How Fast Does A Wave Travel? The speed at which a wave travels depends on several factors, but generally, ocean waves can travel anywhere from a few miles per hour to over 50 mph. At TRAVELS.EDU.VN, we know understanding wave dynamics is key to enjoying coastal destinations like Napa Valley safely and making the most of your trip. We provide insights into wave behavior, including wave velocity and how it affects your coastal experience, along with personalized Napa Valley tour packages.
1. What Factors Influence Wave Speed?
Several factors influence how fast a wave travels. These include wind speed, fetch (the distance over which the wind blows), and water depth. Deeper water generally allows waves to travel faster.
- Wind Speed: Higher wind speeds transfer more energy to the water, resulting in faster waves.
- Fetch: A longer fetch allows the wind to act on the water for a greater distance, building larger, faster waves.
- Water Depth: In deep water, wave speed is related to wavelength. In shallow water, wave speed is primarily determined by water depth.
2. How is Wave Speed Calculated?
Wave speed can be calculated using different formulas depending on the water depth. Here are the basic formulas:
-
Deep Water: In deep water (depth greater than half the wavelength), wave speed (velocity) is approximately:
-
v = √(gL / 2π)Where:
vis the wave speedgis the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.8 m/s²)Lis the wavelength
-
-
Shallow Water: In shallow water (depth less than 1/20 of the wavelength), wave speed is approximately:
-
v = √(gh)Where:
vis the wave speedgis the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.8 m/s²)his the water depth
-
3. What are Typical Wave Speeds?
Typical wave speeds vary depending on the conditions. Here’s a general guide based on wind speed and fetch, according to data adapted from a study.
| Wind Speed (km/h) | Fetch (km) | Duration (h) | Amplitude (m) | Wavelength (m) | Wave Period (s) | Wave Velocity (m/s) | Wave Velocity (km/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 | 19 | 2 | 0.27 | 8.5 | 3.0 | 2.8 | 10.2 |
| 37 | 139 | 10 | 1.5 | 33.8 | 5.7 | 5.9 | 19.5 |
| 56 | 518 | 23 | 4.1 | 76.5 | 8.6 | 8.9 | 32.0 |
| 74 | 1,313 | 42 | 8.5 | 136 | 11.4 | 11.9 | 42.9 |
| 92 | 2,627 | 69 | 14.8 | 212 | 14.3 | 14.8 | 53.4 |
4. How Does Wave Speed Change as Waves Approach the Shore?
As waves approach the shore, they enter shallower water, causing their speed and wavelength to decrease, while their height increases. This process, known as shoaling, results in the waves becoming steeper and eventually breaking. The wave “orbits” are flattened and slowed by the seabed, leading to an increase in wave amplitude (height) and a decrease in wavelength. This culminates in the waves leaning forward and breaking, creating the surf we see on beaches.
 Waves approaching the shore of Long Beach in Pacific Rim National Park, showing refraction and decreasing wavelength
Waves approaching the shore of Long Beach in Pacific Rim National Park, showing refraction and decreasing wavelength
5. What is the Significance of Wave Speed for Coastal Activities?
Wave speed is crucial for understanding coastal dynamics and ensuring safety during various activities. Higher wave speeds can lead to stronger currents and more powerful surf, affecting swimming, surfing, and boating conditions. It’s essential to be aware of wave conditions and heed any warnings from local authorities.
6. How Does Wave Speed Affect Longshore Currents?
Waves approaching the shore at an angle generate longshore currents, which flow parallel to the shoreline within the surf zone. The speed of these currents is influenced by the angle at which waves approach and their speed. Stronger and faster waves create more substantial longshore currents, which can transport sediment and affect beach erosion and deposition.
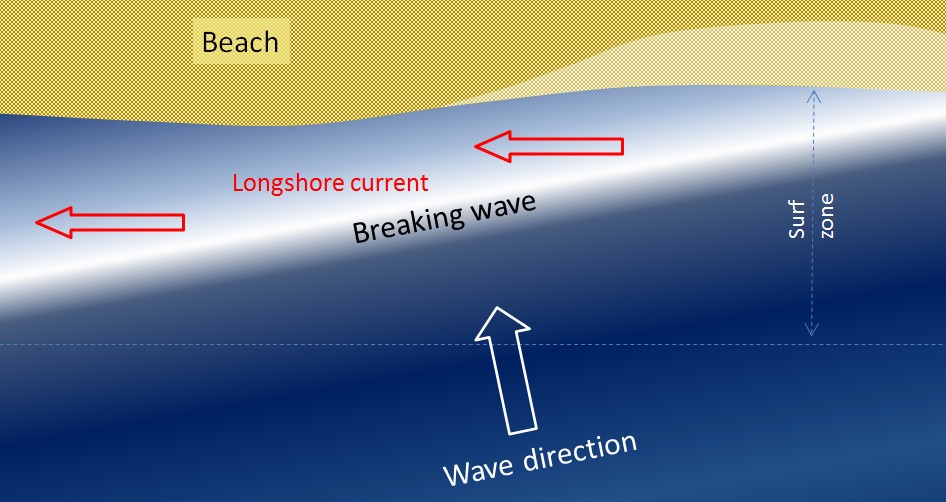 Diagram illustrating the generation of a longshore current by waves approaching the shore at an angle
Diagram illustrating the generation of a longshore current by waves approaching the shore at an angle
7. What Role Does Wave Speed Play in Rip Currents?
Rip currents are strong, narrow currents that flow away from the shore, posing a significant risk to swimmers. Wave speed indirectly influences the formation and strength of rip currents. When waves break, they push water towards the shore, and this water needs to find a way to return to the sea. Rip currents are one mechanism for this return flow, often forming in areas where there are breaks or irregularities in the shoreline.
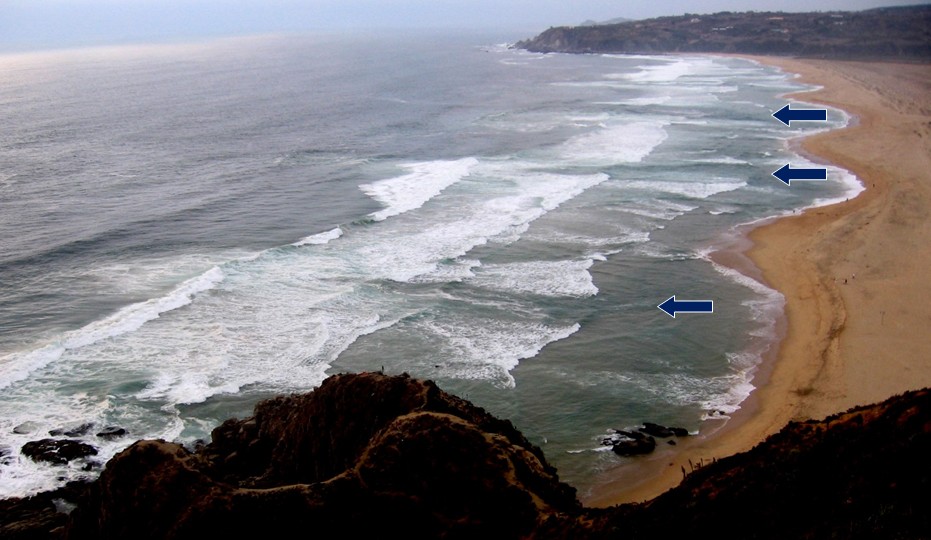 Rip currents on Tunquen Beach in central Chile, showing their formation in embayments
Rip currents on Tunquen Beach in central Chile, showing their formation in embayments
8. How Does Wave Speed Relate to Wave Steepness?
Wave steepness, defined as the ratio of wave height to wavelength, is directly related to wave speed. Larger waves generally have steeper slopes and travel faster. Waves with amplitudes over 10 m have much steeper slopes (amplitude is 6% to 7% of wavelength).
9. How Can TRAVELS.EDU.VN Enhance My Coastal Experience in Napa Valley?
TRAVELS.EDU.VN provides comprehensive travel packages that include insights into local wave conditions, ensuring you have a safe and enjoyable coastal experience. Our services include:
- Real-time Wave Updates: Access to current wave conditions in Napa Valley.
- Expert Guidance: Advice on the best times and locations for surfing, swimming, and other water activities.
- Customized Tours: Tailored itineraries that consider wave conditions for optimal experiences.
10. How Do Tides Relate to Wave Speed?
Tides are essentially very long-wavelength, low-amplitude waves caused by the gravitational forces of the Sun and Moon. While they don’t have the same immediate impact as wind waves, they do affect water levels and can influence the speed and behavior of other waves near the shore.
11. What are the Effects of Wave Refraction on Wave Speed?
Wave refraction occurs when waves approach the shore at an angle. As one part of the wave enters shallower water and slows down, the rest of the wave bends (refracts) to become more parallel to the shoreline. This process affects wave speed along different parts of the wave crest, with the shallower sections moving slower than the deeper ones.
12. How Does Amplitude Affect Wave Speed?
While amplitude (wave height) doesn’t directly determine wave speed, it is related to the energy of the wave. Larger amplitude waves typically have more energy and can travel faster, especially in open ocean conditions.
13. How Does Wavelength Affect Wave Speed?
Wavelength is a crucial factor in determining wave speed, particularly in deep water. The longer the wavelength, the faster the wave travels. This relationship is described by the deep-water wave speed formula: v = √(gL / 2π), where L is the wavelength.
14. What is the Wave Base and How Does it Affect Wave Speed?
The wave base is the depth to which a wave’s motion is felt beneath the surface, approximately one-half of the wavelength. In deep water, the wave base doesn’t interact with the ocean floor, and wave speed is determined by wavelength. However, as waves approach shallow water and the wave base interacts with the bottom, wave speed decreases due to friction and energy dissipation.
15. How Does Wave Speed Influence Coastal Erosion?
Wave speed plays a significant role in coastal erosion. Faster waves carry more energy and can exert greater force on coastal structures and landforms. The impact of these waves can erode cliffs, beaches, and other coastal features over time.
16. What is Swash and Backwash and How Do They Relate to Wave Speed?
Swash is the water that rushes up onto the beach after a wave breaks, while backwash is the water that flows back down the beach. The speed of swash and backwash is related to the speed and energy of the incoming waves. Faster, more powerful waves produce swash and backwash that can transport sediment and reshape the beach profile.
 Diagram illustrating the generation of a longshore current by waves approaching the shore at an angle
Diagram illustrating the generation of a longshore current by waves approaching the shore at an angle
17. What is Longshore Drift and How is it Affected by Wave Speed?
Longshore drift is the movement of sediment along the coast, driven by the combined action of longshore currents and the swash and backwash of waves. Wave speed influences the strength of longshore currents and the amount of sediment transported, affecting the shape and stability of coastlines.
18. How Do Seasonal Changes Affect Wave Speed in Napa Valley?
Seasonal changes can impact wave speed due to variations in wind patterns and storm activity. During the winter months, stronger storms can generate larger, faster waves, while summer months typically see calmer conditions with slower waves. TRAVELS.EDU.VN provides updated information on seasonal wave conditions to help you plan your trip accordingly.
19. What Safety Measures Should Be Taken Based on Wave Speed?
Based on wave speed, several safety measures should be taken:
- Check Local Forecasts: Always check the local weather and surf forecasts before engaging in water activities.
- Heed Warnings: Pay attention to any warnings or advisories issued by local authorities.
- Swim in Designated Areas: Only swim in designated swimming areas where lifeguards are present.
- Be Aware of Rip Currents: Learn to identify rip currents and know how to escape them.
- Use Appropriate Gear: Use appropriate safety gear, such as life jackets or surf leashes, depending on the activity.
20. How Does TRAVELS.EDU.VN Provide Real-Time Wave Updates?
TRAVELS.EDU.VN partners with local weather services and coastal monitoring agencies to provide real-time wave updates. Our website and mobile app offer access to current wave height, speed, period, and direction, as well as tide information and water temperature.
21. What Types of Waves are Common in Napa Valley?
Napa Valley’s coastal areas experience a variety of wave types, including:
- Wind Waves: Generated by local winds.
- Swell Waves: Generated by distant storms and can travel long distances.
- Breaking Waves: Waves that break near the shore, creating surf.
22. How Does TRAVELS.EDU.VN Customize Tours Based on Wave Conditions?
TRAVELS.EDU.VN customizes tours based on wave conditions by:
- Selecting Optimal Locations: Choosing beaches and coastal areas with suitable wave conditions for your desired activities.
- Adjusting Timing: Planning activities around low tide or high tide, depending on your preferences.
- Providing Expert Guides: Offering knowledgeable guides who can provide real-time assessments of wave conditions and ensure your safety.
23. What Are the Best Times of Year to Visit Napa Valley for Surfing Based on Wave Speed?
The best times of year to visit Napa Valley for surfing based on wave speed are typically during the fall and winter months (October to March). During this time, larger swells generated by storms in the Pacific Ocean can produce consistent and powerful waves suitable for surfing.
24. How Does TRAVELS.EDU.VN Ensure Safety During Water Activities?
TRAVELS.EDU.VN ensures safety during water activities by:
- Providing Safety Briefings: Conducting thorough safety briefings before each activity.
- Offering Certified Instructors: Employing certified instructors and guides who are trained in water safety and rescue techniques.
- Supplying Safety Equipment: Providing all necessary safety equipment, such as life jackets, helmets, and first-aid kits.
- Monitoring Conditions: Continuously monitoring wave conditions and adjusting activities as needed to ensure your safety.
25. What are the Environmental Factors That Affect Wave Speed?
Environmental factors such as sea surface temperature, salinity, and ocean currents can also affect wave speed. Changes in sea surface temperature can alter the density of the water, which can influence wave propagation. Salinity variations can also impact water density and wave speed. Ocean currents can either enhance or impede wave speed, depending on their direction and strength.
26. How Does Wind Direction Influence Wave Speed?
Wind direction plays a critical role in wave formation and speed. Waves typically travel in the direction of the wind that generates them. Onshore winds (winds blowing from the sea towards the land) can increase wave height and speed as they push waves towards the shore. Offshore winds (winds blowing from the land towards the sea) can flatten waves and decrease their speed.
27. What Role Does Atmospheric Pressure Play in Wave Speed?
Atmospheric pressure can indirectly affect wave speed by influencing wind patterns. Low-pressure systems are often associated with stronger winds and storm activity, which can generate larger, faster waves. High-pressure systems typically bring calmer winds and smaller waves.
28. How Does the Shape of the Coastline Influence Wave Speed?
The shape of the coastline can significantly influence wave speed and behavior. Headlands (sections of land that jut out into the sea) can focus wave energy, resulting in higher wave speeds and larger waves in those areas. Bays (indentations in the coastline) can dissipate wave energy, leading to lower wave speeds and smaller waves.
29. What is a Tsunami and How Fast Does it Travel?
A tsunami is a series of powerful ocean waves caused by large-scale disturbances, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or underwater landslides. Unlike wind-generated waves, tsunamis have extremely long wavelengths (often hundreds of kilometers) and can travel at incredible speeds, sometimes exceeding 800 kilometers per hour (500 mph) in the open ocean.
30. What Are Rogue Waves and How Fast Do They Travel?
Rogue waves are unusually large and unexpected waves that can occur in the open ocean. They are often much larger than the surrounding waves and can pose a significant threat to ships and offshore structures. Rogue waves typically travel at the same speed as the other waves in the area, but their exceptional height and steepness make them particularly dangerous.
31. How Does the Earth’s Rotation Affect Wave Speed?
The Earth’s rotation can influence wave speed through the Coriolis effect, which deflects moving objects (including waves) to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. This effect is more pronounced for large-scale ocean currents and can indirectly affect wave speed by altering wind patterns and ocean circulation.
32. How Can Wave Speed Be Predicted?
Wave speed can be predicted using a combination of weather forecasts, wave models, and real-time monitoring data. Weather forecasts provide information on wind speed, direction, and duration, which are key factors in wave generation. Wave models use these data to simulate wave conditions and predict wave height, speed, and direction. Real-time monitoring data from buoys and coastal radar systems provide valuable information for validating and refining wave predictions.
33. What are the Different Types of Wave Measurement Technologies?
There are several different types of wave measurement technologies used to monitor wave conditions:
- Buoys: Floating devices equipped with sensors to measure wave height, period, and direction.
- Coastal Radar Systems: Ground-based radar systems that measure wave characteristics over a wide area.
- Satellite Altimeters: Instruments on satellites that measure the height of the sea surface.
- Pressure Sensors: Devices placed on the seabed to measure pressure variations caused by waves.
34. How Do Climate Change and Sea Level Rise Affect Wave Speed?
Climate change and sea level rise can have complex effects on wave speed. Rising sea levels can increase water depths, which can potentially increase wave speed in some areas. However, changes in wind patterns and storm intensity due to climate change can also alter wave conditions, potentially leading to changes in wave speed.
35. How Does TRAVELS.EDU.VN Use Wave Speed Data to Plan Safe and Enjoyable Coastal Excursions?
TRAVELS.EDU.VN uses wave speed data to plan safe and enjoyable coastal excursions by:
- Monitoring Wave Conditions: Continuously monitoring real-time wave data to assess current and future conditions.
- Selecting Safe Locations: Choosing beaches and coastal areas with wave conditions suitable for the planned activities.
- Adjusting Itineraries: Modifying itineraries as needed to avoid hazardous wave conditions.
- Providing Expert Guidance: Offering experienced guides who can provide on-the-spot assessments of wave conditions and ensure the safety of participants.
36. What Are the Benefits of Understanding Wave Speed for Coastal Communities?
Understanding wave speed is essential for coastal communities for several reasons:
- Coastal Protection: Predicting wave speed helps in designing and maintaining coastal protection structures, such as seawalls and breakwaters.
- Navigation Safety: Knowing wave speed is crucial for safe navigation of ships and boats in coastal waters.
- Emergency Preparedness: Predicting wave speed helps in preparing for and responding to coastal hazards, such as storm surges and tsunamis.
- Recreational Planning: Understanding wave speed allows for planning safe and enjoyable recreational activities, such as swimming, surfing, and boating.
37. What are the Future Trends in Wave Speed Research?
Future trends in wave speed research include:
- Improved Wave Models: Developing more sophisticated wave models that can accurately predict wave conditions under a wider range of scenarios.
- Enhanced Monitoring Technologies: Improving wave measurement technologies to provide more accurate and comprehensive data.
- Climate Change Impacts: Studying the impacts of climate change and sea level rise on wave conditions and coastal hazards.
- Artificial Intelligence: Using artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques to improve wave prediction and coastal management.
38. How Does TRAVELS.EDU.VN Contribute to Coastal Education and Awareness?
TRAVELS.EDU.VN contributes to coastal education and awareness by:
- Providing Informative Content: Offering informative content on wave dynamics, coastal safety, and environmental issues through our website and mobile app.
- Conducting Educational Programs: Organizing educational programs and workshops for tourists and local communities.
- Supporting Coastal Research: Supporting coastal research and conservation initiatives.
- Promoting Responsible Tourism: Promoting responsible tourism practices that minimize the impact on coastal environments.
Planning a trip to Napa Valley and want to make the most of its stunning coastal areas? Contact TRAVELS.EDU.VN today! Let our expert travel consultants create a personalized itinerary that considers wave conditions for a safe and unforgettable experience. Call us at +1 (707) 257-5400 or visit our office at 123 Main St, Napa, CA 94559, United States. Visit TRAVELS.EDU.VN for more information.
FAQ: Understanding Wave Speed
1. How does wind affect wave speed?
Wind directly impacts wave speed. Stronger winds blowing over a longer distance (fetch) transfer more energy to the water, creating faster waves.
2. What is the relationship between wavelength and wave speed?
In deep water, wave speed is directly proportional to wavelength. Longer wavelengths result in faster wave speeds, as described by the formula v = √(gL / 2π).
3. Why do waves slow down as they approach the shore?
As waves enter shallower water, they interact with the sea bottom. This friction slows the wave speed and decreases the wavelength, causing the wave height to increase.
4. What is the wave base, and how does it relate to wave speed?
The wave base is the depth to which a wave’s motion is felt, about half the wavelength. When waves enter water shallower than their wave base, they start to interact with the sea floor, slowing down.
5. How do tides influence wave speed?
Tides, caused by the gravitational pull of the Sun and Moon, are essentially very long waves. They don’t directly affect the speed of wind-generated waves but influence water levels, which can indirectly affect wave behavior near the shore.
6. What are rip currents, and how does wave speed relate to them?
Rip currents are strong, narrow currents flowing away from the shore. Higher wave speeds can contribute to stronger rip currents by pushing more water towards the beach, which then needs to return to the ocean.
7. How can I find real-time information on wave speed in Napa Valley?
TRAVELS.EDU.VN provides real-time wave updates through partnerships with local weather services and coastal monitoring agencies. Check our website or mobile app for current wave conditions.
8. How does the shape of the coastline affect wave speed?
The shape of the coastline affects how waves refract (bend). Headlands concentrate wave energy, increasing wave speed and size, while bays disperse energy, reducing wave speed.
9. What role does wave speed play in coastal erosion?
Faster waves carry more energy, leading to greater force against coastal structures. This can erode cliffs, beaches, and other coastal features over time.
10. How does TRAVELS.EDU.VN use wave speed data to ensure safety during coastal excursions?
travels.edu.vn uses wave speed data to select safe locations, adjust itineraries, provide expert guidance, and ensure all participants are safe during coastal activities.