in diverse aquatic environments and undertake long-distance travels across varying temperature zones.
15. What is the impact of noise pollution on dolphin travel and navigation?
Noise pollution from ships, sonar, and other human activities can interfere with dolphin echolocation and communication, making it difficult for them to navigate and find food.
Noise pollution poses a significant threat to dolphin populations worldwide. According to the Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC), loud underwater noises can disrupt dolphin echolocation and communication, impairing their ability to navigate, find food, and maintain social bonds. Chronic exposure to noise pollution can also lead to stress, hearing damage, and displacement from critical habitats. Mitigating noise pollution is essential for protecting dolphin populations and ensuring their continued survival.
16. How do dolphins use visual cues for navigation?
Dolphins use visual cues such as coastlines, landmarks, and the position of the sun and stars to help them navigate, especially in clear, shallow waters.
Visual cues play a complementary role in dolphin navigation, particularly in clear, shallow waters where visibility is good. Dolphins can recognize coastlines, landmarks, and other visual features to orient themselves and maintain direction. Additionally, they can use the position of the sun and stars as celestial compasses, helping them navigate over long distances. This combination of visual and acoustic cues enhances their navigational abilities and allows them to thrive in diverse marine environments.
17. What are the challenges dolphins face when traveling in polluted waters?
Polluted waters can harm dolphins by exposing them to toxic chemicals, reducing prey availability, and increasing the risk of disease, making their travels more dangerous and less productive.
TRAVELS.EDU.VN emphasizes that polluted waters pose numerous challenges for dolphins. Exposure to toxic chemicals can weaken their immune systems, making them more susceptible to disease. Pollution can also reduce the availability of prey, forcing dolphins to travel farther to find food. Additionally, polluted waters can degrade their habitats and disrupt their social structures. Addressing pollution is crucial for protecting dolphin populations and ensuring their long-term health and survival.
18. How do dolphins communicate with each other while traveling in large pods?
Dolphins communicate using a variety of vocalizations, including whistles, clicks, and pulsed calls, which help them coordinate their movements, maintain social bonds, and share information about food sources and potential threats.
Effective communication is essential for dolphins traveling in large pods. According to research from the University of St Andrews, dolphins use a complex repertoire of vocalizations to coordinate their movements, maintain social bonds, and share information. Signature whistles allow individual dolphins to identify themselves, while clicks and pulsed calls convey information about food sources, potential threats, and navigational cues. This sophisticated communication system enables dolphins to function cohesively and thrive in their dynamic marine environment.
19. Do dolphins ever travel alone, and what are the circumstances?
While dolphins are highly social animals, they may sometimes travel alone due to factors such as injury, separation from their pod, or the pursuit of specific prey.
Dolphins are typically social animals that prefer to travel in pods. However, there are circumstances in which dolphins may travel alone. An injured dolphin may separate from its pod to seek calmer waters or avoid slowing down the group. A dolphin may also become separated from its pod due to storms or human activities. In some cases, dolphins may travel alone temporarily to pursue specific prey or explore new areas. However, solitary travel can increase their vulnerability to predators and other threats.
20. What are the long-term effects of human encroachment on dolphin travel routes?
Human encroachment, such as coastal development and increased boat traffic, can disrupt dolphin travel routes, reduce habitat availability, and increase the risk of collisions and entanglement, leading to population declines.
Human encroachment poses a significant threat to dolphin populations and their travel routes. Coastal development can destroy critical habitats, while increased boat traffic can disrupt their movements and increase the risk of collisions. Entanglement in fishing gear and exposure to pollution can also have devastating effects. According to the Center for Biological Diversity, protecting dolphin habitats and mitigating human impacts are essential for ensuring their long-term survival.
Ready to experience the magic of marine life responsibly? Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN today to book your ethical dolphin encounter and support conservation efforts! Let us help you create unforgettable memories while ensuring the well-being of these incredible creatures. Call us at +1 (707) 257-5400 or visit our location at 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States. Plan your visit now through TRAVELS.EDU.VN and embark on an adventure that makes a difference!
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Dolphin Travel
How long can dolphins stay underwater?
Dolphins can typically hold their breath for 5 to 10 minutes, depending on the species and their activity level.
Do dolphins sleep while traveling?
Dolphins exhibit unihemispheric sleep, meaning they rest one half of their brain at a time, allowing them to remain partially alert while swimming.
What do dolphins eat during their travels?
Dolphins primarily feed on fish, squid, and crustaceans, adjusting their diet based on the availability of prey in their environment.
How do dolphins find fresh water to drink?
Dolphins obtain most of their water from the food they eat and are highly efficient at conserving water.
Are there specific dolphin travel seasons?
Some dolphin species migrate seasonally, while others exhibit more localized movements depending on resource availability.
How can I support dolphin conservation efforts?
You can support dolphin conservation by reducing pollution, practicing responsible boating, and supporting conservation organizations.
What is the biggest threat to dolphin travel?
The biggest threats to dolphin travel include habitat destruction, noise pollution, entanglement in fishing gear, and climate change.
How far can dolphins hear underwater?
Dolphins can hear sounds from up to 15 miles (24 kilometers) away underwater, thanks to their acute hearing and echolocation abilities.
Do dolphins ever get lost during their travels?
While dolphins are skilled navigators, they can sometimes become disoriented due to storms, human activities, or other factors.
How do dolphins protect their young during long journeys?
Dolphin mothers stay close to their calves and rely on the protection of the pod to shield them from predators and other threats.
Don’t wait to discover the wonders of Napa Valley with TRAVELS.EDU.VN! Let us curate the perfect getaway for you. Contact us now at +1 (707) 257-5400 or visit our website TRAVELS.EDU.VN for exclusive deals. We are located at 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States. Book your Napa Valley adventure with TRAVELS.EDU.VN today and create memories that will last a lifetime!
Let travels.edu.vn turn your travel dreams into reality.